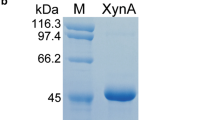
Abstract
Daily agro-industrial waste, primarily cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose, poses a significant environmental challenge. Harnessing lignocellulolytic enzymes, particularly endo-1,4-β-xylanases, for efficient saccharification is a cost-effective strategy, transforming biomass into high-value products. This study focuses on the cloning, expression, site-directed mutagenesis, purification, three-dimensional modeling, and characterization of the recombinant endo-1,4-β-xylanase (XlnA) from Aspergillus clavatus in Escherichia coli. This work includes evaluation of the stability at varied NaCl concentrations, determining kinetic constants, and presenting the heterologous expression of XlnAΔ36 using pET22b(+). The expression led to purified enzymes with robust stability across diverse pH levels, exceptional thermostability at 50 °C, and 96–100% relative stability after 24 h in 3.0 M NaCl. Three-dimensional modeling reveals a GH11 architecture with catalytic residues Glu 132 and 22. XlnAΔ36 demonstrates outstanding kinetic parameters compared to other endo-1,4-β-xylanases, indicating its potential for industrial enzymatic cocktails, enhancing saccharification. Moreover, its ability to yield high-value compounds, such as sugars, suggests a promising and ecologically positive alternative for the food and biotechnology industries.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Bhardwaj N, Verma VK, Chaturvedi V, Verma P (2020) Cloning, expression and characterization of a thermo-alkali-stable xylanase from Aspergillus oryzae LC1 in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Protein Expr Purif 168:105551
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carli S, Meleiro LP, Rosa JC, Moraes LAB, Jorge JA, Masui DC et al (2016) A novel thermostable and halotolerant xylanase from Colletotrichum graminicola. J Mol Catal B Enzym 133:S508–S517
Chakdar H, Kumar M, Pandiyan K, Singh A, Nanjappan K, Kashyap PL et al (2016) Bacterial xylanases: biology to biotechnology. 3 Biotech 6:150
Charalambous K, O’Reilly AO, Bullough PA, Wallace BA (2009) Thermal and chemical unfolding and refolding of a eukaryotic sodium channel. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:1279–1286
Coutinho PM, Reilly PJ (1997) Glucoamylase structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 29:334–347
Dalton AC, Barton WA (2014) Over-expression of secreted proteins from mammalian cell lines. Protein Sci 23:517–525
Damásio ARdL, Silva TM, Almeida FBdR, Squina FM, Ribeiro DA, Leme AFP et al (2011) Heterologous expression of an Aspergillus niveus xylanase GH11 in Aspergillus nidulans and its characterization and application. Process Biochem 46:1236–1242
Ferreira RDG, Azzoni AR, Freitas S (2018) Techno-economic analysis of the industrial production of a low-cost enzyme using E. coli: the case of recombinant beta-glucosidase. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:81
Gai Z, Nakamura A, Tanaka Y, Hirano N, Tanaka I, Yao M (2013) Crystal structure analysis, overexpression and refolding behaviour of a DING protein with single mutation. J Synchrotron Radiat 20:854–858
Gopalakrishna KN, Stewart BH, Kneen MM, Andricopulo AD, Kenyon GL, McLeish MJ (2004) Mandelamide hydrolase from Pseudomonas putida: characterization of a new member of the amidase signature family. Biochemistry 43:7725–7735
Heinen PR, Pereira MG, Rechia CGV, Almeida PZ, Monteiro LMO, Pasin TM et al (2017) Immobilized endoxylanase of Aspergillus tamarii Kita: an interesting biological tool for production of xylooligosaccharides at high temperatures. Process Biochem 53:145–152
Hokanson CA, Cappuccilli G, Odineca T, Bozic M, Behnke CA, Mendez M et al (2011) Engineering highly thermostable xylanase variants using an enhanced combinatorial library method. Protein Eng Des Sel 24:597–605
Juturu V, Wu JC (2012) Microbial xylanases: engineering, production and industrial applications. Biotechnol Adv 30:1219–1227
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJ (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10:845–858
Khandeparker R, Parab P, Amberkar U (2017) Recombinant xylanase from Bacillus tequilensis BT21: biochemical characterisation and its application in the production of xylobiose from agricultural residues. Food Technol Biotechnol 55:164–172
Khasa YP, Khushoo A, Tapryal S, Mukherjee KJ (2011) Optimization of human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression using asparaginase and xylanase gene’s signal sequences in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165:523–537
Kumar V, Marin-Navarro J, Shukla P (2016) Thermostable microbial xylanases for pulp and paper industries: trends, applications and further perspectives. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:34
Kumar V, Dangi AK, Shukla P (2018) Engineering thermostable microbial xylanases toward its industrial applications. Mol Biotechnol 60:226–235
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lakkaraju AK, Thankappan R, Mary C, Garrison JL, Taunton J, Strub K (2012) Efficient secretion of small proteins in mammalian cells relies on Sec62-dependent posttranslational translocation. Mol Biol Cell 23:2712–2722
Larentis AL, Alves TLM, Martins OB (2005) Cloning and expression of meta-cleavage enzyme (CarB) of carbazole degradation pathway from Pseudomonas stutzeri. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:127–134
Liu Z, Zhao X, Bai F (2013) Production of xylanase by an alkaline-tolerant marine-derived Streptomyces viridochromogenes strain and improvement by ribosome engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4361–4368
Liu MQ, Li JY, Rehman AU, Xu X, Gu ZJ, Wu RC (2019) Laboratory evolution of GH11 endoxylanase through DNA shuffling: effects of distal residue substitution on catalytic activity and active site architecture. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:350
Madeira F, Park YM, Lee J, Buso N, Gur T, Madhusoodanan N et al (2019) The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W636–W641
Marinho GO, Nogueira EA, Pasin TM, Oliveira TBd, Roa JPB, Nelson DL et al (2023) An environmentally safe production of xylanases by Fusarium sp. EA 1.3.1 using agroindustrial residues: biochemical characterization and potential applications. Asian J Biochem Genet Mol Biol 14:11–26
Michaelis L, Menten ML, Johnson KA, Goody RS (2011) The original Michaelis constant: translation of the 1913 Michaelis-Menten paper. Biochemistry 50:8264–8269
Miller GL (2002) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mital S, Christie G, Dikicioglu D (2021) Recombinant expression of insoluble enzymes in Escherichia coli: a systematic review of experimental design and its manufacturing implications. Microb Cell Fact 20:208
Nordberg Karlsson E, Schmitz E, Linares-Pasten JA, Adlercreutz P (2018) Endo-xylanases as tools for production of substituted xylooligosaccharides with prebiotic properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9081–9088
Paes G, Berrin JG, Beaugrand J (2012) GH11 xylanases: structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol Adv 30:564–592
Pasin TM, Benassi VM, Heinen PR, Damasio ARL, Cereia M, Jorge JA et al (2017) Purification and functional properties of a novel glucoamylase activated by manganese and lead produced by Aspergillus japonicus. Int J Biol Macromol 102:779–788
Pasin TM, Salgado JCS, Scarcella ASA, de Oliveira TB, de Lucas RC, Cereia M et al (2020a) A halotolerant endo-1,4-beta-xylanase from Aspergillus clavatus with potential application for agroindustrial residues saccharification. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191:1111–1126
Pasin TM, Scarcella ASA, de Oliveira TB, Lucas RC, Cereia M, Betini JHA et al (2020b) Paper industry wastes as carbon sources for Aspergillus species cultivation and production of an enzymatic cocktail for biotechnological applications. Ind Biotechnol 16:56–60
Pasin TM, Moreira EA, Benassi VM, Spencer PVD, Peres NTA, Cereia M et al (2022) Effects of ultraviolet exposure on the tropical fungi Aspergillus carbonarius and Aspergillus japonicus: survival, amylase production, and thermostability. Trop Conserv Sci 15:1–7
Pasin TM, Betini JHA, de Lucas RC, Polizeli M (2023) Biochemical characterization of an acid-thermostable glucoamylase from Aspergillus japonicus with potential application in the paper bio-deinking. Biotechnol Prog 40:e3384
Polizeli MdLTM, Cereia M, Oliveira TBd, Lucas RCd, Scarcella ASdA, Pasin TM (2021) An eco-friendly production of a novel and highly active endo-14-beta-xylanase from Aspergillus clavatus. Asian J Biochem Genet Mol Biol 9:20–33
Porter JL, Rusli RA, Ollis DL (2016) Directed evolution of enzymes for industrial biocatalysis. ChemBioChem 17:197–203
Raduly Z, Szabo L, Madar A, Pocsi I, Csernoch L (2019) Toxicological and medical aspects of Aspergillus-derived mycotoxins entering the feed and food chain. Front Microbiol 10:2908
Romero FA, Vodonick SM, Criscione KR, McLeish MJ, Grunewald GL (2004) Inhibitors of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase that are predicted to penetrate the blood-brain barrier: design, synthesis, and evaluation of 3-fluoromethyl-7-(N-substituted aminosulfonyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines that possess low affinity toward the alpha2-adrenoceptor. J Med Chem 47:4483–4493
Scarcella ASdA, Pasin TM, de Oliveira TB, de Lucas RC, Ferreira-Nozawa MS, Freitas ENd et al (2021) Saccharification of different sugarcane bagasse varieties by enzymatic cocktails produced by Mycothermus thermophilus and Trichoderma reesei RP698 cultures in agro-industrial residues. Energy 226:120360
Seetaraman Amritha TM, Mahajan S, Subramaniam K, Chandramohan Y, Dhanasekaran A (2020) Cloning, expression and purification of recombinant dermatopontin in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 15:e0242798
Segato F, Damasio AR, de Lucas RC, Squina FM, Prade RA (2014) Genomics review of holocellulose deconstruction by aspergilli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78:588–613
Silva MT, Lopes PHS, Pasin TM, Nelson DL, Benassi VM (2023) Produção de beta-D-frutofuranosidases por Aspergillus sp. M2.4 e caracterização bioquímica. J Eng Exact Sci 9:15943–16001
Sorensen HP, Mortensen KK (2005) Advanced genetic strategies for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 115:113–128
Squina FM, Mort AJ, Decker SR, Prade RA (2009) Xylan decomposition by Aspergillus clavatus endo-xylanase. Protein Expr Purif 68:65–71
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41:207–234
Teo SC, Liew KJ, Shamsir MS, Chong CS, Bruce NC, Chan KG et al (2019) Characterizing a halo-tolerant GH10 xylanase from Roseithermus sacchariphilus strain RA and its CBM-truncated variant. Int J Mol Sci 20:2284
Theisen M, Liao JC (2017) Industrial biotechnology: Escherichia coli as a host. In: Wittmann C, Liao J (eds) Industrial biotechnology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 149–181
Wang K, Luo H, Bai Y, Shi P, Huang H, Xue X et al (2014) A thermophilic endo-1,4-beta-glucanase from Talaromyces emersonii CBS394.64 with broad substrate specificity and great application potentials. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7051–7060
**ang L, Lu Y, Wang H, Wang M, Zhang G (2019) Improving the specific activity and pH stability of xylanase XynHBN188A by directed evolution. Bioresour Bioprocess 6:2463–2477
You S, **e C, Ma R, Huang HQ, Herman RA, Su XY et al (2019) Improvement in catalytic activity and thermostability of a GH10 xylanase and its synergistic degradation of biomass with cellulase. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:278
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Shivansh Mahajan for assistance in the gene cloning and expression and Mauricio de Oliveira for technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)/Brasil-financing Code 001, Programa de Doutorado Sanduíche no Exterior (PDSE/CAPES no. 88881.186934/2018-01), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)—Process numbers 2010/52322-3, 2018/07522-6, and 2014/50884-5, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, process 563260/2010-6), and the National Institute of Science and Technology of the Bioethanol (465319/2014-9). T.M.P. was recipient of PDSE/CAPES Fellowship; R.C.L. was recipient of CAPES Fellowship; T.B.O. was recipient of FAPESP Fellowship (process 2017/09000-4); and M.L.T.M.P. is Research Fellow of CNPq (process 301963/2017–7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.M.P, R.C.L, M.J.M, and M.L.T.M.P conceived and designed the experiments. T.M.P performed the experiments. T.M.P, T.B.O, M.J.M, and M.L.T.M.P analyzed the data. T.M.P, R.C.L, T.B.O, M.J.M, and M.L.T.M.P wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pasin, T.M., Lucas, R.C., de Oliveira, T.B. et al. A new halotolerant xylanase from Aspergillus clavatus expressed in Escherichia coli with catalytic efficiency improved by site-directed mutagenesis. 3 Biotech 14, 178 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-04021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-04021-7