Abstract
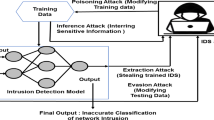
Information hiding techniques like steganography are used by hackers to obfuscate malicious attack codes to carry malware scripts and deliver to crypto-miners in on-demand platforms like Cloud. Stegware is a type of information-hiding malware that employs steganography to avoid detection by modern malware detection systems. This work proposes a Stegware detection system that recognizes obfuscated payloads from input images and verifies whether the obfuscated payload is the target of any stegware attack. The proposed system detects the stegware in four phases: Obfuscated Payload Detection phase that detects the presence of any obfuscated item concealed inside the digital medium; Obfuscated Payload Extraction phase that decodes stego-repository images to extract the data that are steganographically obfuscated inside the input; Obfuscated Payload Classification phase that detects whether the extracted data is legitimate or malicious stegware file, using binary classifier; Calculation of malicious percentage phase that uses fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm to calculate the quantum and frequency of malicious activities. The proposed system is experimentally tested on real dataset and analyzed with existing models. The simulation results illustrate that the proposed Stegware detection system detects the steganographically-hidden attacks and identifies malicious activities in percentage terms as compared to other models.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai J, Wang J, Zou G (2014) ‘‘A malware detection scheme based on mining format information. Sci World J 2014(260905):11
Caviglione L, Choras M (2020) Tight arms race: overview of current malware threats and trends in their detection. IEEE 9:5371–5396. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3048319
Caviglione L, Mazurczyk W, Repetto M, Schaffhauser A, Zuppelli M (2021) Kernel-level tracing for detecting stegomalware and covert channels in Linuxenvironments. Int J Comput Telecommun Netw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108010
Chen M, Yang Y, Lei M, Dong Z (2020) Joint multi-domain feature learning for image steganalysis based on CNN. EURASIP J Image Video Process 2020:1–2
Chinnasamy P, Deepalakshmi P (2021) HCAC-EHR: hybrid cryptographic access control for secure EHR retrieval in healthcare cloud. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-02942-2
Choudhury S, Amritha PP, Sethumadhavan M (2019) Stegware destruction using showering methods. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng (IJITEE) 8:256–259
Cohen A, Nissim N, Elovici Y (2020) MalJPEG: machine learning based solution for detection of malicious JPEG images. Expert Syst Appl 8:19997–20011
De Paula S, Mendonça (2020) Synthetic datasets generator for testing information visualization and machine learning techniques and tools. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991949
Fridrich J (2023) Steganographic algorithms. Stegware. http://dde.binghamton.edu/download/stego_algorithms/
Gan J, Liu J, Luo X, Yang C, Liu F (2018) Reliable steganalysis of HUGO steganography based on partially known plaintext. Multimed Tools Appl 77:18007–18027
George G, Savaridassan P, Devi K (2018) Detect images embedded with malicious programs. Int J Pure Appl Math. 120(6):2763–2777
Gu X, Guo J (2019) A study on subtractive pixel adjacency matrix features. Multimed Tools Appl 78:19681–19695
Holub V, Fridrich J, Denemark T (2014) Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP J Inf Secur 2014(1):1
Kaur J, Singh S (2018) Feature selection using mutual information and adaptive particle swarm optimization for image steganalysis. 7th international conference on reliability infocom technologies and optimization (ICRITO) (trends and future directions). IEEE, pp 29–31
Kodovsky J, Fridrich J (2011) Steganalysis in high dimensions fusing classifiers built on random subspaces. Proc SPIE Electr Imaging Secur Forensics Multimed XIII 7880:1–13
Li B, Wang M, Huang J, Li X (2014) A new cost function for spatial image steganography. IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 4206–4210
Lichy K, Lipinski P, Grzelak M (2020) Deep convolutional network for steganalysis of HUGO WOW and UNIWARD algorithms. 16th international conference on control automation robotics and vision (ICARCV). IEEE
Monika A, Eswari R (2021) Ensemble-based stegomalware detection system for hidden ransomware attack. Inventive systems and control. Springer, Singapore, pp 599–619
Monika A, Eswari R (2022) ‘Prevention of hidden information security attacks by neutralizing stego-malware. Comput Electr Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107990
Pinhero A, Anupama ML, Vinod P, Visaggioc CA, Aneesh N, Abhijith S, Krishnan A (2021) Malware detection employed by visualization and deep neural network. J Comput Secur. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102247
Prasad SS, Hadar O, Polian I (2020) Detection of malicious spatial-domain steganography over noisy channels using convolutional neural networks. Media Watermarking Secur Forensics 76–1:2020
Roseline SA, Geetha S (2021) A comprehensive survey of tools and techniques mitigating computer and mobile malware attacks. J Comput Elect Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107143
Stergiopoulos G, Gritzalis D, Vasilellis E, Anagnostopoulou A (2021) Drop** malware through sound injection: a comparative analysis on android operating systems. Comput Secur 105:102228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102228
Tian H, Liu J, Chang CC, Chen CC, Huang Y (2019) Steganalysis of AMR speech based on multiple classifiers combination. IEEE 7:140957–140968. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943504
Usman N, Usman S (2021) Intelligent dynamic malware detection using machine learning in IP reputation for forensics data analytics. J Future Gener Comput Syst 118:124–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.01.004
Wang H, Pan X (2021) Steganalysis of convolutional neural network based on neural architecture search. J Multimed Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-021-00779-5
WeikeYou HZ, Zhao X (2020) A Siamese CNN for image steganalysis. IEEE Transac Inform Forensics Secur 16:291–306
Zhao D, Liu L, Yu F, Heidari AA, Wang M (2021) Ant colony optimization with horizontal and vertical crossover search: fundamental visions for multi-threshold image segmentation. J Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114122
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Monika, A., Eswari, R. An ensemble-based stegware detection system for information hiding malware attacks. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 4401–4417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-023-04559-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-023-04559-z