Abstract
In this study, a comprehensive comparison of the poplar wood fermentation process and fermentation-coupled gasification process was carried out from energy, environmental, and economic perspectives. The process of fuel ethanol from poplar wood fermentation (Case 1) and fuel ethanol from poplar wood fermentation coupled with lignin gasification for jet fuel (Case 2) was simulated using aspen plus software. The exergy analysis showed that the exergy efficiency of Case 1 and Case 2 were 36% and 35.6%, respectively. The product separation process contributed the most to the exergy losses, and the Case 2 had a 4.5% increase in revenue exergy over Case 1. The life cycle assessment (LCA) results showed that biofuels had a lower environmental impact than conventional petrol, and Case 2 was lower than Case 1. The production stage contributed the most to the global warming potential (GWP) of Case 1 and Case 2 with 49.4% and 51.2%, respectively. The techno-economic analysis showed that the fixed investment in Case 2 had increased by $112.9 million, and the annual operating costs had increased by $27 million compared to Case 1. The costs of fuel production in Case 1 and Case 2 were $1079.3/ton and $1033.4/ton, respectively.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
Fermentation to ethanol (Case 1) and its coupled pathway (Case 2) were simulated.
The simulation results were analyzed in terms of energy, environment, and economy.
Minimum selling price of biofuel was $0.054/MJ in Case 1 and $0.055/MJ in Case 2.
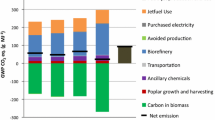
Case 2 has less impact on the environment than Case 1.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data can be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Kundu, A., Sahu, J.N., Redzwan, G., Hashim, M.A.: An overview of cathode material and catalysts suitable for generating hydrogen in microbial electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrog Energy. 38(4), 1745–1757 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.11.031
Vanhala, P., Bergström, I., Haaspuro, T., Kortelainen, P., Holmberg, M., Forsius, M.: Boreal forests can have a remarkable role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions locally: Land use-related and anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and sinks at the municipal level. Sci. Total Environ. 557–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.040
Huiyan, Z., Rui, X., Baosheng, J., Guomin, X., Ran, C.: Biomass catalytic pyrolysis to produce olefins and aromatics with a physically mixed catalyst. Bioresour Technol. 140, 256–262 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.094
Stummann, M.Z., Høj, M., Gabrielsen, J., Clausen, L.R., Jensen, P.A., Jensen, A.D.: A perspective on catalytic hydropyrolysis of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 143, 110960 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110960
Espada, J.J., Villalobos, H., Rodriguez, R.: Environmental assessment of different technologies for bioethanol production from Cynara cardunculus: A Life Cycle Assessment study. Biomass Bioenerg. 144, 105910 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105910
Oliveira, M., Rosentrater, K.A.: Environmental and economic analysis of low-moisture anhydrous ammonia (LMAA) as a pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production. J. Clean. Prod. 315, 128173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128173
Naik, S.N., Goud, V.V., Rout, P.K., Dalai, A.K.: Production of first and second generation biofuels: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14(2), 578–597 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.003
van der Pol, E.C., Bakker, R.R., Baets, P., Eggink, G.: By-products resulting from lignocellulose pretreatment and their inhibitory effect on fermentations for (bio)chemicals and fuels. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98(23), 9579–9593 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6158-9
Singh, S.K., Ekhe, J.D.: Towards effective lignin conversion: HZSM-5 catalyzed one-pot solvolytic depolymerization/hydrodeoxygenation of lignin into value added compounds. Rsc Adv. 4(53), 27971–27978 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA02968B
Pandey, M.P., Kim, C.S.: Lignin Depolymerization and Conversion: A review of thermochemical methods. Chem. Eng. Technol. 34(1), 29–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201000270
Li, C.C., Gillum, C., Toupin, K., Donaldson, B.: Biomass boiler energy conversion system analysis with the aid of exergy-based methods. Energy Conv Manag. 103, 665–673 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.014
Ojeda, K., Sánchez, E., El-Halwagi, M., Kafarov, V.: Exergy analysis and process integration of bioethanol production from acid pre-treated biomass: Comparison of SHF, SSF and SSCF pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 176–177, 195–201 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.06.083
Ofori-Boateng, C., Lee, K.T.: Comparative thermodynamic sustainability assessment of lignocellulosic pretreatment methods for bioethanol production via exergy analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 162–171 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.082
Michailos, S., Parker, D., Webb, C.: A techno-economic comparison of Fischer–Tropsch and fast pyrolysis as ways of utilizing sugar cane bagasse in transportation fuels production. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 118, 206–214 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.01.001
Finnveden, G., Hauschild, M.Z., Ekvall, T., Guinée, J., Heijungs, R., Hellweg, S., Koehler, A., Pennington, D., Suh, S.: Recent developments in Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Manage. 91(1), 1–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.06.018
Lee, M., Lin, Y., Chiueh, P., Den, W.: Environmental and energy assessment of biomass residues to biochar as fuel: A brief review with recommendations for future bioenergy systems. J. Clean. Prod. 251, 119714 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119714
Cox, K., Renouf, M., Dargan, A., Turner, C., Klein-Marcuschamer, D.: Environmental life cycle assessment (LCA) of aviation biofuel from microalgae, Pongamia pinnata, and sugarcane molasses. Biofuel Bioprod. Bior. 8(4), 579–593 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1488
Seber, G., Malina, R., Pearlson, M.N., Olcay, H., Hileman, J.I., Barrett, S.R.H.: Environmental and economic assessment of producing hydroprocessed jet and diesel fuel from waste oils and tallow. Biomass Bioenerg. 67, 108–118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.04.024
Aden, A., Foust, T.: Technoeconomic analysis of the dilute sulfuric acid and enzymatic hydrolysis process for the conversion of corn stover to ethanol. Cellulose. 16(4), 535–545 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9327-8
Zhao, J., Feng, D., Lee, J.: Life cycle assessment of calcium oxide pretreatment of corn stover with carbon dioxide neutralization for ethanol production. Bioresour Technol. 379, 129042 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129042
Rodríquez-Machín, L., Ronsse, F., Casas-Ledón, Y., Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.: Fast pyrolysis of raw and acid-leached sugarcane residues en route to producing chemicals and fuels: Economic and environmental assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 296, 126601 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126601
Yao, Y.Q., He, M.L., Ren, Y.B., Ma, L.Y., Luo, Y., Sheng, H.M., **ang, Y., Zhang, H., Li, Q., An, L.Z.: Anaerobic digestion of poplar processing residues for methane production after alkaline treatment. Bioresour Technol. 134, 347–352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.160
Wu, P.W., Li, L.H., Zhou, Y.Y., Wang, W., Sun, Y.M., Guo, Y.F., Kang, X.H.: Biorefining of ethanol and methane from NaOH pretreated poplar residues: Mass balance and energy flow analyses. Fuel. 333, 126293 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126293
Ji, H.R., Wang, L., Pang, Z.Q., Zhu, W.Y., Yang, G.H., Dong, C.H.: Using a recyclable acid hydrotrope and subsequent short-term ultrasonic pretreatment to facilitate high-value lignin extraction and high-titer ethanol production. Cellulose. 27(13), 7561–7573 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03285-5
Ji, H.R., Wang, L., Tao, F.R., Yao, Z.P., Li, X.Z., Dong, C.H., Pang, Z.Q.: A hydrotrope pretreatment for stabilized lignin extraction and high titer ethanol production. Bioresour Bioprocess. 9(1), 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-022-00530-6
Humbird, D., Hsu, R.D.L.T.D., Schoen, A.A.A.P., Sexton, J.L.B.O.D.: A.D.D.: Process Design and Economics for Biochemical Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Ethanol: Dilute-Acid Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Corn Stover. Report NREL/TP-5100-47764. National Renewable Energy Laborotary, USA (2011)
Hanaoka, T., Miyazawa, T., Shimura, K., Hirata, S.: Jet fuel synthesis from Fischer-Tropsch product under mild hydrocracking conditions using Pt-loaded catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 263, 178–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.042
Yang, Q., Chen, B., Ji, X., He, Y.F., Chen, G.Q.: Exergetic evaluation of corn-ethanol production in China. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14(5), 2450–2461 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2007.08.011
Yahya, M., Fudholi, A., Sopian, K.: Energy and exergy analyses of solar-assisted fluidized bed drying integrated with biomass furnace. Renew. Energy. 105, 22–29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.049
Keedy, J., Prymak, E., Macken, N., Pourhashem, G., Spatari, S., Mullen, C.A., Boateng, A.A.: Exergy Based Assessment of the production and Conversion of Switchgrass, Equine Waste, and Forest Residue to Bio-oil using fast pyrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(1), 529–539 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5035682
Ibrahim, T.K., Basrawi, F., Awad, O.I., Abdullah, A.N., Najafi, G., Mamat, R., Hagos, F.Y.: Thermal performance of gas turbine power plant based on exergy analysis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 115, 977–985 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.032
Saket, V.: Effects of varying composition of biogas on performance and emission characteristics of compression ignition engine using exergy analysis. Energy Conv Manag. 138, 346–359 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.01.066
Zhang, Q., **ao, J., Hao, J.: Cumulative exergy analysis of lignocellulosic biomass to bio-jet fuel through aqueous-phase conversion with different lignin conversion pathways. Energy. 265, 126301 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.126301
Miao, G., Jade, L., James, J.: The environmental profile of bioethanol produced from current and potential future poplar feedstocks in the EU. Green. Chem. 16(11), 4680–4695 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc01124d
Michał, K., Mariusz, J.S., Kazimierz, W.: Life cycle assessment of poplar production: Environmental impact of different soil enrichment methods. J. Clean. Prod. 206, 785–796 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.180
Janine, S., Saúl, M.H., Andrea, G., Rüdiger, G., Eugenio, D.P., Jürgen, K., Edwin, H., Klaus, B.B., Heinz, R., Jörg, P.S., Gero, B.: Environmental impacts of bioenergy wood production from poplar short-rotation coppice grown at a marginal agricultural site in Germany. Gcb Bioenergy. 9(7), 1207–1221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12423
Huang, H., Ramaswamy, S., Al-Dajani, W., Tschirner, U., Cairncross, R.A.: Effect of biomass species and plant size on cellulosic ethanol: A comparative process and economic analysis. Biomass Bioenerg. 33(2), 234–246 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.05.007
Zhu, R., Hu, J., Bao, X., He, L., Lai, Y., Zu, L., Li, Y., Su, S.: Investigation of tailpipe and evaporative emissions from China IV and Tier 2 passenger vehicles with different gasolines. Transp. Res. Part. D-Transport Environ. 50, 305–315 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2016.10.027
Liu, G., Yan, B., Chen, G.: Technical review on jet fuel production. Renew. Sust Energ. Rev. 25, 59–70 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.03.025
Jiqing, F., David, R.S., Tom, N.K., Peter, B.J., Serin, R.: A life cycle assessment of pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) -derived jet fuel and diesel. Biomass Bioenerg. 55, 87–100 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.040
Yanan, Z., Tristan, R.B., Gui**, H., Robert, C.B.: Techno-economic analysis of monosaccharide production via fast pyrolysis of lignocellulose. Bioresour Technol. 127, 358–365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.070
Ryan, M., Swanson, J.A.S.A., Platon, A., Hsu, D.D.: Techno-Economic Analysis of Biofuels Production Based on Gasification. Report NREL/TP-5100-47764. National Renewable Energy Laborotary, USA (2010)
Vlysidis, A., Binns, M., Webb, C., Theodoropoulos, C.: A techno-economic analysis of biodiesel biorefineries: Assessment of integrated designs for the co-production of fuels and chemicals. Energy. 36(8), 4671–4683 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.04.046
Nizami, M., Slamet, Purwanto, W.W.: Solar PV based power-to-methanol via direct CO2 hydrogenation and H2O electrolysis: Techno-economic and environmental assessment. J. Co2 Util. 65, 102253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102253
Zheng, X., Zhong, Z., Zhang, B., Du, H., Wang, W., Li, Q., Yang, Y., Qi, R., Li, Z.: Techno - economic analysis and life cycle assessment of hydrogenation upgrading and supercritical ethanol upgrading processes based on fast pyrolysis of cornstalk for biofuel. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04096-x
Loh, S.R., Tan, I.S., Foo, H.C.Y., Tan, Y.H., Lam, M.K., Lim, S.: Exergy analysis of a holistic zero waste macroalgae-based third-generation bioethanol biorefinery approach: Biowaste to bioenergy. Environ. Technol. Innov. 30, 103089 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103089
Açıkkalp, E., Aras, H., Hepbasli, A.: Advanced exergy analysis of an electricity-generating facility using natural gas. Energy Conv Manag. 82, 146–153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.03.006
Zhou, F., Zhu, L.J., Yang, L., Hong, Y., Xu, J.G.: Analysis of a novel power plant based on tars from biomass gasifier as fuel gas. Appl. Therm. Eng. 233, 121148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.121148
Cherubini, F., Bird, N.D., Cowie, A., Jungmeier, G., Schlamadinger, B., Woess-Gallasch, S.: Energy- and greenhouse gas-based LCA of biofuel and bioenergy systems: Key issues, ranges and recommendations. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 53(8), 434–447 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.03.013
Valente, A., Iribarren, D., Dufour, J.: Comparative life cycle sustainability assessment of renewable and conventional hydrogen. Sci. Total Environ. 756, 144132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144132
Francisco, J.G.O.: Techno-economic assessment of supercritical processes for biofuel production. J. Supercrit Fluids. 160, 104788 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2020.104788
Aui, A., Wang, Y., Mba-Wright, M.: Evaluating the economic feasibility of cellulosic ethanol: A meta-analysis of techno-economic analysis studies. Renew. Sust Energ. Rev. 145, 111098 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111098
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the financial support from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB1501405) on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology, Software, Writing-Review & Editing, Visualization: X.Z; Investigation, Data Curation, Formal analysis, Writing-Original Draft: Z.S; Project administration, Funding acquisition: Z.Z; Validation. Resources. W.W; Conceptualization, Supervision: X.P.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Shen, Z., Zhong, Z. et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Fuel Ethanol Production from Poplar Wood Fermentation and its Coupled Pathway with Lignin Gasification Based on Energy-Environment-Economy. Waste Biomass Valor (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02534-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02534-z