Abstract
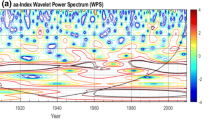
Based on the simulation results derived from ECHO-G global coupled climate model, several East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) indices are compared in order to choose the most suitable one for signaling the intensity of winter monsoon in the last millennium. The index I_shi, which is defined with normalized sea level pressure difference between sea and land in mid and low latitudes, is selected to describe the winter monsoon intensity variation owing to its better capability for reflecting the variation of winter monsoon subsystems, such as the continental high pressure, Aleutian low, East Asian major trough, westerly jet stream, and surface air temperature than the other indices examined. Wavelet analysis on index I_shi shows that the EAWM intensity is characterized by multi-timescale variation with inter-annual, decadal, inter-decadal and inter-centennial oscillations on the background of a slight descending trend. Correlation analysis between the EAWM index and sea surface temperature (SST) at various timescales reveals that the SST in mid-latitudes might provide the background of the EAWM strength changes above decadal timescales, and a negative-feedback process lasting for about two years is found between the EAWM intensity and the SST in the eastern equatorial Pacific. According to the correlation, the El Nino occurrence in the second-half of the year leads to weaker EAWM than normal in the following winter and the weakened EAWM corresponds to lower SST in eastern equatorial Pacific after about half a year, which will then strengthen the EAWM intensity in the next winter. It is a stable feedback process and its mechanism is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baquero-Bernal, A., M. Latif, and S. Legutke, 2002: On dipole-like variability of sea surface temperature in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Climate, 15(11), 1358–1368.
Blunier, T., J. A. Chappellaz, J. Schwander, and D. Raynaud, 1995: Variations in atmospheric methan concentration during the Holocene epoch. Nature, 374, 46–49.
Chang, C. P., and K. M. Lau, 1980: Northeasterly cold surges and nearequatorial disturbances over the winter MONEX area during December 1974. Part 2: Planetary-scale aspects. Mon. Wea. Rev., 108, 298–312.
_____, and ______, 1982: Short-term planetary-scale interaction over the tropics and midlatitudes during northern winter. Part I: Contrast between active and inactive periods. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 933–946.
_____, J. E. Millard, and G. T. J. Chen, 1983: Gravitational character of cold surges during winter MONEX. Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, 293–307.
_____, Z. Wang, and H. Hendon, 2006: The Asian winter monsoon. In B. Wang (Ed.): The Asian Monsoon, Praxis, New York, pp 89.
Chen, H. S., and Z. B. Sun, 2001: An index of China winter temperature anomaly: East Asian regional westerly index. J. Nan**g Institute of Meteorol., 24(4), 458–466. (In Chinese)
Chen, J., and S. Q. Sun, 1999: Eastern Asian winter monsoon anomaly and variation of global circulation Part I: A comparison study on strong and weak winter monsoon, Chinese J. of Atmos. Sci., 23(1), 101–111. (In Chinese)
Ding, Y. H, and T. N. Krishnamurti. 1987: Heat budget of the Siberian high and the winter monsoon, Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 2428–2449.
Ding, Y. H., 1990: A statistical study of winter monsoon in East Asia. J. Tropical Meteorol., 6(2), 119–128. (In Chinese)
Etheridge, D., L. P. Steele, R. L. Langenfelds, R. J. Francey, J.-M. Barnola, and V. I. Morgan, 1996: Morgan natural and anthropogenic changes in atmospheric CO2 over the last 1000 years from air in Antarctic ice and firn. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 4115–4128.
Gonzalez-Ruoco F., H. von Storch, E. Zorita., 2003: Deep soil temperature as proxy for surface air-temperature in a coupled model simulation of the last thousand years. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 2116–2114.
Guo, Q. Y., 1994: Relationship between the variations of East Asian winter monsoon and temperature anomalies in China. Quat. J. Appl. Meteorol. 5(2), 218–225. (In Chinese)
Ji, L. R., and S. Q. Sun, 1997: Model study on the interannual variability of Asian winter monsoon and its influence, Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14(1), 1–22.
Juhn Jong-Ghap and Eun-Jeong Lee, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics ofthe winter monsson, J. Climate, 17, 711–726.
Kalnay, E., M., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project, Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–472.
Kuang, X. Y., J. Liu, H. L. Wang Wang, R. Ti, S. Wang, 2009: Comparison of simulated and reconstructed precipitation in China during Last millennium, Adv. in Earth Sci., 24, 159–171. (In Chinese)
Lau, K M, and C. P. Chang., 1987: Planetary scale aspects of the winter monsoon and atmospheric teleconnections: Monsoon Meteorology, C. P. Chang and T. N. Krishnamurti, Eds., Oxford University Press, 161–201.
Li, C. Y., 2000: Introduction to climate dynamics. Bei**g, Meteorological Press, 515 pp. (In Chinese)
Liu, J., H. von Storch, X. Chen, E. Zorita, J. Zheng, and S. Wang, 2005: Simulated and reconstructed winter temperature in the eastern China during the last millennium. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(24), 2872–2877.
Legutke, S., and R. Voss., 1999: The Hamburg Atmosphere-Ocean Coupled Circulation Model ECHO-G. Technical Report No. 18. Hamburg, Germany: German Climate Computer Center (DKRZ).
Marsland, S. J., M. Latif, S. Legutke., 2003: Variability of the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. Ocean Dynamics, 53(4), 323–331.
Min H.J., and J. G. Jhun, 2010: The Change in the East Asian Summer Monsoon Simulated by the MIROC3.2 High-Resolution Coupled Model under Global Warming Scenarios, Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 73–88.
Raible, C., and Coauthors, 2001: North Atlantic decadal regimes in a coupled GCM simulation. Climate Dyn., 18, 321–330.
Robock, A., M. Free., 1996: The volcanic record in ice cores for the past 2000 years. In: Jones P, Bradley R, Jouzel J eds. Climatic Variation and Forcing Mechanisms of the Last 2000 Years. New York: Springer-Verlag, 533–546.
Shi, N., 1996: Features of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity on multiple time scales in recent 40 years and there elation to climate. Quart. J. Appl. Meteor., 7(2), 175–182. (In Chinese)
Shi, N., and Q. G. Zhu., 1996: Anomalous East Asian winter monsoon intensity and its relation to summer 500 hPa atmospheric circulation and climate anomaly in China. J. of Tropical Meteor., 12(1), 26–33. (In Chinese)
Sun, S. Q., and B. M. Sun., 1995: The relationship between the anomalous winter monsoon circulation over East Asia and summer drought/flooding in the Yangtze and Huaihe River Valley. Acta Metoerologica Sinica, 53(4), 440–450. (In Chinese)
Tao, S. Y., 1957: A study of activities of cold airs in East Asian winter, Handbook of Short-Term Forecast (in Chinese), China Meteorological Administration, Eds., Meteorology Press, Bei**g, 60–92.
Tomita, T., and T. Yasunari., 1996: Role of the northeast winter monsoon on the biennial oscillation of the ENSO/monsoon system. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 399–413.
Usokin, I., and Coauthors. 2003: Millennium-scale sunspot number reconstruction: evidence for an unusual active sun since the 1940s. Physical Review Letters, 91: art. 211101.
Wang, B., and T. Li., 2004: East Asian monsoon and ENSO interaction. In C.-P. Chang (ed.) East Asian Monsoon, World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore, 172–212.
Wang, B, Z. W. Wu, C. P. Chang, J. Liu, J. Li, and T. Zhou, 2010: Another look at interannual to interdecadal variations of the East Asian Winter Monsoon: the northern and southern temperature modes. J. Climate, 23, 1495–1512.
Wang, H. J., and D. B. Jiang., 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and atmospheric circulation comparison between and weak composite. Quaternary Sciences, 24(1), 19–27. (In Chinese)
Wolff, J. O., E. Maier-Reimer, and S. Legutke., 1997: The Hamburg Ocean Primitive Equation Model. German Climate Computer Center (DKRZ) Technical Report No 13, 98 pp.
Wu, A. M., and Y. Q. Ni., 1997: The influence of Tibetan Plateau on the interannual variability of Asian monsoon, Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 491–504.
Wu, B.Y., and J. Wang., 2002: Winter Arctic Oscillation, Siberian High, and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett, 29, 1897, doi: 10.1029/2002GL051373.
Wu, B.Y., R. Zhang, and R. D’Arrigo, 2006: Distinct modes of the East Asian winter monsoon. Mon. Wea. Rev., 134, 2165–2179.
Yan, H. M., X. Duan, and Z. N. **ao., 2003: A study on relation between East Asian winter monsoon and climate change during raining season in China. J. Trop. Meteorol, 19(4), 367–376. (In Chinese)
Yang, S., K. M. Lau, and K. M. Kim., 2002: Variations of the East Asian jet stream and Asia Pacifi American winter climate anomalies. J. Climate, 15, 306–325.
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto., 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the’ 86/87 and’ 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhang, Y., K. R. Sperber, and J. S. Boyle., 1997: Climatology and Interannual of the East Asian winter monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 2605–2619.
Zhou, Y. H., and D. W. Zheng, 1999: Monte Carlo Simulation Tests of Correlation Significance Levels. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 28(4), 313–318. (In Chinese)
Zhu, Q., Study of winter monsoon over East Asia. 1994: In Asia Monsoon, edited by Y.-H. Ding and H. Murakami, China Meteorological Press, Bei**g, 93–104.
Zhu, C. W, J. H. He, and G. X. Wu, 2000: East Asian monsoon index and its interannual relationship with large-scale thermal dynamic circulation. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 58, 391–402. (In Chinese)
Zorita, E., J. F. González-Rouco, H. von Storch, J. P. Montavez, and F. Valero, 2005: Natural and anthropogenic modes of surface temperature variations in the last thousand years. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L08707, doi: 10.1029/2004GL021563.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xueyuan, K., Jian, L., Yaocun, Z. et al. Multi-timescale variation of East Asian winter monsoon intensity and its relation with sea surface temperature during last millennium based on ECHO-G simulation. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 47, 485–495 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-011-0033-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-011-0033-8