Abstract
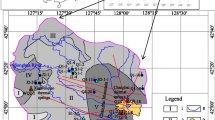
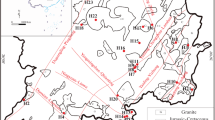
To identify the mechanism of geothermal water in **aoyangkou Geothermal Field, the earliest medium-temperature, high-yield geothermal resource found in Subei Basin, based on the water quality indicators of four geothermal water and one groundwater samples, hydrogeochemical and isotopic methods were used to analysis the hydrochemical characteristics, recharge sources and circulation depth of geothermal water, and to determine the reservoir temperature. Results show that the temperature of the thermal reservoir of the Neogene Yancheng Formation is about 39.5–41.64 °C. The geothermal waters are HCO3 type with TDS of 616–638 mg/L. The temperature of the Paleogene Funing Formation and Devonian–Silurian sandstone reservoir is about 95.45–110.78 °C. The geothermal waters are SO4 type with TDS of 1446–1812 mg/L. The concentrations of trace elements F, Sr and Li increased rapidly with the increase of temperature. The isotopic compositions of δ18O and δD indicates that the geothermal water is mainly recharged by atmospheric precipitation from the elevation of 145.5–524.5 m. The atmospheric precipitation infiltration is heated by the heat flow in the deep part and transported upward along the water-conducting structure through deep circulation (3.37 km) to the karst fissure at the top of the underlying strata of Yancheng Formation, forming a convective geothermal system. The upper Yancheng formation is an associated-conduction geothermal system. The research results provide reference and basis for the rational development and utilization of geothermal resources in the region.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data may be provided upon reasonable requests.
References
Ármannsson H (2016) The fluid geochemistry of Icelandic high temperature geothermal areas. Appl Geochem 66:14–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.10.008
Arnórsson S (1983) Chemical equilibria in icelandic geothermal systems—implications for chemical geothermometry investigations. Geothermics 12(2–3):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(83)90022-6
Ba J, Su C, Li Y et al (2018) Characteristics of heat flow and geothermal fields in Ruidian, Western Yunnan Province, China. Int J Heat Technol 36(4):1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijht.360407
Boudoukha A, Athamena M (2012) Caractérisation des eaux thermales de l’ensemble Sud sétifien. Est algérien [J]. J Water Sci 25(2):103–118. https://doi.org/10.7202/1011602ar
Chen ZS (2021) The formation mechanism of physiotherapy thermomineral water (hot spring) in Guizhou and its effect on human health. Guizhou University, Guiyang. https://doi.org/10.27047/d.cnki.ggudu.2021.000008
Chenaker H, Houha B, Vincent V (2018) Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of thermal water from northeastern Algeria. Geothermics 75:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.04.009
Craig HI (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dai W, Jiang XW, Luo YF et al (2021) Identification and quantification of factors controlling hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of geothermal water: an example from the Guide Basin, Qinghai Province. Earth Sci Front 28(1):420–427. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.7.8
Ellis AJ, Wilson SH (1960) The geochemistry of alkali metal ions in the Wairakei hydrothermal system. N Z J Geol Geophys 3(4):593–617
Fan DF, Xu NL (2015) A study of the occurrence of geothermal resources of low to mediun temperature in the Subei Basin. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 42(04):164–170. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.04.28
Fan DF, Xu XQ, Dai KM (2012) Origin study of geothermal field in **aoyangkou of Rudong County in Jiangsu. J Geol 36(02):192–197. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2012.02.192
Fournier RO (1977) Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 5(1–4):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(77)90007-4
Fournier RO, Rowe JJ (1966) Estimation of underground temperatures from the silica content of water from hot springs and wet-steam wells. Amerj 264(9):685–697
Fournier RO, Truesdell AH (1973) An empirical Na–K–Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37(5):1255–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4
Fu HY (2021) A study on the genesis of geothermal system in Baoshan Basin. Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming. https://doi.org/10.27200/d.cnki.gkmlu.2021.000614
Gao ZJ, Liu JT, Li FQ et al (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and temporal variations of geothermal water quality in Tangtou, Shandong, China. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081643
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria derivation of Na–K–Mg–Ca geoindicators. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52(12):2749–2765. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
Gu XM, Zhang QL, Cui YL et al (2017) Hydrogeochemistry and genesis analysis of thermal and mineral springs in Arxan, Northeastern China. Water 9(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010061
Guo Q (2012) Hydrogeochemistry of high-temperature geothermal systems in China: a review. Appl Geochem 27(10):1887–1898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.07.006
Hu JW, Yan JW, Wang SJ (2018) The development and utilization of geothermal energy in China. Environ Prot 46(08):45–48. https://doi.org/10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2018.08.011
Li C, Chen ZS, Wang GL et al (2020a) Geochemical characteristics and origin of geothermal water in Southeastern Guizhou, China. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 39(03):614–625. https://doi.org/10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2020.39.010
Li X, Huang X, Liao X et al (2020b) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and conceptual model of the geothermal waters in the **anshuihe Fault Zone, Southwestern China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020500
Li MH, Yuan JF, Huang C J et al (2020c) A study of the characteristics of geothermal reservoir and genesis of thermal groundwater in the Tongluoshan anticline near Guang’an in east Sichuan. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 47(06):36–46. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008038
Liu ML, He T, Wu QF et al (2020) Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal waters from **ongan new area and its indicating significance. Earth Sci 45(06):2221–2231. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2019.270
Lu LH, Pang ZH, Kong YL et al (2018) Geochemical and isotopic evidence on the recharge and circulation of geothermal water in the Tangshan Geothermal System near Nan**g, China: implications for sustainable development. Hydrogeol J 26(5):1705–1719
Lu ZQ, Peng MZ, Dong Y et al (2022) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of geothermal water in **yin of Shandong Province. Geol Surv China 9(01):104–114. https://doi.org/10.1938/j.zgdzdc.2022.01.11
Luo MM, Chen ZH, Zhou H et al (2018) Hydrological response and thermal effect of karst springs linked to aquifer geometry and recharge processes. Hydrogeol J 26(2):629–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1664-3
Luo J, Li Y, Tian J et al (2021) Geochemistry of geothermal fluid with implications on circulation and evolution in Fengshun-Tangkeng geothermal field, South China. Geothermics 100:102323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102323
Mohammadi Z, Bagheri R, Jahanshahi R (2010) Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of Changal thermal springs, Zagros region, Iran. Geothermics 39(3):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.06.007
Mohammadi Z, Zare M, Sharifzade B (2012) Delineation of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer, Bousheher, South of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 67:1473–1484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1591-5)
Papp DC, Niţoi E (2006) Isotopic composition and origin of mineral and geothermal waters from Tunad Bi Spa, Harghita Mountains, Romania. J Geochem Explor 89(1–3):314–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2005.12.008
Perez-Martinez I, Villanueva-Estadar RE et al (2019) Hydrogeochemical reconnaissance of the Atotonilco el Alto-Santa Rita geothermal system in the northeastern Chapala graben in Mexico. Geothermics 83:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.10173
Qin DJ, Pang ZH, Turner JV, Wen XR, Zhao YD, Xu XL, Liu T (2005) Isotopes of geothermal water in **’an area and implications on its relation to karstic groundwater in North Mountains. Acta Petrol Sin 21(5):1489–1500
Şener MF, Baba A (2019) Geochemical and hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of Kozakl geothermal fluids, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Geothermics 80(1):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.02.012
Song XQ, Peng Q, Duan QS et al (2019) Hydrochemistry characteristics and origin of geothermal water in Northeastern Guizhou. Earth Sci 44(09):2874–2886. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2019.146
Su YJ (2021) Geochemical characteristics and origin of geothermal water in Southeastern Guizhou, China. Jilin University, Jilin
Sun HL, Ma F, Lin WJ et al (2015) Geochemical characteristics and geothermometer application in high temperature geothermal field in Tibet. Bull Geol Sci Technol 34(03):171–177
Surendra P, Verma et al (1997) New improved equations for Na/K, Na/Li and SiO2 geothermometers by outlier detection and rejection. J Volcanol Geotherm Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0377-0273(97)00024-3
Tassi F, Aguilera F, Darrah T et al (2010) Fluid geochemistry of hydrothermal systems in the Arica-Parinacota, Tarapacá and Antofagasta regions (northern Chile). J Volcanol Geotherm Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.02.006
Wang XQ (2017) hydrogeochemical processes and genesis machenism of high-temperature geothermal system in Gudui, Tibet. China University of Geosciences, Bei**g
Wang X (2018) Formation conditions and hydrogeochemical characteristics of the geothermal water in typical coastal geothermal field with deep faults. China University of Geosciences, Guangdong
Wang Y (2021) A research on geochemical characteristics of geothermal fluids in Southeast Yunnan Province, China. Institute of Geophysics, China. Earthq Adm. https://doi.org/10.2748/d.cnki.gzdws.2021.000011
Wang LS, Li C et al (1995) Distributions of geotemperature and terrestrial heat flow density in Lower Yangtse area. Chin J Geophys 34(4):669–676 (in Chinese)
Wang P, Chen X, Shen L et al (2016) Geochemical features of the geothermal fluids from the Mapamyum non-volcanic geothermal system (Western Tibet, China). J Volcanol Geotherm Res 320:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.04.002
Xu PY, Ding ZN (1997) Formation of potable natural mineral spring water containing satrontium. Site Investig Sci Technol 05:36–38
Xu PP, Zhang QY, Qian H (2019) Characterization of geothermal water in the piedmont region of Qinling Mountains and Lantian-Bahe Group in Guanzhong Basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8418-6
Xu CH, Yu DD, Luo ZJ (2021) Recharge sources and genetic model of geothermal water in Tangquan, Nan**g, China. Sustainability 13(8):4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084449
Yang N, Wang AD, Sun ZX et al (2023) Hydrochemistry and hydrogen-oxygen isotope characteristics of geothermal water in Zhangzhou, Fujian. J East China Univ Technoly (Nat Sci) 46(02):167–178
Zhang BJ (2011) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation conditions of the geothermal water in Northwestern Shandong Province. China University of Geosciences, Bei**g
Zhao H (2009) Study on hydrogeochemistry and environmental impacts from exploitation and utilization of geothermal water in Guanzhong Basin. Chang’an University, **’an
Zhao YH, Yang JY, Wang H et al (2017) Hydrogen and oxygen isotope distribution characteristics of geothermal water. Prog Geophys (in Chin) 32(6):2415–2423. https://doi.org/10.6038/pg20170618
Zhou HF, Tan HB, Zhang XY et al (2011) Recharge source, hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Nantong, Jiangsu Province. Geochimica 40(06):566–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8418-6
Zhu JL, Hu KY, Lu XL et al (2015) A review of geothermal energy resources, development, and applications in China: current status and prospects. Energy 93:466–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.08.098
Zou PF, Qiu Y, Fan DF (2022) Study on geochemical characteristics of mid-low temperature geothermal fluid in representative area of Subei Basin. Geol J China Univ 28(02):262–273. https://doi.org/10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2020099
Zuo LQ, Wang CH, **g H, Qiu Y (2016) The application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method to geothermal prospecting in **aoyangkou of Nantong city in Jiangsu. Chin J Eng Geophys 13(01):122–129
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutralization Science and Technology Innovation Special Fund of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant no. BE2022859).
Funding
Funding was supported by Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutralization Science and Technology Innovation Special Fund of Jiangsu Province, China, Grant no. BE2022859.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ: writing original draft. ZL: methodology. JD and LW: analyse data. ZL and XW: validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Luo, Z., Du, J. et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal water in **aoyangkou, Nantong, China. Environ Earth Sci 82, 456 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11140-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11140-6