Abstract
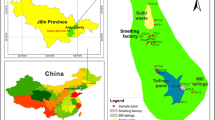
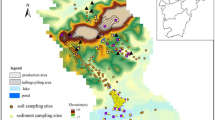
Cyanide and potentially toxic elements in tailings from gold mining can cause serious pollution, and harm the surrounding environment through rainfall seepage and leakage from tailings ponds. In this study, 40 surface soil samples were collected from the Liujiadian tailings pond basin in **gu District, Bei**g, and the contents of cyanide, Sb, As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Hg were determined. A spatial distribution map of these pollutants was drawn, the pollution degrees of cyanide, Sb, As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Hg were evaluated, and the ecological risk degrees of As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Hg were preliminarily evaluated. The pollution sources were analysed using multivariate statistical methods. The contents of potentially toxic elements in 17 plant samples collected in the study area were analysed, and the pollution levels were evaluated. The results show that the seriously polluted areas are mainly around the tailings pond and its downstream areas, and the pollution degree decreases with increasing distance. Arsenic, Pb and Cd are the main pollutants, followed by cyanide, Cu and Zn. Antimony and Hg occur as minor pollutants. The potential ecological risk of the whole study area is very high, and the high ecological risk area is around the tailings pond and its downstream areas. The risk is mainly associated with As and Cd. The multivariate statistical analysis results show that pollution mainly comes from the tailings pond, and agricultural activities have a certain impact. According to the detected potentially toxic element concentrations in the 17 plant samples, the plants are essentially not polluted by potentially toxic elements.


Modified from Bei**g Institute of Geology 1982





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
My manuscript has data include as electronic supplementary materials.
References
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martínez-Martínez S, Zornoza R, Carmona DM, Kabas S (2011) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. J Geochem Explor 109:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.01.004
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. Environ Pollut 22:11–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4470-7_2
Assawincharoenkij T, Hauzenberger C, Sutthirat C (2017) Mineralogy and geochemistry of tailings from a gold mine in northeastern Thailand. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 23(2):364–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2016.124889
Bei**g Institute of Geology (1982) 1: 100,000 manual for revision of geological map of Bei**g (in Chinese)
Bruger A, Fafilek G, Rojas-Mendoza L (2018) On the volatilization and decomposition of cyanide contaminations from gold mining. Sci Total Environ 627:1167–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.320
Buttafuoco G, Tarvainen T, Jarva J, Guagliardi I (2016) Spatial variability and trigger values of arsenic in the surface urban soils of the cities of Tampere and Lahti. Finland Environ Earth Sci 75:896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5707-1
Cheng HX, Li M, Zhao CD, Li K, Peng M, Qin A, Cheng XM (2014) Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China. J Geochem Explor 139:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.012
Davies BE, White HM (1981) Trace elements in vegetables grown on soils contaminated by base metal mining. J Plant Nutr 3:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168109362846
Deng XL, Li LH, Li XX, Tan YF (2015) Geohazard susceptibility assessment of **gu District. J Eng Gel 23(s1):266–277. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2015.s1.043(inChinese)
Devi NL, Yadav IC (2018) Chemometric evaluation of heavy metal pollutions in Patna region of the Ganges alluvial plain, India: implication for source apportionment and health risk assessment. Environ Geochem Hlth 40:2343–2358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0101-4
Ding Q, Wang Y, Zhuang DF (2018) Comparison of the common spatial interpolation methods used to analyze potentially toxic elements surrounding mining regions. J Environ Manage 212:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.074
Doabi SA, Karami M, Afyuni M (2019) Heavy metal pollution assessment in agricultural soils of Kermanshah province. Iran Environ Earth Sci 78:70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8093-7
El Azhari A, Rhoujjati A, El Hachimi ML, Ambrosi J (2017) Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-plant system and the sediment-water column around a former Pb/Zn-mining area in ne morocco. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:464–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.051
Environmental Protection Agency of **gu District (EPAP) (2004) Report of the treatment scheme of gold tailings sand (in Chinese)
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00243-8
Fang B, Qi XX, Qiao WF (2014) Spatial distribution effect and analysis contamination degree of farmland soil heavy metals in Pujiang County. J Northeast Agric Univ 45:88–95. https://doi.org/10.19720/j.cnki.issn.1005-9369.2014.12.014
Feng X, Dai Q, Qiu G, Li G, He L, Wang D (2006) Gold mining related mercury contamination in Tongguan, Shaanxi Province, PR China. Appl Geochem 21:1955–1968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.08.014
Guan Y, Shao CF, Ju MT (2014) Heavy metal contamination assessment and partition for industrial and mining gathering areas. Int J Env Res Pub He 11:7286–7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110707286
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hedjazi F, Monhemius AJ (2018) Industrial application of ammonia-assisted cyanide leaching for copper-gold ores. Miner Eng 126:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.07.005
Hu ZG, Wang CS, Li KQ, Zhu XY (2018) Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals over a typical nonferrous metal mine area in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Earth Sci 77:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7771-1
Johnson CA (2015) The fate of cyanide in leach wastes at gold mines: An environmental perspective. Appl Geochem 57:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.05.023
Khalil A, Hanich L, Bannari A, Zouhr L, Pourret O, Hakkou R (2013) Assessment of soil contamination around an abandoned mine in a semi-arid environment using geochemistry and geostatistics: Pre-work of geochemical process modeling with numerical models. J Geochem Explor 125:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.11.018
Kowalska J, Mazurek R, Gasiorek M, Setlak M, Zaleski T, Waroszewski J (2016) Soil pollution indices conditioned by medieval metallurgical activity-a case study from krakow (Poland). Environ Pollut 218:1023–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.053
Li J, Heap AD (2011) A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performance and impact factors. Ecol Inform 6:228–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2010.12.003
Li HY, Hu LZ (2006) The impacts of gold mines on the ecoenvironment of Bei**g. City Geol 1:37–40. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2006.01.010(inChinese)
Li X, Lee SL, Wong SC, Shi W, Thornton I (2004) The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ Pollut 129:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.030
Li F, Zhang JD, Liu WC, Liu JA, Huang JH, Zeng GM (2018b) An exploration of an integrated stochastic-fuzzy pollution assessment for heavy metals in urban topsoil based on metal enrichment and bioaccessibility. Sci Total Environ 644:649–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.366
Li HY, Chen XZ, Ge CF, Zhang HJ (2018a) Environmental impact of gold mine production in Bei**g and the countermeasures, China. Energy Environ Protect 40:83–86. https://doi.org/10.19389/j.cnki.1003-0506.2018.01.016(inChinese)
Lim HS, Lee JS, Chon HT, Sager M (2008) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au-Ag mine in Korea. J Geochem Explor 96:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2007.04.008
Lindsay MBJ, Moncur MC, Bain JG (2015) Geochemical and mineralogical aspects of sulfide mine tailings. Appl Geochem 57:157–177
Liu W, Xu HM, Liao Y, Wang YL, Yan NQ, Qu Z (2020) Co-doped ZnS with large adsorption capacity for recovering Hg0 from non-ferrous metal smelting gas as a co-benefit of electrostatic demisters. Environ Sci Pollut R. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08401-3
Lu XW, Zhang XL, Li Loretta Y, Chen H (2014) Assessment of metals pollution and health risk in dust from nursery schools in **’an, China. Environ Res 128:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.11.007
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00273-5
Mcgrath D, Zhang C, Carton OT (2004) Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in silver mines area, Ireland. Environ Pollut 127:248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2003.07.002
Mcgrory ER, Brown C, Bargary N, Williams NH, Mannix A (2016) Arsenic contamination of drinking water in Ireland: a spatial analysis of occurrence and potential risk. Sci Total Environ 579:1863–1875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.171
Mukherjee I, Singh UK, Singh RP, Anshumali KD, Jha PK, Mehta P (2019) Characterization of heavy metal pollution in an anthropogenically and geologically influenced semi-arid region of east India and assessment of ecological and human health risks. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135801
Oves M, Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahmad E (2012) Soil contamination, nutritive value, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals: an overview. Toxicity of Heavy Metals to Legumes and Bioremediation. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0730-0_1
Pan LB, Ma J, Hu Y, Su BY, Fang GL, Wang Y, Wang ZS, Wang L, **ang B (2016) Assessments of levels, potential ecological risk, and human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi province, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:19330–19340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7044-z
Phenrat T (2020) Community citizen science for risk management of a spontaneously combusting coalâ mine waste heap in Ban Chaung, Dawei District, Myanmar. GeoHealth. doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2020gh000249
Sahoo HB, Gandre DK, Das PK, Karim MA, Bhuyan GC (2018) Geochemical map** of heavy metals around Sukinda-Bhuban area in Jajpur and Dhenkanal districts of Odisha. India Environ Earth Sci 77(2):34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7208-2
Sakan S, Dević G, Relić D, Anđelković I, Sakan N, Đorđević D (2014) Risk assessment of trace element contamination in river sediments in Serbia using pollution indices and statistical methods: a pilot study. Environ Earth Sci 73:6625–6638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3886-1
Santos-Frances F, Martinez-Grana A, Zarza CA, Sanchez AG, Rojo PA (2017) Spatial distribution of heavy metals and the environmental quality of soil in the northern plateau of Spain by geostatistical methods. Int J Evn Res Pub He 14:568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060568
Shah MH, Ilyas A, Gulraiz A, Bashir A (2019) Pollution assessment and source apportionment of selected metals in rural (Bagh) and urban (Islamabad) farmlands. Pakistan Environ Earth Sci 78:189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8198-z
Shao WW (2009) Strike hard and end the “sequel” of gold mining. Modern Occupational Safety 5:37–39
Sun YB, Zhou QX, **e XK, Liu R (2010) Spatial, source and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.074
Sun H, Li J, Mao XJ (2012) Heavy metals’ spatial distribution characteristics in a copper mining area of Zhejiang Province. J Geogr Inf Syst 4:46–54. https://doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2012.41007
Tran QB, Phenrat T, Lohitnavy M (2019b) Human continuous hydrogen cyanide inhalation predictor with a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06033-w
Tran QB, Lohitnavy M, Phenrat T (2019a) Assessing potential hydrogen cyanide exposure from cyanide-contaminated mine tailing management practices in Thailand’s gold mining. J Environ Manage 249:109357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109357
Uchimiya M, Bannon D, Nakanishi H, McBride M, Williams M, Yoshihara T (2020) Chemical speciation, plant uptake, and toxicity of heavy metals in agricultural soils. J Agric Food Chem 68:12856–12869. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00183
Wang HY, Lu SG (2011) Spatial distribution, source identification and affecting factors of heavy metals contamination in urban–suburban soils of Lishui city, China. Environ Earth Sci 64:1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1005-0
**ao Q, Zong YT, Lu SG (2015) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotox Environ Safe 120:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.019
**e BN, Jia XX, Qin ZF, Zhao CL, Shao MA (2020) Comparison of interpolation methods for soil moisture prediction on China's Loess Plateau. Vadose Zone J. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/vzj2.20025
Yan WB, Mahmood Q, Peng DL, Fu WJ, Chen T, Wang Y, Li S, Chen JR, Liu D (2015) The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals and risk assessment of moso bamboo forest soil around lead–zinc mine in Southeastern China. Soil till Res 153:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.05.013
Yang ZX, Zhou HP, **e XY, Guan CL, Che L (2015) Effect of long-term fertilization on Pb, As contents of soil and maize grain. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 23:4827–4836
Zahran MA, El-Amier YA, Elnaggar AA, Mohamed HA, El-Alfy MA (2015) Assessment and distribution of heavy metals pollutants in manzala lake. Egypt J Geogr Inf Syst 3:107–122. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2015.36017
Zaranyika MF, Nyati W (2017) Uptake of heavy metals by Typha capensis from wetland sites polluted by effluent from mineral processing plants: implications of metal-metal interactions. 3 Biotech 7(5):286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0916-1
Zhang CS (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.028
Zhang AX, Nie YN, Ji HB, Feng JG, Qin F (2014b) Spatial distribution, fractionation and pollution assessment of heavy metals in Wanzhuang gold mining field in upstream part of water conservation area of Bei**g, China. J Agro Environ Sci 33:2321–2328. https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2014.12.007(inChinese)
Zhang Z, Yu D, Shi X, Wang N, Zhang G (2014a) Priority selection rating of sampling density and interpolation method for detecting the spatial variability of soil organic carbon in China. Environ Earth Sci 73:2287–2297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3580-3
Zhang C, Nie S, Liang J, Zeng G, Wu H, Hua S, Liu J, Yuan Y, **ao H, Deng L, **ang H (2016) Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Sci Total Environ 557–558:785–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.170
Zhang PY, Qin CZ, Hong X, Kang GH, Qin MZ, Yang D, Pang B, Li YY, He JJ, Dick RP (2018) Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of yellow river irrigation in China. Sci Total Environ 633:1136–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.228
Zhao L, Xu YF, Hou H, Shangguan YX, Li FS (2014) Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tian**, China. Sci Total Environ 468–469:654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.094
Zhong LY, Liu LM, Yang JW (2012) Characterization of heavy metal pollution in the paddy soils of **angyin county, Dongting lake drainage basin, Central South China. Environ Earth Sci 67:2261–2268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1671-6
Zhong BQ, Liang T, Wang LQ, Li KX (2014) Applications of stochastic models and geostatistical analyses to study sources and spatial patterns of soil heavy metals in a metalliferous industrial district of China. Sci Total Environ 490:422–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.127
Zhou J, Feng K, Pei ZP, Lu MJ (2016) Pollution assessment and spatial variation of soil heavy metals in Lixia River Region of Eastern China. J Soils Sediment 16:748–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1289-x
Zou JM, Liu XX, Dai W, Luan YN (2018) Pollution assessment of heavy metal accumulation in the farmland soils of Bei**g’s suburbs. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:27483–27492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2708-5
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the project of Bei**g Tailings Ponds Investigation and Impact Assessment (No. TC170855A). The assistance of the Bei**g Branch of ALS Analytical Testing (Shanghai) Co. Ltd in detecting the pollution elements content in the soil and the assistance of the Bei**g Center for Physical and Chemical Analysis in detecting the pollution elements content in the plants are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
The project of Bei**g Tailings Ponds Investigation and Impact Assessment (No. TC170855A) have been provided for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhongjian Zhang and Hao Zhang conceived of the study, designed this study, and carried out field investigation. Hao Zhang and Qiguo Zhang carried out the lab work and analysed data. Hao Zhang wrote the manuscript. Zhongjian Zhang and **aolei Ma critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Ma, X. et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of pollutants in a tailings pond for gold mining in **gu District, Bei**g, China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 416 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09710-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09710-7