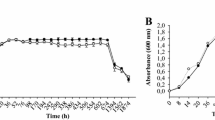
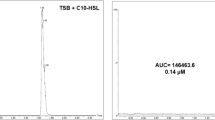
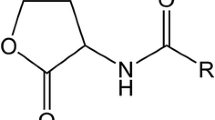
Abstract
Bacteria communicate with each other using a language based on the use of autoinducer molecules (AI) to collectively control gene expression through the process known as quorum sensing (QS). The N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) are the most common AIs known in Gram-negative bacteria. Numerous genes encoding QS systems have been reported in plant beneficial endophytic bacterial genomes although there are fewer studies evaluating the participation of QS in the mechanisms of plant growth promotion. The aim of this study was to describe the genetic background and the types of AHLs produced by a phosphate-solubilizing bacterial strain isolated from the roots of peanut Serratia sp. S119, and to evaluate the participation of these AIs in promoting the growth of plants of agronomic importance.
Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the genome of S119 strain harbors genes encoding proteins involved in the production and detection of AHLs. This strain was found to produce the QS molecules C8-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-OH-C8-HSL and 3-OH-C10-HSL with the latter being the most abundant AHL. By overexpressing a heterologous lactonase enzyme in Serratia sp. S119, this strain was depleted in the production of all AHLs with the exception of 3-OH-C10-HSL which levels were reduced by 50%. The ability to solubilize phosphate, produce biofilms and promote plant growth was analyzed in the AHL attenuated strain. This strain was able to maintain the ability to solubilize phosphate while biofilm production was significantly reduced. Plant inoculation assays with the QS attenuated strain showed differences responses on growth parameters of the three plants employed.
These results indicate that the AHLs from the phosphate solubilizing Serratia sp. S119 strain may not affect its ability to solubilize phosphate. However, they play a role in biofilm formation that is a key trait for bacterial colonization in its interaction with plant species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abisado RG, Benomar S, Klaus JR, Dandekar AA, Chandler JR (2018) Bacterial quorum sensing and microbial community interactions.mBio.9(3)
Ahmer BM (2004) Cell-to‐cell signalling in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. Mol Microbiol 52(4):933–945
Alabid I, Hardt M, Imani J, Hartmann A, Rothballer M, Li D et al (2020) The N-acyl homoserine-lactone depleted Rhizobium radiobacter mutant RrF4NM13 shows reduced growth-promoting and resistance-inducing activities in mono-and dicotyledonous plants. J Plant Dis Prot 127(6):769–781
Altaf MM, Khan MSA, Abulreesh HH, Ahmad I (2017) Quorum sensing in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and its impact on plant-microbe interaction. Plant-microbe interactions in agro-ecological perspectives. Springer, Singapore, pp 311–331
Angus AA, Hirsch AM (2013) Biofilm formation in the rhizosphere: multispecies interactions and implications for plant growth. Mol Microb Ecol rhizosphere 1:701–712
Ansari FA, Jafri H, Ahmad I, Abulreesh HH (2017) Factors affecting biofilm formation in in vitro and in the rhizosphere. Biofilms in plant and soil health. John Wiley and Sons NJ, USA, pp 275–290
Anzuay MS, Frola O, Angelini JG, Ludueña LM, Fabra A, Taurian T (2013) Genetic diversity of phosphate-solubilizing peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) associated bacteria and mechanisms involved in this ability. Symbiosis 60(3):143–154
Anzuay MS, Ludueña LM, Angelini JG, Fabra A, Taurian T (2015) Beneficial effects of native phosphate solubilizing bacteria on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L) growth and phosphorus acquisition. Symbiosis 66(2):89–97
Bai X, Todd CD, Desikan R, Yang Y, Hu X (2012) N-3-oxo-decanoyl-l-homoserine-lactone activates auxin-induced adventitious root formation via hydrogen peroxide-and nitric oxide-dependent cyclic GMP signaling in mung bean. Plant Physiol 158(2):725–736
Barrios AFG, Covo V, Medina LM, Vives-Florez M, Achenie L (2009) Quorum quenching analysis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli: network topology and inhibition mechanism effect on the optimized inhibitor dose. Bioprocess and biosystems engineering 32(4):545–556
Barriuso J (2017) Quorum sensing mechanisms in rhizosphere biofilms. Biofilms in Plant and Soil Health. John Wiley and Sons NJ, USA, pp 99–110
Barriuso J, Ramos Solano B, Fray RG, Cámara M, Hartmann A, Gutiérrez Mañero FJ (2008) Transgenic tomato plants alter quorum sensing in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Biotechnol J 6(5):442–452
Bassler BL, Losick R (2006) Bacterially speaking. Cell 125(2):237–246
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobiurn Zegurninosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Bertels F, Silander OK, Pachkov M, Rainey PB, Van Nimwegen E (2014) Automated reconstruction of whole-genome phylogenies from short-sequence reads. Mol Biol Evol 31(5):1077–1088
Boyer M, Bally R, Perrotto S, Chaintreuil C, Wisniewski-Dyé F (2008) A quorum-quenching approach to identify quorum-sensing-regulated functions in Azospirillum lipoferum. Res Microbiol 159(9–10):699–708
Cámara M, Williams P, Hardman A (2002) Controlling infection by tuning in and turning down the volume of bacterial small-talk. Lancet Infect Dis 2(11):667–676
Das AC, Debnath A (2006) Effect of systemic herbicides on N2-fixing and phosphate solubilizing microorganisms in relation to availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in paddy soils of West Bengal. Chemosphere 65(6):1082–1086
Degrassi G, Mortato V, Devescovi G, Hoshino R, Chatnaparat T, Kojic M et al (2019) Many plant pathogenic Pseudomonas savastanoi pv glycinea isolates possess an inactive quorum sensing ahlR gene via a point mutation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(12):fnz149
Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini MG, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo CW InfoStat versión 2018. Grupo InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. URL http://www.infostat.com.ar
Eberl L (1999) N-acyl homoserinelactone-mediated gene regulation in gram-negative bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 22(4):493–506
Fatima Q, Zahin M, Khan MSA, Ahmad I (2010) Modulation of quorum sensing controlled behaviour of bacteria by growing seedling, seed and seedling extracts of leguminous plants. Indian J Microbiol 50(2):238–242
Fiske EH, Subbarow Y (1925) The solubilization of phosphate: the action of various organic compounds on dicalcium and tricalcium phosphate. New Z J Sci Technol 33:436–444
Fuqua C, Greenberg EP (2002) Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(9):685–695
Hanif MK, Malik KA, Hameed S, Saddique MJ, Fatima K, Naqqash T et al (2020) Growth stimulatory effect of AHL producing Serratia spp. from potato on homologous and non-homologous host plants. Microbiol Res 238:126506
Harris AK, Williamson NR, Slater H, Cox A, Abbasi S, Foulds I et al (2004) The Serratia gene cluster encoding biosynthesis of the red antibiotic, prodigiosin, shows species-and strain-dependent genome context variation. Microbiology 150(11):3547–3560
Hartmann A, Klink S, Rothballer M (2021) Plant growth promotion and induction of systemic tolerance to drought and salt stress of plants by quorum sensing auto-inducers of the N-acyl-homoserine lactone type: recent developments. Front Plant Sci 12:1026
Hartmann A, Schikora A (2012) Quorum sensing of bacteria and trans-kingdom interactions of N-acyl homoserine lactones with eukaryotes. J Chem Ecol 38(6):704–713
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular. California Agricultural Experiment Station. 347(2nd edit)
Horng YT, Deng SC, Daykin M, Soo PC, Wei JR, Luh KT et al (2002) The LuxR family protein SpnR functions as a negative regulator of N-acylhomoserine lactone‐dependent quorum sensing in Serratia marcescens. Mol Microbiol 45(6):1655–1671
Jha P, Panwar J, Jha PN (2018) Mechanistic insights on plant root colonization by bacterial endophytes: a symbiotic relationship for sustainable agriculture. Environmental Sustainability, pp 1–14
Jung BK, Ibal JC, Pham HQ, Kim MC, Park GS, Hong SJ et al (2020) Quorum sensing system affects the plant growth promotion traits of Serratia fonticola GS2. Frontiers in microbiology, 2746
Jung BK, Khan AR, Hong SJ, Park GS, Park YJ, Kim HJ et al (2017) Quorum sensing activity of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Serratia glossinae GS2 isolated from the sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) rhizosphere. Ann Microbiol 67(9):623–632
Kandel SL, Joubert PM, Doty SL (2017) Bacterial endophyte colonization and distribution within plants.Microorganisms.5(77)
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547
Lerat E, Moran NA (2004) The evolutionary history of quorum-sensing systems in bacteria. Mol Biol Evol 21(5):903–913
Liu F, Bian Z, Jia Z, Zhao Q, Song S (2012) The GCR1 and GPA1 participate in promotion of Arabidopsis primary root elongation induced by N-acyl-homoserine lactones, the bacterial quorum-sensing signals. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 25(5):677–683
Liu X, Jia J, Popat R, Ortori CA, Li J, Diggle SP et al (2011) Characterisation of two quorum sensing systems in the endophytic Serratia plymuthica strain G3: differential control of motility and biofilm formation according to life-style. BMC Microbiol 11(1):1–12
Lucero CT, Lorda GS, Anzuay MS, Ludueña LM, Taurian T (2021) Peanut endophytic phosphate solubilizing bacteria increase growth and p content of soybean and maize plants. Curr Microbiol 78(5):1961–1972
Lucero CT, Lorda GS, Ludueña LM, Anzuay MS, Taurian T (2020) Motility and biofilm production involved in the interaction of phosphate solubilizing endophytic strains with peanut, maize and soybean plants. Rhizosphere 15:100228
Ludueña LM, Anzuay MS, Angelini JG, McIntosh M, Becker A, Rupp O et al (2018) Strain Serratia sp. S119: a potential biofertilizer for peanut and maize and a model bacterium to study phosphate solubilization mechanisms. Appl Soil Ecol 126:107–112
McClean KH, Winson MK, Fish L, Taylor A, Chhabra SR, Camara M, Daykin M et al (1997) Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 143(12):3703–3711
Medina-Martínez MS, Uyttendaele M, Rajkovic A, Nadal P, Debevere J (2007) Degradation of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones by Bacillus cereus in culture media and pork extract. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(7):2329–2332
Mehta S, Nautiyal CS (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 43(1):51–56
Meyer F, Goesmann A, McHardy AC, Bartels D, Bekel T, Clausen J, PuÈhler A (2003) GenDB—an open source genome annotation system for prokaryote genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 31(8):2187–2195
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Laboratory Press
Morgulis A, Coulouris G, Raytselis Y, Madden TL, Agarwala R, Schäffer AA (2008) Database indexing for production MegaBLAST searches. Bioinformatics 24(16):1757–1764
Morohoshi T, Shiono T, Takidouchi K, Kato M, Kato N, Kato J, Ikeda T (2007) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Serratia marcescens AS-1 by synthetic analogs of N-acylhomoserine lactone. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(20):6339–6344
Ng WL, Bassler BL (2009) Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annual Rev Genet 43:197–222
Ortori CA, Halliday N, Cámara M, Williams P, Barrett DA (2014) LC-MS/MS quantitative analysis of quorum sensing signal molecules. Pseudomonas Methods and Protocols. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 255–270
O’toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28(3):449–461
Parsek MR, Greenberg EP (2000) Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(16), 8789–8793
Patel HK, Suárez-Moreno ZR, Degrassi G, Subramoni S, Gonzalez JF, Venturi V (2013) Bacterial LuxR solos have evolved to respond to different molecules including signals from plants. Frontiers in plant science. 4(447)
Rashid R, Morohoshi T, Someya N, Ikeda T (2011) Degradation of N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signaling molecules by potato root surface-associated Chryseobacterium strains. Microbes and environments 26(2):144–148
Reimmann C, Ginet N, Michel L, Keel C, Michaux P, Krishnapillai V et al (2002) Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 148(4):923–932
Rivas R, Peix A, Mateos PF, Trujillo ME, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2007) Biodiversity of populations of phosphate solubilizing rhizobia that nodulates chickpea in different spanish soils. First international meeting on microbial phosphate solubilization. Springer Netherlands, pp 23–33
Sakuraoka R, Suzuki T, Morohoshi T (2019) Distribution and genetic diversity of genes involved in quorum sensing and prodigiosin biosynthesis in the complete genome sequences of Serratia marcescens. Genome Biol Evol 11(3):931–936
Schenk ST, Hernández-Reyes C, Samans B, Stein E, Neumann C, Schikora M et al (2014) N-acyl-homoserine lactone primes plants for cell wall reinforcement and induces resistance to bacterial pathogens via the salicylic acid/oxylipin pathway. The Plant Cell 26(6):2708–2723
Schenk ST, Stein E, Kogel KH, Schikora A (2012) Arabidopsis growth and defense are modulated by bacterial quorum sensing molecules. Plant Signal Behav 7(2):178–181
Schikora A, Schenk ST, Hartmann A (2016) Beneficial effects of bacteria-plant communication based on quorum sensing molecules of the N-acyl homoserine lactone group. Plant Mol biology 90(6):605–612
Schikora A, Schenk ST, Stein E, Molitor A, Zuccaro A, Kogel KH (2011) N-acyl-homoserine lactone confers resistance toward biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens via altered activation of AtMPK6. Plant Physiol 157(3):1407–1418
Shrestha A, Grimm M, Ojiro I, Krumwiede J, Schikora A (2020) Impact of quorum sensing molecules on plant growth and immune system. Front Microbiol 11:1545
Soto MJ, Sanjuan J, Olivares J (2006) Rhizobia and plant-pathogenic bacteria: common infection weapons. Microbiology 152(11):3167–3174
Taurian T, Anzuay MS, Angelini JG, Tonelli ML, Ludueña LM, Pena D, Ibañez F, Fabra A (2010) Phosphate-solubilizing peanut associated bacteria: screening for plant growth-promoting activities. Plant and Soil 329(1–2):421–431
Thomson NR, Crow MA, McGowan SJ, Cox A, Salmond GPC (2000) Biosynthesis of carbapenem antibiotic and prodigiosin pigment in Serratia is under quorum sensing control. Mol Microbiol 36(3):539–556
Van Houdt R, Givskov M, Michiels CW (2007b) Quorum sensing in Serratia. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31(4):407–424
Van Houdt R, Moons P, Aertsen A, Jansen A, Vanoirbeek K, Daykin M et al (2007a) Characterization of a luxI/luxR-type quorum sensing system and N-acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent regulation of exo-enzyme and antibacterial component production in Serratia plymuthica RVH1. Res Microbiol 158(2):150–158
von Rad U, Klein I, Dobrev PI, Kottova J, Zazimalova E, Fekete A et al (2008) Response of Arabidopsis thaliana to N-hexanoyl-DL-homoserine-lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing molecule produced in the rhizosphere. Planta 229(1):73–85
Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:319–346
Wei JR, Lai HC (2006) N-acylhomoserine lactone-dependent cell-to-cell communication and social behavior in the genus Serratia. Int J Med Microbiol 296(2–3):117–124
Wei JR, Tsai YH, Horng YT, Soo PC, Hsieh SC, Hsueh PR et al (2006) A mobile quorum-sensing system in Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol 188(4):1518–1525
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7(1–2):203–214
Zhu J, Kaufmann GF (2013) Quo vadis quorum quenching? Curr Opin Pharmacol 13(5):688–698
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank for the help provided by Dr. Stephan Heeb and Dr. Manuel Romero (Centre for Biomolecular Sciences, University of Nottingham) for sending the strains E.coli pME6863 and pME6000, and in the protocol to study the production of biofilms. The authors thanks to Dr. Fernando Ibañez (Instituto de Investigaciones Agrobiotecnológicas UNRC-CONICET) for the assistance provided in the phylogenetic analysis of the amino acid sequence of LuxI proteins.
This research was supported by Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales de la Universidad Nacional de La Pampa (FCEyN-UNLPam), Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica de la Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto (SECYT-UNRC), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT) and the National Biofilms Innovation Centre (NBIC) which is an Innovation and Knowledge Centre funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research 1549 Council, Innovate UK and Hartree Centre [Award Number 1550 BB/R012415/1].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lucero, C.T., Lorda, G.S., Halliday, N. et al. Impact of quorum sensing from native peanut phosphate solubilizing Serratia sp. S119 strain on interactions with agronomically important crops. Symbiosis 89, 107–121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-022-00893-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-022-00893-6