Abstract
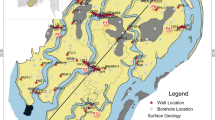
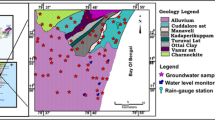
Coastal aquifers are considered as major sources for freshwater supply worldwide, especially in arid zones. The weak rainfall as well as the intensive extraction of groundwater from coastal aquifers reduce freshwater budget and create local water aquifer depression, causing both seawater intrusion and a threat to groundwater. This phenomenon was observed in the Jerba Island which is located in southeast Tunisia. Jerba’s unconfined aquifer shows high values of groundwater salinity reaching, locally, 17 g/l and a strong contrast between some zones of the aquifer. High pum** rates and weak recharge disturb the natural equilibrium between fresh and saline water causing water salinization in most areas of the island. This study aims at establishing the salinity map of the aquifer and identifying the origin of groundwater salinization. The salinity map shows that zones characterized by low groundwater salinity are located in the center of the study area. High groundwater salinities are observed near the coast and in some parts having low topographic and piezometric levels. Groundwater geochemical characterization, and Br/Cl and Na/Cl ratios suggest that the origin of abnormal salinity is seawater intrusion. Considering groundwater salinity values and Br concentrations, a seawater intrusion map is established. It shows that many areas of the unconfined aquifer are contaminated by mixed groundwater and seawater. The statistical analysis demonstrates that high mineralization of the groundwater is due to gypsum and carbonate dissolution coupled with the mixed groundwater and seawater in many areas.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfib B, Cavalera T, Gilli E (2006) Influence de l’hydrodynamisme sur l’intrusion saline en aquifère karstique côtier. C R Geosci 338:757–767
Avisar D, Rosenthal E, Flexer A, Shulman H, Ben-Avraham Z, Guttman J (2003) Salinity sources of Kefar Uriya wells in the Judea Group aquifer of Israel. Part 1-conceptual hydrogeological model. J Hydrol 270:27–38
Ben Hamouda MF, Tarhouni J, Leduc Ch, Zouari K (2011) Understanding the origin of salinization of the Plio-quaternary eastern coastal aquifer of Cap Bon (Tunisia) using geochemical and isotope investigations. Environ Earth Sci 63(5):889–901
Boluda-Botella N, Gomis-Yagües V, Ruiz-Bevia F (2008) Influence of transport parameters and chemical properties of the sediment in experiments to measure reactive transport in seawater intrusion. J Hydrol 357:29–41
Boschetti T, Venturelli G, Toscani L, Barbieri M, Mucchino C (2005) The Bagni di Lucca thermal waters (Tuscany, Italy): an example of Ca–SO4 waters high Na/Cl and low Ca/SO4 ratios. J Hydrol 307:270–293
Bouaziz S, Jedoui Y, Barrier E, Angelier J (2003) Néotectonique affectant les dépôts marins tyrrhéniens du littoral sud-est tunisien: implication pour les variations du niveau marin. C R Geosci 335:247–254
Bouri S, Abida H, Khanfir H (2008) Impacts of wastewater irrigation in arid and semiarid regions: case of Sidi Abid region. Tunis Environ Geol 53(7):1421–1432
Chamtouri I, Abida H, Khanfir H, Bouri S (2008) Impacts of at-site wastewater disposal systems on the groundwater aquifer in arid regions: case of Sfax City, Southern Tunisia. Environ Geol 55:1123–1133
Davaud E, Jedoui Y, Strasser A (1996) Holocene peritidal and evaporitic sedimentation in Southern Tunisia. 17th African European Meeting of Sedimentology, Sfax, 26–28 March 1996, Field Trip Guidebook, pp 71–82
De Montely V, Radakovitch O, Vallet-Coulomb C, Blavoux B, Hermitte D, Valles V (2008) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in a confined coastal aquifer: case of the Rhône delta (Southern France). Appl Geochem 23:2337–2349
Gattacceca JC, Vallet-Coulomb C, Mayer A, Claude C, Radakovitch O, Conchetto E, Hamelin B (2009) Isotopic and geochemical characterization of salinization in the shallow aquifers of a reclaimed subsiding zone: the southern Venise lagoon coastland. J Hydrol 378:46–61
Ghabayen SMS, McKee M, Kemblowski M (2006) Ionic and isotopic ratios for identification of salinity sources and missing data in the Gaza aquifer. J Hydrol 318:360–373
Giambastiani BMS, Antonellini M, Oude Essink GHP, Stuurman RJ (2007) Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): a numerical model. J Hydrol 340:91–104
Gómez-Hernánez JJ, Sahuquillo A, Capilla JE (1997) Stochastic simulation of transmissivity fields conditional to both transmissivity and piezometric data—I. Theory J Hydrol 203:162–174
Jedoui Y (2000) Sédimentologie et géochimie des dépôts littoraux quaternaires: reconstitution des variations des climats et du niveau marin dans le sud est tunisien. Thèse de doctorat es-sciences géologiques, Université de Tunis II
Jorgensen NO, Andersen MS, Engesgaard P (2008) Investigation of a dynamic seawater event using strontium isotopes (87Sr/86Sr). J Hydrol 348:257–269
Kafri U, Arad A (1979) Current subsurface intrusion of Mediterranean sea water—a possible source of groundwater salinity in the rift valley system. Isr J Hydrol 44:267–287
Khalili B (1986) Hydrogeological study of Jerba unconfined aquifer. Water resources direction, Ministry of Agriculture
Kim Y, Lee KS, Koh DC, Lee DH, Lee SG, Park WB, Koh GW, Woo NC (2003) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in costal aquifer: a case study in Jesu volcanic island. Korea J Hydrol 270:282–294
Martos FS, Bosch AP, Sanchez LM, Izquierdo AV (2002) Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using minor ions (lower Andarax, Southeast Spain). J S Total Env 297:43–58
Petalas C, Lambrakis N (2006) Simulation of intense salinization phenomena in costal aquifers-the case of the costal aquifers of Thrace. J Hydrol 324:51–64
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Am Geophys Union Trans 25:914–923
Prieto C, Kotronarou A, Destouni G (2006) The influence of temporal hydrological randomness on seawater intrusion in costal aquifers. J Hydrol 330:285–300
Rao U, Hollocher K, Sherman J, Eisele I, Frunzi MN, Swatkoski SJ, Hammons AL (2005) The use of 36Cl and chloride/bromide ratios in discerning salinity sources and fluid mixing patterns: a case study at Saratoga Springs. Chem Geol 222:94–111
Rosenthal E, Zilberbrand M, Livshitz Y (2007) The hydrochemical evolution of brackish groundwater in central and northern Sinai (Egypt) and in the western Negev (Israel). J Hydrol 337:294–314
Saidi S, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2009) Groundwater vulnerability and risk map** of the Hajeb-jelma aquifer (Central Tunisia) using a GIS-based DRASTIC model. Environ Earth Sci 59(7):1579–1588
Subyani AM (2005) Hydrochemical identification and salinity problem of ground-water in Wadi Yalamlam basin, Western Saudi Arabia. J Arid Environ 60:53–66
Teissier JL (1967) Hydrogeological study of Jerba unconfined aquifer. Water resources direction, Ministry of Agriculture
Trabelsi R, Zairi M, Smida H, Ben Dhia H (2005) Salinisation des nappes côtières: cas de la nappe nord du Sahel de Sfax, Tunisie. C R Geosci 337:515–524
Trabelsi R, Abid K, Zouari K, Yahyaoui H (2011) Groundwater salinization processes in shallow coastal aquifer of Djeffara plain of Medenine, Southeastern Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1273-8
Van Tonder GJ, Hodgson FD (1986) Interpretation of hydrogeochemical facies by multivariate statistical methods. Water S Afr 12(1):1–6
Vengosh A, Gill J, Davisson ML, Huddon GB (2002) A multi isotope (B, Sr, O, H, C) and age dating (3H-3He, 14C) study of groundwater from Salinas Valley, California: hydrochemistry, dynamics, and contamination processes. Water Resour Res 38:9-1–9-17
Acknowledgments
The authors warmly thank the anonymous reviewers for their detailed and constructive criticisms, which were of great help in improving this manuscript. The authors also wish to express their thanks to Fathi BOURMECH from the Faculty of Arts at Sfax for carefully editing and proofreading the English of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharroubi, A., Tlahigue, F., Agoubi, B. et al. Hydrochemical and statistical studies of the groundwater salinization in Mediterranean arid zones: case of the Jerba coastal aquifer in southeast Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 67, 2089–2100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1648-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1648-5