Abstract
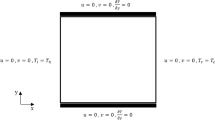
Natural convection in L-shaped geometries has many applications in many branches of engineering science, such as cooling of electronic equipment, nuclear reactors, and design of ventilation systems. The present paper studied the natural convective heat transfer and flow field in differentially heated L-shaped enclosures with viscous fluid using the multi-relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method (LBM-MRT). The study investigates the effect of the edge of L-shaped geometry on fluid flow and temperature field. We have also investigated the effect of non-dimensional parameters like Rayleigh number in the range of \((10^3\text {-}10^7)\)and Prandtl number (0.71, 1, 7). Nusselt number (Nu) and average Nu are also calculated along heated walls to study the heat transfer behavior.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Afrand Int. J. Thermal Sci.118 12 (2017)
M Afrand, S Farahat, A H Nezhad, G A Sheikhzadeh and F Sarhaddi Heat Transf. Res.45 749 (2014)
M Afrand, S Farahat, A H Nezhad, G A Sheikhzadeh, F Sarhaddi and S Wongwises Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf.60 13 (2015)
K B Nasr, R Chouikh, C Kerkeni and A Guizani Appl. Thermal Eng.26 772 (2006)
M H Joshi, P Balamurugan, V P Venugopalan and T S Rao Biofouling27 621 (2011)
D H Lim and S C Kim Appl. Thermal Eng.63 577 (2014)
WaelAl-Kouz, B Mahanthesh, M S Alqarni and K Thriveni Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf.126 105364 (2021)
J Mackolil and B Mahanthesh Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf.126 105361 (2021)
B Mahanthesh, J Mackolil and S M Mallikarjunaiah Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf.125 105348 (2021)
B Mahanthesh, S A Shehzad, J Mackolil and N S Shashikumar Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.171 121081 (2021)
B Mahanthesh, B J Gireesha, M Archana, T Hayat and A Alsaedi Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow28 2423 (2018)
W A Khan, S Farooq, S Kadry, M Hanif, F J Iftikhar and S Z Abbas Comput. Methods Programs Biomed.190 105355 (2020)
W A Khan, A S Alshomrani, A K Alzahrani, M Khan and M Irfan Pramana J. Phys.91 63 (2018)
W A Khan and M Ali Appl. Phys. A125 1 (2019)
C Cianfrini, M Corcione and P P Dell’Omo Int. J. Thermal Sci.44 441 (2005)
M Al-Arabi and M K El-Riedy Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.19 1399 (1976)
S W Churchill and H H Chu Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.18 1323 (1975)
R Ruiz and E M Sparrow Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.30 2539 (1987)
P Kandaswamy, J Lee and A K Abdul Hakeem Nonlinear Anal.: Model. Control12 203 (2007)
M Mahmoodi Int. J. Thermal Sci.50 1731 (2011)
M Kalteh and H Hasani Superlattices Microstruct.66 112 (2014)
F Y Zhao G F Tang and D Liu Int. J. Eng. Sci.44 148 (2006)
A I Alsabery, I Hashim, A J Chamkha, H Saleh and B Chanane Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow27 1365 (2017)
A I Alsabery, M A Sheremet, A J Chamkha and I J S R Hashim Sci. Rep. 8 1 (2018)
I Hashim, A I Alsabery, M A Sheremet and A J Chamkha Adv. Powder Technol.30 399 (2019)
G R McNamara and G Zanetti Phys. Rev. Lett.61 2332 (1988)
F J Higuera, S Succi and R Benzi Europhys. Lett.9 345 (1989)
H Chen, S Chen and W H Matthaeus Phys. Rev. A45 R5339 (1992)
Y H Qian, D d’Humières and P Lallemand, P Europhys. Lett.17 479 (1992)
D d’Humieres Rarefied Gas Dyn. 1992 450 (1992)
U Frisch, B Hasslacher and Y Pomeau Phys. Rev. Lett.56 1505 (1986)
P Lallemand and L S Luo Phys. Rev. E61 6546 (2000)
Q Liu, Y L He, Q Li and W Q Tao Int. J. Heat Mass Trans.73 761 (2014)
M E McCracken and J Abraham Phys. Rev. E71 036701 (2005)
A A Mohamad Lattice Boltzmann Method Fundamental and Engineering Applications with Computer Codes (London: Springer) p 68 (2011)
Q Liu, Y L He, D Li and Q Li Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.102 1334 (2016)
B Mliki, M A Abbassi, K Guedri and A Omri Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J.18 503 (2015)
G de Vahl Davis Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids3 249 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahid, H., Khan, W.A. & Yaqoob, I. Natural convection in an L-shaped enclosure using multi-relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method. Indian J Phys 96, 2921–2939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02222-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02222-x



