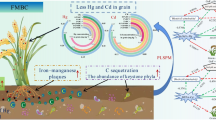
Abstract
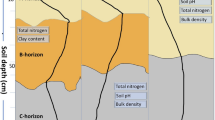
Biological crusts are a collection of mosses, lichens, algae, fungi and heterotrophic bacteria that live in different forms within a few millimeters above the soil surface. These crusts play an important role in the development, stability and improvement of the nutritional status of the surface soil. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the role of biocrust sequences on the soil characteristics in the Inche Barun region, Golestan province (Iran). In the study area, biological and physical crusts as well as the soil under their surface were sampled after identifying the sequences of biocrust (moss, lichen and cyanobacteria). Then, the physicochemical characteristics of soil under their surface (In the depths 0–2, 2–4, 4–8, 8–10, 10–25, and 25–50 cm) were measured. The results showed that the presence of biological crusts compared to physical crust in the surface parts (0 to 2 cm depth) improved the physicochemical properties of the soil. The content of nitrogen, soil organic carbon, phosphorus, cation exchange capacity, sodium, potassium and mean-weight diameter of soil in the soil under their surface increased from the first (physical crust) to the last sequence (moss biological crust). The values of these parameters decreased with increasing soil depth. Biological crusts improve soil stability and reduce soil erosion. They also serve as food sources for organisms residing in soils. Therefore, it can be concluded that the presence of biological crusts on the soil surface improves soil quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acea MJ, Prieto-Fernández A, Diz-Cid N (2003) Cyanobacterial inoculation of heated soils: effect on microorganisms of C and N cycles and on chemical composition in soil surface. Soil Biol Biochem 35:513–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00005-1
Aprile F, Lorandi R (2012) Evaluation of cation exchange capacity (CEC) in tropical soils using four different analytical methods. J Agric Sci. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v4n6p278
Azhdari Z, Bazrafshan J (2022) A hybrid drought Index for assessing agricultural drought in arid and semi-arid coastal areas of Southern Iran. IntJ Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04154-3
Belnap J (2003) The world at your feet: desert biological soil crusts. Front Ecol Environ 1:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1890/1540-9295(2003)001[0181:TWAYFD]2.0.CO;2
Belnap J, Harper KT (1995) Influence of cryptobiotic soil crusts on elemental content of tissue of two desert seed plants. Arid Soil Res Rehab 9:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324989509385879
Benavent-González A, Delgado-BaquerizoM F-B, Singh BK, Maestre FT, Sancho LG (2018) Identity of plant, lichen and moss species connects with microbial abundance and soil functioning in Maritime Antarctica. Plant Soil DOI TBD (this Issue). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3721-7
Bian DD, Liao CY, Sun CZ, et al (2011) Effect of soil biological crust on the distribution of soil microorganisms in the loess hilly region. Agric Res Arid Areas 229(4): 109−114. http://scholar.google.com/.
Bowker MA, Belnap J, Miller ME (2006) Spatial modeling of biological soil crusts to support rangeland assessment and monitoring. Rangel Ecol Manag 59:519–529
Bowker MA, Mu RL, Maestre FT, Escolar C, Castillo-Monroy AP (2011) Functional profiles reveal unique ecological roles of various biological soil crust organisms. Funct Ecol 25:787–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2011.01835.x
Bu N, Zhu QK, Wang R et al (2009) Anti-scour ability of microbiotic soil crust in the loess area of northern Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. J Bei**g for Univ 31(5):96–101. https://doi.org/10.2111/05-179R1.1
Cantón Y, Domingo F, Solé-Benet A, Puigdefábregas J (2001) Hydrological and erosion response of a badlands system in semiarid SE Spain. J Hydrol 252:65–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00450-4
Chamizo S, Stevens A, Cantón Y, Miralles I, Domingo F, van Wesemael B (2012) Discriminating soil crust type, development stage, and degree of disturbance in semi-arid environments from their spectral characteristics. Eur J Soil Sci 63:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2011.01406.x
Chaudhary VB, Bowker MA, O’Dell TE, Grace JB, Redman AE, Rillig MC, Johnson CNC (2009) Untangling the biological contributions to soil stability in semiarid shrublands. Ecol Appl 19(1):110–122. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-2076.1
Cui Y, Lü YZ, Li BG (2004) Physico-chemical properties of soil microbiotic crusts on Erdos Plateau. Soils 36(2): 197−202. http://scholar.google.com/.
Dümig A, Veste M, Hagedorn F, Fischer T, Lange P, Spröte R, Kögel-Knabner I (2014) Organic matter from biological soil crusts induces the initial formation of sandy temperate soils. CATENA 122:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.06.011
Felde VJMNL, Chamizo S, Felix-Hemmingsen P, Drahorad SL (2018) What stabilizes biological soil crusts in the Negev Desert? Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3459-7
Franzluebbers JA (2022) Soil mean-weight diameter and stability index under contrasting tillage systems for cotton production in North Carolina. Soil Sci Soc Am J. https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20458
Frechen M, Kehl M, Rolf C, Sarvati R, Skowronek A (2009) Loess chronology of the Caspian Lowland in Northern Iran. Quatern Int 128(1–2):220–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2008.12.012
Gangwar DP, Baskar Munusamy (2019) Texture determination of soil by hydrometer method for forensic purpose. Publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333105900. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.16057.60001.
Gao L, Bowker MA, Xu M, Sun H, Tuo D, Zhao Y (2017) Biological soil crusts decrease erodibility by modifying inherent soil properties on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol Biochem 105:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.11.009
Gholamhosseinian A, Sepehr A, Emadodin I (2020) The effect of biocrusts on soil parameters in a semi-arid pediment at north-eastern Iran. Revista De Geomorfologie. https://doi.org/10.21094/rg.2020.094
Green LE, Porras-Alfaro A, Sinsabaugh RL (2008) Translocation of nitrogen and carbon integrates biotic crust and grass production in desert grassland. J Ecol 96:1076–1085. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01388.x
Guo Y, Zhao H, Zuo X, Drake S, Zhao X (2008) Biological soil crust development and its topsoil properties in the process of dune stabilization, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Geol 54:653–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1130-y
Hendershot WH, Lalande H, Duquette M (2007) Soil reaction and exchangeable acidity, In book: Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420005271.ch16.
Herrero J, Artieda O, Weindorf DC (2016) Soil gypsum determination. Soil Sci Soc Am J 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20156
Jha S, Srivastava R (2018) Impact of drought on vegetation carbon storage in arid and semi-arid regions. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 11:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.04.013
Jiao WJ, Zhu QK, Zhang YQ et al (2007) Distribution of biotic crusts and its influencing factors in the grain-for-green land of the loess region, northern Shaanxi Province. J Bei**g for Univ 29(1):102–107
Kakeh J, Gorji M, Sohrabi M, Tavili A, Pourbabaeea AA (2018) Effects of biological soil crusts on some physicochemical characteristics of rangeland soils of Alagol, Turkmen Sahra, NE Iran. Soil Tillage Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.04.007
Kakeh J, Gorji M, Mohammadi MH, Asadi H, Khormali F, Sohrabi M, Cerdà A (2020) Biological soil crusts determine soil properties and salt dynamics under the arid climatic condition in Qara Qir, Iran. Sci Total Environ 732:139168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139168
Kleiner EF, Harper KT (1972) Environment and communiy organization in grasslands of anyonlands National Park. Canyonlands Research Bibliography. Paper 110. https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/crc_research/110
Lan S, Wu L, Zhang D, Hu C (2012) Successional stages of biological soil crusts and their microstructure variability in Shapotou region (China). Environ. Earth Sci. 65:77-88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1066-0
Li XR, Jia RL, Chen YW, Huang L, Zhang P (2011) Association of ant nests with successional stages of biological soil crusts in the Tengger Desert, Northern China. Appl Soil Ecol 47:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.10.010
Li XR, Zhang P, Su YG, Jia RL (2012) Carbon fixation by biological soil crusts following revegetation of sand dunes in arid desert regions of China: a four-year field study. CATENA 97:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.009
Lv JL, Liao CY, Sun CZ, et al (2010) Distribution of algae crusts and its influencing factors on the soil surface of the Loess Plateau. J Northwest Forestry Univ 25(1): 11–14. http://scholar.google.com/.
Mager DM (2010) Carbohydrates in cyanobacterial soil crusts as a source of carbon in southwest Kalahari, Botswana. Soil Biol Biochem 42:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.009
Mager DM, Thomas AD (2011) Extracellular polysaccharides from cyanobacterial soil crusts: a review of their role in dryland soil processes. J Arid Environ 75:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2010.10.001
McCune B, Rosentreter R (2007) Biotic soil crust lichens of the columbia basin. In: Monographs in North American Lichenology, vol 1. Northwest Lichenologists, p 105. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0024282907009085.
Meng J, Bu CF, Zhao YJ et al (2010) Effects of BSC on soil enzyme activities and nutrients content in wind-water erosion crisscross region, Northern Shaanxi Province, China. J Nat Resour 25(11):1864–1874. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.2010.11.006
Miralles I, Lázaro R, Sánchez-Marañón M, Soriano M, Ortega R (2020) Biocrust cover and successional stages influence soil bacterial composition and diversity in semiarid ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 709:134654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134654
Muñoz-Rojas M, Chilton A, Liyanage GS, Erickson TE, Merritt DJ, Neilan BA, Ooi MKJ (2018) Effects of indigenous soil cyanobacteria on seed germination and seedling growth of arid species used in restoration. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3607-8
Naylor D, Sadler N, Bhattacharjee A, Graham EB, Anderton CR, McClure R, Lipton M, Hofmockel KS, Jansson JK (2020) Soil microbiomes under climate change and implications for carbon cycling. Annu Rev Environ Resour 45(1):29–59. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-012320-082720
Olsen SR, Sommers L (1982) Phosphorus. In: AL. Page: Methods of Soil Analysis, Agron. No. 9, Part 2: Chemical and microbiological properties, (ed) Am. Soc. Agron., Madison, WI, USA, pp 40-430
Pietrasiak N, Regus JU, Johansen JR, Lam D, Sachs JL, Santiago LS (2013) Biological soil crust community types differ in key ecological functions. Soil Biol Biochem 65:168–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.05.011
Rahimzadeh N, Gribenski N, Tsukamoto S, Kehl M, Pint A, Kiani F, Frechen M (2019) Timing and development of sand dunes in the Golestan Province, Northern Iran—implications for the Late-Pleistocene history of the Caspian Sea. Aeol Res 41:100538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2019.07.004
Rossi F, Mugnai G, De Philippis R (2018) Complex role of the polymeric matrix in biological soil crusts. Plant Soil 429(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3441-4
Sáez-Plaza P, Michałowski T, Navas MJ, García A (2013) An overview of the Kjeldahl method of nitrogen determination. Part I. Early history, chemistry of the procedure, and titrimetric finish. Crit Rev Analyt Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2012.751787
Shahbazi K (2020) Standard operating procedure for soil calcium carbonate equivalent Volumetric Calcimeter method. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome, pp 1–13
Soil Survey Staff (2010) Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 11th edn. USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington DC
Stewart DR, Majdi AN, John SS (2012) An Image-Based Method for Determining Bulk Density and the Soil Shrinkage Curve. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76(4):1217–1221
Svirčev Z, Markovič BS, Stevens T, Codd AG, Smalley L, Simeunović J, Obreht I, Dulić T, Pantelić D, Hambach U (2013) Importance of biological loess crusts for loess formation in semi-arid environments. Quat Int 296:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.10.048
Thomas AD, Dougill AJ (2007) Spatial and temporal distribution of cyanobacterial soil crusts in the Kalahari: Implications for soil surface properties. Geomorphology 85(1–2):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.029
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Wang W (2009) Feasibility of cyanobacterial inoculation for biological soil crusts formation in desert area. Soil Biol Biochem 41(5):926–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.07.001
Wang R, Zhu Q K, Bu N, et al (2010) Study on physicochemical properties of BSCs in the hilly-gully regions of the Loess Plateau. Arid Zone Res 27(3): 401−408. http://scholar.google.com/
Wu Y, Rao B, Wu P, Liu Y, Li G, Li D (2013) Development of artificially induced biological soil crusts in fields and their effects on topsoil. Plant Soil 370(1/2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1611-6
Zhang Y, Yang WK, Wang XQ, Zhang DY (2005) Influence of cryptogamic soil crusts on accumulation of soil organic matter in Gurbantunggut Desert, northern **njiang China. Acta Ecol Sin 25(12):3420–3425
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Wu N, Chen R, Zhang J (2009) Microalgal species variation at different successional stages in biological soil crusts of the Gurbantunggut Desert, Northwestern China. Biol Fertil Soils 45(5):539–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0364-0
Zhao HL, Guo YR, Zhou RL, Drake S (2010) Biological soil crust and surface soil properties in different vegetation types of Horqin Sand Land, China. CATENA 82(2):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2010.05.002
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources (9713434101).
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF) under Grant Agreement No. 99006758. The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by BA, FK, MS and EM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Behnaz Atashpaz and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Atashpaz, B., Khormali, F., Malekzadeh, E. et al. The effect of different sequences of biological crusts on soil physicochemical properties in dry land. Environ Earth Sci 82, 614 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11258-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11258-7