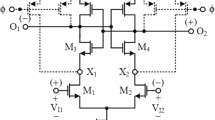
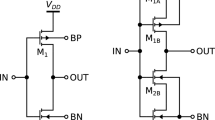
Abstract
This study has clarified the optoelectronic devices based on configurable hysteresis of Schmitt trigger circuit control with the employment of CMOS technology. Schmitt trigger (ST) is an electronics circuit, widely used in a sensor network to detect a signal with low amplitude in a noisy environment. It converts a variable input signal to a constant output level. In contrast to the comparator, an ST offers two independent switching voltages with positive feedback that enhances the depth of the switching threshold. Hysteresis width is an inbuilt feature of the trigger circuit, removing the irregularities or noise near the threshold region and sha** it into smooth output. The hysteresis width can be adjusted by a suitable variation in the aspect ratio of input and feedback transistors. In this work, conventional ST architecture modifies by configuring the series and/or parallel connection of n-channel and p-channel MOS devices to adjust the hysteresis voltage. The simulation result is obtained with Cadence Spectra with BSIM3V3 device models at 90 nm CMOS technology, and hysteresis width falls by reducing the feedback ratio of the increase with feedback ratio.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
Simulation software.
References
L.A.P. Melek, A.L. da Silva, M.C. Schneider, C. Galup-Montoro, analysis and design of the classical CMOS Schmitt trigger in subthreshold operation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 64(4), 869–878 (2016)
T. Aoki, Y. Kurokawa, M. Kozuma, Semiconductor device having Schmitt trigger NAND circuit and Schmitt trigger inverter. U.S. Patent, 9(1), 245–589 (2016)
S.H. Park, et al, FM noise immunity enhancement using Schmitt trigger logic gates in CMOS process, in Proceeding URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference (URSI AP-RASC). Seoul, South Korea (2016)
D. Kualshetra, S. Akashe, Design and analysis of low voltage high performance Schmitt trigger using efficient leakage reduction technique. J. Act. Passive Electron. Dev. 14(2/3), 239–247 (2019)
S. Hwang, S. Jang, S. Bae, S.K. Lee, S.H. Lee, S. Fabiano, T.W. Kim, All-solid-state organic Schmitt trigger implemented by twin two-in-one ferroelectric memory transistor. Adv Electron. Mater. 10(5), 1901263 (2020)
A. Kumar, Effect of body biasing over CMOS inverter. Int. J. Electron. Commun. Technol. 4(2), 1–3 (2013)
L. Khanfir, J. Mouine, Clock delay-based design for hysteresis programming and noise reduction in dynamic comparators. Analog Integr. Circuits Sig. Process. 12(1), 103–110 (2020)
A. Kumar, B. Chaturvedi, S. Maheshwari, A fully electronically controllable schmitt trigger and duty cycle-modulated waveform generator. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 45(12), 2157–2180 (2017)
N. Lotze, Y. Manoli, Ultra-sub-threshold operation of always-on digital circuits for IoT applications by use of Schmitt trigger gates. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 64(11), 2920–2933 (2017)
B. Chaturvedi, A. Kumar, A novel electronically controlled Schmitt trigger with clockwise and anticlockwise hysteresis. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 89(1), 136–145 (2018)
Z. Chen, S. Chen, A high-speed low voltage CMOS Schmitt trigger with adjustable hysteresis, in Proceeding IEEE/ACIS 16th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS) Wuhan, China (2017)
A. Nejati, Y. Bastan, P. Amiri, M.H. Maghami, A low-voltage bulk-driven differential CMOS Schmitt trigger with tunable hysteresis. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 28(07), 1920004 (2019)
J.I. Morales, F. Chierchie, P.S. Mandolesi, E.E. Paolini, A high resolution all digital pulse width modulator architecture with a tunable delay element in CMOS. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 32(4), 897–906 (2020)
A. Kumar, R.S. Mishra, Challenge-response pair (CRP) generator using Schmitt trigger physical unclonable function. proc. Adv. Comput. Commun. Technol. 33(1), 213–223 (2019)
A. Kumar, S.L. Tripathi, U. Subramaniam, Variability analysis of SBOX with CMOS 45 nm technology. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 45(3), 1277–1288 (2021)
A. Kumar, S.L. Tripathi, R.S. Mishra, METAPUF: a challenge response pair generator. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 6(2), 58–63 (2018)
A. Kumar, S. Tripathi, SBOX under PVT variation. Analog Integr. Circuits Sig. Process. 105(1), 73–82 (2020)
“CD40106BM.Hex Schmitt Trigger CMOS Hex Schmitt triggers” Texas instruments datasheet (2017)
A.L. da Silva Júnior, L.A. PasiniMelek, C. Galup-Montoro, M. Cherem Schneider, Inadequacy of the classical formulation of the CMOS Schmitt trigger. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 49(5), 1261–1273 (2021)
W. Lew, R. Cadotte Jr, Gate pulsing gate ladder, U.S. Patent 9(2), 57–628 (2017)
V. Chauhan, P. Garg, Compensated Schmitt trigger circuit for providing monotonic hysteresis response, U.S. Patent No US20060017482A1 (2017)
S.M. Sharroush, Inverter-based voltage-controlled and programmable comparators. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 45(1), 1–23 (2020)
J.B. Kuang, SOI CMOS Schmitt trigger circuits with controllable hysteresis, U.S. Patent 6(2), 441–663 (2002)
F. Yuan, A high-speed differential CMOS Schmitt trigger with regenerative current feedback and adjustable hysteresis. Analog Integr. Circuits Sig. Process. 63(1), 121–127 (2020)
M. Janveja, A. Khan, V. Niranjan, Performance evaluation of subthreshold Schmitt trigger using body bias techniques, in Proceeding International Conference on Computational Techniques in Information and Communication Technologies (ICCTICT), New Delhi, India (2016)
S. Minaei, E. Yuce, A simple Schmitt trigger circuit with grounded passive elements and its application to square/triangular wave generator. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 31, 877–888 (2012)
C. Zhang, A. Srivastava, P.K. Ajmera, Low voltage CMOS Schmitt trigger circuits. Electron. Lett. 39(24), 1696–1698 (2003)
J.B. Kuang, C.-T. Chuang, Restoration of controllable hysteresis in partially depleted SOI CMOS Schmitt trigger circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 51(7), 349–353 (2007)
J.M. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital Integrated Circuit Design: A Design Perspective” 2nd edn. 273–275 Pearson education
D.S. Barlow, Self-adjusting Schmitt trigger, U.S. Patent. 7(1), 167–333 (2007).
S. Song, Y. Kim, Novel in-memory computing adder using 8+ T SRAM. Electronics 11(6), 929 (2022)
S.K. Kingra, V. Parmar, C.C. Chang, B. Hudec, T.H. Hou, M. Suri, SLIM: simultaneous logic-in-memory computing exploiting bilayer analog OxRAM devices. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 2567 (2020)
C. Yeswanth, A. Acharya, In-memory computing based boolean and logical circuit design using 8T SRAM, in Proceedings of the 2021 Devices for Integrated Circuit (DevIC), Kalyani, India, 430–434 (2021)
M.M. Eid, S. Urooj, N.M. Alwadai, A.N.Z. Rashed, AlGaInP optical source integrated with fiber links and silicon avalanche photo detectors in fiber optic systems. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 23, 847–54 (2021)
S. Urooj, N.M. Alwadai, A. Ibrahim, A.N.Z. Rashed, Simulative study of raised cosine impulse function with hamming grating profile based chirp Bragg grating fiber. J. Opt. Commun. 42(1), 350–365 (2021)
A.N.Z. Rashed, W.F. Zaky, M.M. Eid, O.S. Faragallah, Dynamic response based on non-linear material for electrical and optical analogy of full optical oscillator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 53(1), 234–250 (2021)
A.N.Z. Rashed, W.F. Zaky, H.M. El-Hageen, A.M. Alatwi, Technical specifications for an all-optical switch for information storage and processing systems. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(8), 1100–1112 (2021)
V. Sorathiya, O.S. Faragallah, H.S. El-Sayed, M.M. Eid, A.N.Z. Rashed, Nanofocusing of optical wave using staircase tapered plasmonic waveguide. Appl. Phys. B 128(6), 104 (2022)
L.K. Smirani, A.N.Z. Rashed, S.H. Ahammad, M.A. Hossain, M.G. Daher, E. Fahmy, Conventional/linear/Lorentzian material gain semiconductor optical amplifiers performance signature with four wave mixing (FWM) nonlinearity in optical fiber communication systems. J. Opt. Commun. 43(2), 202–218 (2022)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors contributed equally in this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Srinivas, M., Sahoo, S. et al. Optoelectronic devices based on configurable hysteresis of Schmitt trigger circuit control with the employment of CMOS technology. J Opt (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01503-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01503-4