Abstract
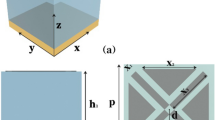
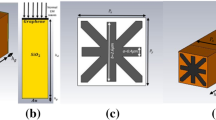
In this paper, a tunable multiband metamaterial perfect absorber based on a metal-graphene multilayer structure is proposed, and the absorber consists of a metal layer, graphene, and a dielectric layer. We demonstrate that the absorber has 99.51% and 99.96% absorption at 2.78 THz and 6.78 THz, respectively. The surface plasmonic excitonic resonance of graphene at terahertz frequencies, as well as electromagnetic resonance, is used to produce multiple absorption peaks. We studied the physical mechanism of a perfect absorber using the impedance matching idea and electric field distribution. The absorbance of the absorption spectrum can be tuned by adjusting the Fermi energy level, relaxation time, medium thickness, or breadth of the cut graphene rectangle. Due to the geometrical symmetry of the structure, the proposed absorber is polarization-insensitive and has unique optical performance over a wide range of incidence angles. The proposed structure is simple to implement and is appropriate for sensing, imaging, and filtering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
E Barchiesi et al Math. Mech. Solids 24 212 (2019)
A Poddubny et al Nat. Photonics 7 948 (2013)
D R Smith et al Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 4184 (2000)
R A Shelby et al Science 292 77 (2001)
Z Song et al Mater. Lett. 234 138 (2019)
S Huang et al J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 145 254 (2019)
S X **a et al Opt. Lett. 42 3052 (2017)
D Shin et al Nat. Commun. 3 1213 (2012)
J B Pendry et al Science 312 1780 (2006)
X J Ni et al Science 349 1310 (2015)
H T Chen et al Opt. Lett. 32 1620 (2007)
X D Zhao et al IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60 221 (2015)
A Widmann et al J. Neurosci. Methods 250 34 (2015)
J Y Mao et al Int. J. Syst. Sci. 52 1110 (2021)
P Kharel et al Optica 8 357 (2021)
W Li et al Nano Lett. 14 955 (2014)
F Q Zhou et al Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23 17041 (2021)
Z P Zheng et al Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24 2527 (2022)
X L Wu et al Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23 26864 (2021)
C Liang et al Opt. Commun. 436 57 (2019)
A A Rifat et al Opt. Express 24 2485 (2016)
J T Lu et al Opt. Express 19 21532 (2011)
M Faraji et al Opt. Commun. 355 352 (2015)
H Tao et al Opt. Express 16 7181 (2008)
X S Liu et al Mater. Express 9 704 (2019)
M L Huang et al Opt. Commun. 415 194 (2018)
A S Arezoomand et al Opt. Commun. 352 121 (2015)
J W Park et al Opt. Express 21 9691 (2013)
H L Zhu et al Opt. Express 28 38626 (2020)
B-X Wang et al Results Phys. 17 103077 (2020)
Y Ren et al Opt. Express 29 7666 (2021)
M A Ordal et al Appl. Opt. 22 1099 (1983)
R Cheng et al Opt. Mater. Express 10 501 (2020)
R Zhang et al Opt. Express 29 42989 (2021)
X Y Fang et al Phys. Lett. A 379 2245 (2015)
P Alonso-González et al Science 344 1369 (2014)
S Y **ao et al Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18 26661 (2016)
S C ** et al Opt. Express 27 11137 (2019)
J Zhang et al Nanoscale 7 13530 (2015)
X He et al Opt. Mater. Express 8 1031 (2018)
Y Zhang et al Plasmonics 14 1621 (2019)
J Ding et al Sci. Rep. 4 6128 (2014)
G E Town et al IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 7 78 (1995)
X H Deng et al Opt. Express 22 24 (2014)
F Wu et al Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 064022 (2018)
B Shen et al Optic 1 5 (2014)
Y She et al Phys. Lett. A 494 129299 (2024)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NSFC Grant Nos. 11664025 and 11964018, the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing (Wuhan University of Technology) No. 2022-KF-15, the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves No. K201606, the NSF from the Jiangxi Province No. 20224BAB202032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Zhang, P.S., Deng, XH. et al. Tunable multiband metamaterial perfect absorber based on a metal-graphene multilayer structure. Indian J Phys (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-024-03277-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-024-03277-2