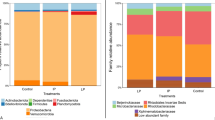
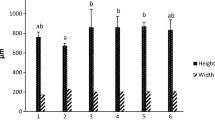
Abstract
Dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 was used to relieve the impacts of aflatoxin B1 toxicity on the performances of Liza ramada. The control diet was without any additives, while the second and third diets were supplemented with aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg. The fourth diet was supplemented with Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 at 1 × 106 CFU/mL per kg diet, while the fifth with aflatoxin B1 at 1 mg/kg and Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 at 1 × 106 CFU/mL per kg diet. The growth performance markedly increased (p < 0.05) in L. ramada fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356, while aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg groups showed a severe reduction. The red blood cells, hemoglobulin, hematocrit, and white blood cells were markedly increased in L. ramada fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 while decreased (p < 0.05) in fish fed aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg. The blood total protein and albumin were markedly increased (p < 0.05) in L. ramada fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 while reduced in aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg groups. The levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides were meaningfully increased in fish of the Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 and aflatoxin B1 at 1 mg/kg groups while decreased in aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg groups. Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, creatinine, and urea levels were markedly decreased (p < 0.05) in fish-fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 while increased in aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg groups. The highest levels of blood glucose and cortisol were seen in fish contaminated with aflatoxin B1 at 1 mg/kg, while the lowest levels were observed in the fish fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 group (p < 0.05). The catalase and superoxide dismutase were markedly enhanced in the Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 group and severely declined in aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg groups (p < 0.05). The malondialdehyde level was markedly reduced in fish fed Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 with or without aflatoxin B1 at 1 mg/kg diets while increased in fish contaminated with aflatoxin B1 at 0.5 and 1 mg/kg (p < 0.05). The control group had lower malondialdehyde levels than the aflatoxin B1 at 1 mg/kg group and higher than the Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 with or without aflatoxin B1 toxicity (p < 0.05). Histopathological examination revealed impaired intestines and livers in fish contaminated with aflatoxin B1 while Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 relieves the inflammation and protected the intestines and livers. In conclusion, dietary Lb. acidophilus ATCC 4356 is recommended to relieve the impacts of aflatoxicosis-induced hepatorenal failure and oxidative stress in L. ramada.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
FAO (2020) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. Sustainability in action, Rome. [Online]. Available: http://www.fao.org/3/i5555e/i5555e.pdf. Accessed Oct 2021
Dawood MAO (2021) Nutritional immunity of fish intestines: important insights for sustainable aquaculture. Rev Aquac 13(1):642–663. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12492
de Freitas SC, Baldissera MD, Baldisserotto B, Petrolli TG, da Glória EM, Zanette RA, Da Silva AS (2020) Dietary vegetable choline improves hepatic health of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed aflatoxin-contaminated diet. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C: Toxicol Pharmacol 227:108614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.108614
Abdel-Daim MM, Dawood MAO, AlKahtane AA, Abdeen A, Abdel-Latif HMR, Senousy HH, Aleya L, Alkahtani S (2020) Spirulina platensis mediated the biochemical indices and antioxidative function of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Toxicon 184:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.06.001
Oliveira M, Vasconcelos V (2020) Occurrence of mycotoxins in fish feed and its effects: a review. Toxins (Basel) 12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12030160
Tasa H, Imani A, Sarvi Moghanlou K, Nazdar N, Moradi-Ozarlou M (2020) Aflatoxicosis in fingerling common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and protective effect of rosemary and thyme powder: growth performance and digestive status. Aquaculture 527:735437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735437
Gonçalves RA, Schatzmayr D, Albalat A, Mackenzie S (2020) Mycotoxins in aquaculture: feed and food. Rev Aquac 12(1):145–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12347
de Freitas SC, Baldissera MD, Descovi S, Eslava-Mocha PR, Zeppenfeld CC, Glória EM, Baldisserotto B, Da Silva AS (2020) Tea tree oil attenuates cerebral damage in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) fed with an aflatoxin-contaminated diet. Aquaculture 523:735223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735223
Ghafarifarsani H, Imani A, Niewold TA, Pietsch-Schmied C, Sarvi Moghanlou K (2021) Synergistic toxicity of dietary aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and zearalenone (ZEN) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is attenuated by anabolic effects. Aquaculture 541:736793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736793
Hassaan MS, Nssar KM, Mohammady EY, Amin A, Tayel SI, El-Haroun ER (2020) Nano-zeolite efficiency to mitigate the aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) toxicity: effects on growth, digestive enzymes, antioxidant, DNA damage and bioaccumulation of AFB1 residues in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 523:735123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735123
Anater A, Araújo CMTD, Rocha DCC, Ostrensky A, Filho JRE, Ribeiro DR, Pimpão CT (2020) Evaluation of growth performance, hematological, biochemical and histopathological parameters of Rhamdia quelen fed with a feed artificially contaminated with aflatoxin B1. Aquacult Rep 17:100326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100326
Yang J, Wang T, Lin G, Li M, Zhu R, Yiannikouris A, Zhang Y, Mai K (2020) The assessment of diet contaminated with aflatoxin B1 in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) and the evaluation of the efficacy of mitigation of a yeast cell wall extract. Toxins 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090597
Fang H, Wang B, Jiang K, Liu M, Wang L (2020) Effects of Lactobacillus pentosus HC-2 on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, immune-related genes and intestinal microbiota of Penaeus vannamei affected by aflatoxin B1. Aquaculture 525:735289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735289
Ismael NE, Abd El-hameed SA, Salama AM, Naiel MA, Abdel-Latif HM (2021) The effects of dietary clinoptilolite and chitosan nanoparticles on growth, body composition, haemato-biochemical parameters, immune responses, and antioxidative status of Nile tilapia exposed to imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12693-4
Naiel MAE, Ismael NEM, Shehata SA (2019) Ameliorative effect of diets supplemented with rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) on aflatoxin B1 toxicity in terms of the performance, liver histopathology, immunity and antioxidant activity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 511:734264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734264
Ghafarifarsani H, Kachuei R, Imani A (2021) Dietary supplementation of garden thyme essential oil ameliorated the deteriorative effects of aflatoxin B1 on growth performance and intestinal inflammatory status of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 531:735928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735928
El-Saadony MT, Alagawany M, Patra AK, Kar I, Tiwari R, Dawood MAO, Dhama K, Abdel-Latif HMR (2021) The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: an overview. Fish Shellfish Immunol 117:36–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2021.07.007
Morshedi V, Bojarski B, Hamedi S et al (2021) Effects of dietary bovine lactoferrin on growth performance and immuno-physiological responses of Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) fingerlings. Probiotics Antimicro Prot. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09805-4
Van Doan H, Hoseinifar SH, Ringø E, Ángeles Esteban M, Dadar M, Dawood MAO, Faggio C (2020) Host-associated probiotics: a key factor in sustainable aquaculture. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 28(1):16–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2019.1643288
Balcázar JL, Blas ID, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Cunningham D, Vendrell D, Múzquiz JL (2006) The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet Microbiol 114(3–4):173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.01.009
Melo-Bolívar JF, Ruiz Pardo RY, Hume ME, Villamil Díaz LM (2021) Multistrain probiotics use in main commercially cultured freshwater fish: a systematic review of evidence. Rev Aquac. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12543
Adel M, Dawood MAO (2021) Probiotics application: implications for sustainable aquaculture. In: Mojgani N, Dadar M (eds) Probiotic bacteria and postbiotic metabolites: role in animal and human health. Microorganisms for sustainability 2:191–219. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0223-8_8
Ushakova NA, Pravdin VG, Kravtsova LZ, Ponomarev SV, Gridina TS, Ponomareva EN, Rudoy DV, Chikindas ML (2021) Complex bioactive supplements for aquaculture-evolutionary development of probiotic concepts. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09835-y
Guardiola FA, Porcino C, Cerezuela R, Cuesta A, Faggio C, Esteban MA (2016) Impact of date palm fruits extracts and probiotic enriched diet on antioxidant status, innate immune response and immune-related gene expression of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Shellfish Immunol 52:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.03.152
Yılmaz S, Yılmaz E, Dawood MAO, Ringø E, Ahmadifar E, Abdel-Latif HM (2021) Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics used to control vibriosis in fish: a review. Aquaculture. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737514
Buck BL, Altermann E, Svingerud T, Klaenhammer TR (2005) Functional analysis of putative adhesion factors in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8344–8351. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.8344-8351.2005
Chen L, Liu W, Li Y, Luo S, Liu Q, Zhong Y, Jian Z, Bao M (2013) Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 attenuates the atherosclerotic progression through modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory process. Int Immunopharmacol 17(1):108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.05.018
Boot HJ, Kolen CP, Van Noort JM, Pouwels PH (1993) S-layer protein of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356: purification, expression in Escherichia coli, and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene. J Bacteriol 175(19):6089–6096. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.175.19.6089-6096.199
Foysal MJ, Fotedar R, Siddik MAB, Tay A (2020) Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. plantarum improve health status, modulate gut microbiota and innate immune response of marron (Cherax cainii). Sci Rep 10(1):5916. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62655-y
Wang X, Zhou Z, Guan X, Dong Y, Zhao Z, Jiang J, Li S, Jiang B, Wang B, Zhang G, Chen Z, **ao Y, Pan Y (2021) Effects of dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus and tussah immunoreactive substances supplementation on physiological and immune characteristics of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus). Aquaculture 542:736897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736897
Adeshina I, Abubakar MIO, Ajala BE (2020) Dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus acidophilus enhanced the growth, gut morphometry, antioxidant capacity, and the immune response in juveniles of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Fish Physiol Biochem 46(4):1375–1385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00796-7
Hassaan MD, El-Sayed AMI, Mohammady EY, Zaki MAA, Elkhyat MM, Jarmołowicz S, El-Haroun ER (2021) Eubiotic effect of a dietary potassium diformate (KDF) and probiotic (Lactobacillus acidophilus) on growth, hemato-biochemical indices, antioxidant status and intestinal functional topography of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fed diet free fishmeal. Aquaculture 533:736147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736147
Hosseini M, Kolangi Miandare H, Hoseinifar SH, Yarahmadi P (2016) Dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus modulated skin mucus protein profile, immune and appetite genes expression in gold fish (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol 59:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.10.026
Lara-Flores M, Olvera-Novoa MA, Guzmán-Méndez BE, López-Madrid W (2003) Use of the bacteria Streptococcus faecium and Lactobacillus acidophilus, and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as growth promoters in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 216(1–4):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00277-6
Villamil L, Reyes C, Martínez-Silva MA (2014) In vivo and in vitro assessment of Lactobacillus acidophilus as probiotic for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Perciformes: Cichlidae) culture improvement. Aquacult Res 45(7):1116–1125. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12051
Akter MN, Hashim R, Sutriana A, Siti Azizah MN, Asaduzzaman M (2019) Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus supplementation on growth performances, digestive enzyme activities and gut histomorphology of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus Sauvage, 1878) juveniles. Aquacult Res 50(3):786–797. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13938
Adeshina I (2018) The effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a dietary supplement on nonspecific immune response and disease resistance in juvenile common carp, Cyprinos carpio. Int Food Res J 25(6)
Hoseinifar SH, Roosta Z, Hajimoradloo A, Vakili F (2015) The effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus as feed supplement on skin mucosal immune parameters, intestinal microbiota, stress resistance and growth performance of black swordtail (**phophorus helleri). Fish Shellfish Immunol 42(2):533–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.12.003
Wang Y, Gu Q (2010) Effect of probiotics on white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) growth performance and immune response. Mar Biol Res 6(3):327–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/17451000903300893
Buszewska-Forajta M (2020) Mycotoxins, invisible danger of feedstuff with toxic effect on animals. Toxicon 182:34–53. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004101012030218X. Accessed Oct 2021
Anater A, Manyes L, Meca G, Ferrer E, Luciano FB, Pimpão CT, Font G (2016) Mycotoxins and their consequences in aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 451:1–10. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0044848615301411. Accessed Oct 2021
Wang X, Jiang J, Guan X, Zhao Z, Dong Y, Wang J, Li S, Jiang B, Liu G, Sun H, Gao S, Jiang P, Wang X, Zhou Z (2021) Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and tussah immunoreactive substances on disease resistance of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) against Vibrio splendidus. Aquacult Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15293
Francesco F, Satheeshkumar P, Senthil Kumar D, Caterina F, Giuseppe P (2012) Comparative study of hematological and blood chemistry of Indian and Italian Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus Linneaus 1758). HOAJ Biology 1–5. SatheesKumar et al. HOAJ Biology 2012. http://www.hoajonline.com/journals/hoajbiology/content/pdf/volume/1/5.pdf. Accessed Oct 2021
Tahoun AA, Suloma A, Hammouda Y, Abo-State H, El-Haroun E (2013) The effect of stocking different ratios of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus, striped mullet Mugil cephalus, and thinlip grey mullet Liza ramada in polyculture ponds on biomass yield, feed efficiency, and production economics. N Am J Aquac 75(4):548–555. https://doi.org/10.1080/15222055.2013.826764
Abdelhiee EY, Elbialy ZI, Saad AH, Dawood MAO, Aboubakr M, El-Nagar SH, El-Diasty EM, Salah AS, Saad HM, Fadl SE (2021) The impact of Moringa oleifera on the health status of Nile tilapia exposed to aflatoxicosis. Aquaculture 533:736110. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0044848620316434. Accessed Oct 2021
AOAC (2012) Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. 19th edition. AOAC International, Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA. www.eoma.aoac.org. Accessed Oct 2021
Führ F, Pereira Junior J, Romano LA, Almeida FDM (2012) Gill injury after treatment with mebendazole on mullets Mugil liza. Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol 32(5):151. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287745605_Gill_injury_after_treatment_with_mebendazole_on_mullets_Mugil_liza. Accessed Oct 2021
Houston A (1990) Blood and circulation. In: Schreck CB, Moyle PB (eds) Methods in fish biology, American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, Maryland 335
Doumas BT, Bayse DD, Carter RJ, Peters T, Schaffer R (1981) A candidate reference method for determination of total protein in serum. I. Development and validation. Clin Chem 27(10):1642–1650. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7285315/. Accessed Oct 2021
Dumas BT, Biggs HG (1972) Standard methods of clinical chemistry. Gerald R. Cooper (ed) Academic Press, New York 1–333. https://www.sciencedirect.com/bookseries/standard-methods-of-clinical-chemistry/vol/7/suppl/C. Accessed Oct 2021
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase an enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244(22):6049–6055. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)63504-5
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Gewaily MS, Abumandour MM (2021) Gross morphological, histological and scanning electron specifications of the oropharyngeal cavity of the hooded crow (Corvus cornix pallescens). Anat Histol Embryol 50(1):72–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahe.12602
Afshar P, Shokrzadeh M, Raeisi SN, Ghorbani-HasanSaraei A, Nasiraii LR (2020) Aflatoxins biodetoxification strategies based on probiotic bacteria. Toxicon 178:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.02.007
Sarlak Z, Rouhi M, Mohammadi R, Khaksar R, Mortazavian AM, Sohrabvandi S, Garavand F (2017) Probiotic biological strategies to decontaminate aflatoxin M1 in a traditional Iranian fermented milk drink (Doogh). Food Control 71:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.06.037
Ji C, Fan Y, Zhao L (2016) Review on biological degradation of mycotoxins. Anim Nutr 2(3):127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2016.07.003
Rashidian G, Boldaji JT, Rainis S, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2021) Oregano (Origanum vulgare) extract enhances Zebrafish (Danio rerio) growth performance, serum and mucus innate immune responses and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Animals 11(2):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020299
Rashidian G, Kajbaf K, Prokić MD, Faggio C (2020) Extract of common mallow (Malvae sylvestris) enhances growth, immunity, and resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fingerlings against Yersinia ruckeri infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 96:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.12.018
Gobi N, Vaseeharan B, Chen JC, Rekha R, Vijayakumar S, Anjugam M, Iswarya A (2018) Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 improves growth performance, mucus and serum immune parameters, antioxidant enzyme activity as well as resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.066
Yang G, Shen K, Yu R, Wu Q, Yan Q, Chen W, Ding L, Kumar V, Wen C, Peng M (2020) Probiotic (Bacillus cereus) enhanced growth of Pengze crucian carp concurrent with modulating the antioxidant defense response and exerting beneficial impacts on inflammatory response via Nrf2 activation. Aquaculture 529:735691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735691
Zuo RY, Chang J, Yin Q, Wang P, Yang Y, Wang X, Wang G, Zheng Q (2013) Effect of the combined probiotics with aflatoxin B1-degrading enzyme on aflatoxin detoxification, broiler production performance and hepatic enzyme gene expression. Food Chem Toxicol 59:470–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.044
Assan D, Kuebutornye FKA, Hlordzi V, Chen H, Mraz J, Mustapha UF, Abarike ED (2022) Effects of probiotics on digestive enzymes of fish (finfish and shellfish); status and prospects: a mini review. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 257:110653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2021.110653
Kavitha M, Raja M, Perumal P (2018) Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquacult Rep 11:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2018.07.001
**a Y, Wang M, Gao F, Lu M, Chen G (2020) Effects of dietary probiotic supplementation on the growth, gut health and disease resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim Nutr 6(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2019.07.002
Ringø E, Van Doan H, Lee SH, Soltani M, Hoseinifar SH, Harikrishnan R, Song SK (2020) Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J Appl Microbiol 129(1):116–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14628
Ahmadifar E, Sadegh TH, Dawood MAO, Dadar M, Sheikhzadeh N (2020) The effects of dietary Pediococcus pentosaceus on growth performance, hemato-immunological parameters and digestive enzyme activities of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 516:734656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734656
Dawood MAO, Abo-Al-Ela HG, Hasan MT (2020) Modulation of transcriptomic profile in aquatic animals: Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics scenarios. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:268–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.12.054
Lakkawar AW, Chattopadhyay SK, Johri TS (2004) Experimental aflatoxin B1 toxicosis in young rabbits-a clinical and patho-anatomical study. Slov Vet Res 41(2):73–81. http://www2.vf.uni-lj.si/ZB/SlovVetRes_41_(2)_pp73_81.pdf. Accessed Oct 2021
Abdelhady D, El-Abasy M, Abou-Asa S, Elbialy Z, Shukry M, Hussein A, Saleh A, El-Magd M (2017) The ameliorative effect of Aspergillus awamori on aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic damage in rabbits. World Mycotoxin J 10(4):363–373. https://doi.org/10.3920/WMJ2017.2188
Fathi MM, Ebeid TA, Al-Homidan I, Soliman NK, Abou-Emera OK (2017) Influence of probiotic supplementation on immune response in broilers raised under hot climate. Br Poult Sci 58(5):512–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2017.1332405
Fadl SE, El-Habashi N, Gad DM, Elkassas WM, Elbialy ZI, Abdelhady DH, Hegazi SM (2019) Effect of adding Dunaliella algae to fish diet on lead acetate toxicity and gene expression in the liver of Nile tilapia. Toxin Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2019.1652652
Madhusudhanan N, KavithaLakshmi SN, Radha Shanmugasundaram K, Shanmugasundaram ERB (2004) Oxidative damage to lipids and proteins induced by aflatoxin B1 in fish (Labeo rohita)—protective role of Amrita Bindu. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 17(2):73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2004.03.002
Tabassum H, Ashafaq M, Khan J, Shah MZ, Raisuddin S, Parvez S (2016) Short term exposure of pendimethalin induces biochemical and histological perturbations in liver, kidney and gill of freshwater fish. Ecol Indic 63:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.11.044
Nasri R, Abdelhedi O, Jemil I, Daoued I, Hamden K, Kallel C, Elfeki A, Lamri-Senhadji M, Boualga A, Nasri M, Karra-Châabouni M (2015) Ameliorating effects of goby fish protein hydrolysates on high-fat-high-fructose diet-induced hyperglycemia, oxidative stress and deterioration of kidney function in rats. Chem Biol Interact 242:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.08.003
Ledbetter MLS, Lippert MJ (2002) Glucose transport in cultured animal cells: an exercise for the undergraduate cell biology laboratory. Cell Biol Educ 1(3):76–86. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.01-11-0002
Birnie-Gauvin K, Costantini D, Cooke SJ, Willmore WG (2017) A comparative and evolutionary approach to oxidative stress in fish: a review. Fish Fish 18(5):928–942. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12215
Ratn A, Prasad R, Awasthi Y, Kumar M, Misra A, Trivedi SP (2018) Zn2+ induced molecular responses associated with oxidative stress, DNA damage and histopathological lesions in liver and kidney of the fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch, 1793). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.058
Martínez-Álvarez RM, Morales AE, Sanz A (2005) Antioxidant defenses in fish: biotic and abiotic factors. Rev Fish Biol Fish 15(1):75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-005-7846-4
Marin DE, Taranu I (2012) Overview on aflatoxins and oxidative stress. Toxin Rev 31(3–4):32–43. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569543.2012.730092
Funding
The work was funded by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/76), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia. This research work was partially supported by Chiang Mai University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalafalla, M.M., Zayed, N.F.A., Amer, A.A. et al. Dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 Relieves the Impacts of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity on the Growth Performance, Hepatorenal Functions, and Antioxidative Capacity of Thinlip Grey Mullet (Liza ramada) (Risso 1826). Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 14, 189–203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09888-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09888-z