Abstract
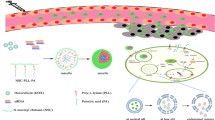
Cancer is one of the most fatal diseases which imposes a serious threat to human health worldwide. Combination therapy of gene drugs with chemotherapeutic drugs is a strategy to improve anticancer effect. In this study, a triblock copolymer was synthesized to enable the codelivery of siRNA and DOX for combination therapy. With a pH-sensitive core, a cationic intermediate layer, and a stable PEG shell, the system can not only load nucleic acid drugs and chemotherapeutic drugs, but also achieve the effect of pH-sensitive drug release. In vitro experiments indicated that the size of micelles could be changed at different pH values, and DOX could be released rapidly at low pH values, which is good for killing cancer cells. And in vivo experiments proved that polymer vector loaded with siRNA and DOX can be enriched in tumor tissues, and release their loads rapidly when they get into tumor. Consequently, the polymeric micelles have a great potential to co-deliver chemotherapeutic drugs and gene drugs to cancer tissues for combination therapy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex MA, Nehate C, Veeranarayanan S, Kumar DS, Kulshreshtha R, Koul V (2017) Self-assembled dual responsive micelles stabilized with protein for co-delivery of drug and siRNA in cancer therapy. Biomaterials 133:94–106
Ball RL, Hajj KA, Vizelman J, Bajaj P, Whitehead KA (2018) Lipid nanoparticle formulations for enhanced co-delivery of siRNA and mRNA. Nano Lett 18(6):3814–3822
Chen L, Zang F, Wu H, Li J, **e J, Ma M, Gu N, Zhang Y (2018) Using pegylated magnetic nanoparticles to describe the EPR effect in tumor for predicting therapeutic efficacy of micelle drugs. Nanoscale 10(4):1788–1797
Debele TA, Yu LY, Yang CS, Shen YA, Lo CL (2018) pH-and GSH-Sensitive hyaluronic acid-MP conjugate micelles for intracellular delivery of doxorubicin to colon cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Biomacromol 19(9):3725–3737
Feng H, Chu D, Li Z, Guo Z, ** L, Fan B, Zhang J, Li J (2018) A DOX-loaded polymer micelle for effectively inhibiting cancer cells. RSC Adv 8(46):25949–25954
Gao GH, Li Y, Lee DS (2013) Environmental pH-sensitive polymeric micelles for cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy. J Control Release 169(3):180–184
Gao H, Feng H, Bai Y, Li Z, Chen L, ** L, Wang J, Georges E, Liu G, Li J, Wang M (2019) Multifunctional polymeric carrier for co-delivery of MRI contrast agents and siRNA to tumors. J Biomed Nanotechnol 15(8):1764–1770
Guo Z, Zhao K, Liu R, Guo X, He B, Yan J, Ren J (2019) pH-Sensitive polymeric micelles assembled by stereocomplexation between PLLA-b-PLys and PDLA-b-mPEG for drug delivery. J Mater Chem B 7(2):334–345
Huang L, Zhang H, Wu S, Xu X, Zhang L, Ji H, He L, Qian Y, Wang Z, Chen Y, Shen J (2019) Charge regulation of self-assembled tubules by protonation for efficiently selective and controlled drug delivery. Science 19:224–231
Li J, Wang T, Wu D, Zhang X, Yan J, Du S, Guo Y, Wang J, Zhang A (2008) Stimuli-responsive zwitterionic block copolypeptides: poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly (lysine-co-glutamic acid). Biomacromol 9(10):2670–2676
Li J, Yu X, Wang Y, Yuan Y, **ao H, Cheng D, Shuai X (2014a) A reduction and pH dual-sensitive polymeric vector for long-circulating and tumor-targeted siRNA delivery. Adv Mater 26(48):8217–8224
Li J, Cheng D, Yin T, Chen W, Lin Y, Chen J, Li R, Shuai X (2014b) Copolymer of poly (ethylene glycol) and poly (L-lysine) grafting polyethylenimine through a reducible disulfide linkage for siRNA delivery. Nanoscale 6(3):1732–1740
Li J, Zhang L, Lin Y, **ao H, Zuo M, Cheng D, Shuai X (2016) A pH-sensitive prodrug micelle self-assembled from multi-doxorubicin-tailed polyethylene glycol for cancer therapy. RSC Adv 6(11):9160–9163
Liu J, He J, Zhang M, Xu G, Ni P (2018) A synergistic polyphosphoester-based co-delivery system of the anticancer drug doxorubicin and the tumor suppressor gene p53 for lung cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B 6(20):3262–3273
Maeda H (2015) Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 91:3–6
Ni Q, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Zhu G, Wang Z, Teng Z, Wang C, Yung B, Niu G, Lu G, Zhang L, Chen X (2018) In situ shRNA synthesis on DNA–polylactide nanoparticles to treat multidrug resistant breast cancer. Adv Mater 30(10):1705737
Peeler DJ, Thai SN, Cheng Y, Horner PJ, Sellers DL, Pun SH (2019) pH-Sensitive polymer micelles provide selective and potentiated lytic capacity to venom peptides for effective intracellular delivery. Biomaterials 192:235–244
Shen J, Zhang W, Qi R, Mao ZW, Shen H (2018) Engineering functional inorganic–organic hybrid systems: advances in siRNA therapeutics. Chem Soc Rev 47(6):1969–1995
Tang S, Meng Q, Sun H, Su J, Yin Q, Zhang Z, Yu H, Chen L, Gu W, Li Y (2017) Dual pH-sensitive micelles with charge-switch for controlling cellular uptake and drug release to treat metastatic breast cancer. Biomaterials 114:44–53
Yu L, Chen Y, Chen H (2017) H2O2-responsive theranostic nanomedicine. Chin Chem Lett 28(9):1841–1850
Zhang F, Ni Q, Jacobson O, Cheng S, Liao A, Wang Z, He Z, Yu G, Song J, Ma Y, Niu G (2018) Polymeric nanoparticles with a glutathione-sensitive heterodimeric multifunctional prodrug for in vivo drug monitoring and synergistic cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int 57(24):7066–7070
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600775 and 21504082, U1904176, U1704175), Medical Science and Technology Program of Henan Province (2018020398, SB201902026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Feng, H., **, L. et al. Polymeric micelle with pH-induced variable size and doxorubicin and siRNA co-delivery for synergistic cancer therapy. Appl Nanosci 10, 1903–1913 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01263-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01263-8