Abstract
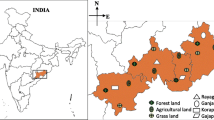
In the present study, the earthworm community structures and their relationship with physico-chemical properties of soil in three wetland ecosystems were studied. A total of six species of earthworms were reported from these sites i.e. Metaphire posthuma, Amynthas morrisi, Lampito mauritii, Octochaetona beatrix, Eutyphoeus waltoni and Eutyphoeus nichlosoni. A significant positive correlation of earthworm individuals with the clay, silt, K and moisture was observed while a negative correlation was observed with soil EC, TDS, Cr, Ni, Zn, and Fe. The principal component analysis was applied to predict the key soil factors responsible for affecting the earthworm abundance. The two major components viz. C1 and C2 with variance (%) of 58.92 and 41.08 respectively were resulted from this analysis which reveals the effects of different soil variables on earthworm distribution and abundance. Harike wetland had minimum earthworm abundance as the soil of Harike wetland has the highest content of EC, TDS and heavy metals. This study is indenture with only soil properties but further investigation is required to predict earthworm species based on vegetation, cultivation and other environmental factors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, S.K. 2009. Heavy metal pollution. New Delhi: A. P. H. Publishing Corporation.
Ahangar, A.G., and A. Keshtehgar. 2015. Influence of heavy metals on earthworms, soil microbial community and mammals. Journal of Novel Applied Sciences 4: 125–134.
Audusseau, H., F. Vandenbulcke, C. Dume, V. Deschins, M. Pauwels, A. Gigon, M. Bagard, and L. Dupont. 2020. Impacts of metallic trace elements on an earthworm community in an urban wasteland: Emphasis on the bioaccumulation and genetic characteristics in Lumbricus castaneus. Science of the Total Environment 718: 137259.
Bartz, M.L.C., A. Pasini, and G.G. Brown. 2013. Earthworms as soil quality indicators in Brazilian no-tillage systems. Applied Soil Ecology 69: 39–48.
Birkas, M., L. Bottlik, A. Stingli, C. Gyuricza, and M. Jolánkai. 2010. Effect of soil physical state on the earthworms in Hungary. Applied and Environmental Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/830853.
Bouyoucos, G.J. 1962. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. Agronomy Journal 54: 464–465.
Bremner, J.M., and R.G. Mulvaney. 1982. Nitrogen total. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Am Sco Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 575–624.
Briones, M.J.I., and O. Schmidt. 2017. Conventional tillage decreases the abundance and biomass of earthworms and alters their community structure in a global meta-analysis. Global Change Biology 23: 4396–4419.
Carnovale, D., G. Baker, A. Bissett, and P. Thrall. 2015. Earthworm composition, diversity and biomass under three land use systems in south-eastern Australia. Applied Soil Ecology 88: 32–40.
Chan, K.Y., and I. Barchia. 2007. Soil compaction controls the abundance, biomass and distribution of earthworms in a single dairy farm in south-eastern Australia. Soil and Tillage Research 94: 75–82.
Crumsey, J.M., J.M. Le Moine, C.S. Vogel, and K.J. Nadelhoffer. 2014. Historical patterns of exotic earthworm distributions inform contemporary associations with soil physical and chemical factors across a northern temperate forest. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 68: 503–514.
Curry, J.P. 2004. Factors affecting the abundance of earthworms in soils. Earthworm Ecology 9: 113.
De Wandeler, H., R. Sousa-Silva, E. Ampoorter, H. Bruelheide, M. Carnol, S.M. Dawud, G. Dănilă, L. Finer, S. Hättenschwiler, M. Hermy, B. Jaroszewicz, F.X. Joly, S. Müller, M. Pollastrini, S. Ratcliffe, K. Raulund-Rasmussen, F. Selvi, F. Valladares, K. Van Meerbeek, K. Verheyen, L. Vesterdal, and B. Muys. 2016. Drivers of earthworm incidence and abundance across European forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 99: 167–178.
Dewi, W.S., and M. Senge. 2015. Earthworm diversity and ecosystem services under threat. Reviews in Agricultural Science 3: 25–35.
Dhar, S., and P.S. Chaudhuri. 2020. Earthworm Communities in Paddy (Oryza sativa) Fields of West Tripura (India). Proceedings of the Zoological Society 73: 273–284.
Edwards, C.A., and P.J. Bohlen. 1996. Biology and Ecology of Earthworms. London: Chapman & Hall.
Ezeokoli, O.T., O.G. Oladipo, C.C. Bezuidenhout, R.A. Adeleke, and M.S. Maboeta. 2021. Assessing the ecosystem support function of South African coal mining soil environments using earthworm (Eisenia andrei) bioassays. Applied Soil Ecology 157: 103771.
Fonte, S.J., T. Winsome, and J. Six. 2009. Earthworm populations in relation to soil organic matter dynamics and management in California tomato crop** systems. Applied Soil Ecology 41: 206–214.
Fragoso, C., and P. Lavelle. 1992. Earthworm communities of tropical rain forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 24: 1397–1408.
Frazao, J., R.G. de Goede, L. Brussaard, J.H. Faber, J.C. Groot, and M.M. Pulleman. 2017. Earthworm communities in arable fields and restored field margins, as related to management practices and surrounding landscape diversity. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 248: 1–8.
Gates, G.E. 1972. Burmese earthworms: An introduction to the systematic and biology of megadrile oligochaetes with special reference to Southeast Asia. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society 62: 1e326.
Giannitsopoulos, M.L., P.J. Burgess, and R.J. Rickson. 2020. Effects of conservation tillage drills on soil quality indicators in a wheat–oilseed rape rotation: Organic carbon, earthworms and water-stable aggregates. Soil Use and Management 36: 139–152.
Jamatia, S.K.S., and P.S. Chaudhuri. 2017. Earthworm community structure under tea plantations (Camellia sinensis) of Tripura (India). Tropical Ecology 58: 105–113.
Jänsch, S., L. Steffens, H. Höfer, F. Horak, M. Roß-Nickoll, D. Russell, A. Toschki, and J. Römbke. 2013. State of knowledge of earthworm communities in German soils as a basis for biological soil quality assessment. Soil Organisms 85: 215–233.
John, M.K. 1970. Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and plant material with ascorbic acid. Soil Science 109: 214–220.
Julka, J.M. 1988. The Fauna of India and Adjacent Countries: Megadrile Oligochaeta (Earthworms), Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata
Kaur, J., H. Walia, S.O. Mabwoga, and S. Arora. 2017. Water quality monitoring of an international wetland at Harike, Punjab and its impact on biological systems. Applied Water Science 7: 1107–1115.
Kumar, S., V. Sharma, R.V. Bhoyar, J.K. Bhattacharyya, and T. Chakrabarti. 2008. Effect of heavy metals on earthworm activities during vermicomposting of municipal solid waste. Water Environment Research 80: 154–161.
Latifi, F., F. Musa, and A. Musa. 2020. Heavy metal content in soil and their bioaccumulation in earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris L.). Agriculture and Forestry 66: 57–67.
Lee, E.P., Y.S. Han, S.I. Lee, K.T. Cho, J.H. Park, and Y.H. You. 2017. Effect of nutrient and moisture on the growth and reproduction of Epilobium hirsutum L., an endangered plant. Journal of Ecology and Environment 41: 1–9.
Liu, C.W., K.H. Lin, and Y.M. Kuo. 2003. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of Total Environment 313: 77–89.
Liu, C., C. Duan, X. Meng, M. Yue, H. Zhang, P. Wang, Y. **ao, Z. Hou, Y. Wang, and Y. Pan. 2020. Cadmium pollution alters earthworm activity and thus leaf-litter decomposition and soil properties. Environmental Pollution 267: 115410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115410.
Moos, J.H., S. Schrader, H.M. Paulsen, and G. Rahmann. 2016. Occasional reduced tillage in organic farming can promote earthworm performance and resource efficiency. Applied Soil Ecology 103: 22–30.
Morgan, J.E., and A.J. Morgan. 1999. The accumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ca) by two ecologically contrasting earthworm species (Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa): Implications for ecotoxicological testing. Applied Soil Ecology 13: 9–20.
Nelson, D.W., and L.E. Sommers. 1996. Total carbon and organic carbon and organic matter. In Method of Soil Analysis, ed. A.L. Page, R.H. Miller, and D.R. Keeney, 539–579. Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Paliwal, R. 2014. Oligochaete Diversity in Gobindsagar and Nangal Dam Wetlands (H. P. & Pb.) India. Records of the Zoological Survey of India 114: 559–562.
Phillips, H.R., C.A. Guerra, M.L. Bartz, M.J. Briones, G. Brown, O. Ferlian, and E.M. Bach. 2019. Global distribution of earthworm diversity. Science 366: 480–485.
Phillips, H.R., E.M. Bach, M.L. Bartz, J.M. Bennett, R. Beugnon, M.J. Briones, and E.R. Webster. 2021. Global data on earthworm abundance, biomass, diversity and corresponding environmental properties. Scientific Data 8: 136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00912-z.
Rybak, A.V., E.S. Belykh, T.A. Maystrenko, D.M. Shadrin, Y.I. Pylina, I.F. Chadin, and I.O. Velegzhaninov. 2020. Genetic analysis in earthworm population from area contaminated with radionuclides and heavy metals. Science of the Total Environment 273: 137920.
Salehi, A., N. Ghorbanzadeh, and E. Kahneh. 2013. Earthworm biomass and abundance, soil chemical and physical properties under different poplar plantations in the north of Iran. Journal of Forest Science 56: 223–229.
Sankar, A.S., and A. Patnaik. 2018. Impact of soil physico-chemical properties on distribution of earthworm populations across different land use patterns in southern India. The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology 79: 50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-018-0066-y.
Sathianarayanan, A., and A.B. Khan. 2006. Diversity, distribution and abundance of earthworms in Pondicherry region. Tropical Ecology 47: 139–144.
Sehar, T., G.S. Gowher, M.Y. Zargar, and Z.A. Baba. 2016. Identification and screening of earthworm species from various temperate areas of Kashmir Valley for Vermicomposting. Advances in Recycling and Waste Management 1: 102.
Shi, Y., Y. Shi, and L. Zheng. 2020. Individual and cellular responses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) to endosulfan at environmentally related concentrations. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 74: 103299.
Shrestha, N. 2021. Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. American Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics 9: 4–11.
Siddiqui, S. 2020. Interaction of Earthworm Activity with Soil Structure and Enzymes. In Biology of Composts (pp. 87–106). Springer, Cham
Singh, S., J. Singh, and A.P. Vig. 2016a. Earthworm as ecological engineers to change the physico-chemical properties of soil: Soil vs vermicast. Ecological Engneering 90: 1–5.
Singh, S., J. Singh, and A.P. Vig. 2016b. Effect of abiotic factors on the distribution of earthworms in different land use patterns. Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology 74: 41–50.
Singh, J., S. Singh, S.A. Bhat, A.P. Vig, and M. Schädler. 2018. Eco-friendly method for the extraction of earthworms: Comparative account of formalin, AITC and Allium cepa as extractant. Applied Soil Ecology 124: 141–145.
Singh, S., A. Sharma, K. Khajuria, J. Singh, and A.P. Vig. 2020. Soil properties changes earthworm diversity indices in different agro-ecosystem. BMC Ecology 20: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12898-020-00296-5.
Singh, J., E. Cameron, T. Reitz, M. Schädler, and N. Eisenhauer. 2021. Grassland management effects on earthworm communities under ambient and future climatic conditions. European Journal of Soil Science 72: 343–355.
Solomou, A.D., A.I. Sfougaris, E.M. Vavoulidou, and C. Csuzdi. 2013. Species richness and density of earthworms in relation to soil factors in olive orchard production systems in Central Greece. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 44: 301–311.
Suthar, S. 2009. Earthworm communities a bioindicator of arable land management practices: A case study in semiarid region of India. Ecological Indicators 9: 588–594.
Tamartash, R., and S.M. Ehsani. 2020. The effect of earthworms on plant diversity and soil properties under different landuses. Acta Ecologica Sinica. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2020.06.008.
Van Schaik, L., J. Palm, J. Klaus, E. Zehe, and B. Schröder. 2016. Potential effects of tillage and field borders on within-field spatial distribution patterns of earthworms. Agriculture Ecosystem and Environment 228: 82–90.
Varol, M., B. Gökot, A. Bekleyen, and B. Şen. 2012. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Tigris River (Turkey) using multivariate statistical techniques—a case study. River Research and Applications 28: 1428–1438.
Verma, R., and S. Suthar. 2018. Performance assessment of horizontal and vertical surface flow constructed wetland system in wastewater treatment using multivariate principal component analysis. Ecological Engineering 116: 121–126.
Verma, F., S. Singh, J. Singh, S.S. Dhaliwal, C. Parkash, V. Kumar, and R. Kumar. 2021a. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and its effect on earthworms in different types of soils. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03297-z.
Verma, F., S. Singh, J. Singh, S.S. Dhaliwal, and C. Parkash. 2021b. Assessment of Earthworm Community Structure in Industrial and Non-industrial Soils. Asian Journal of Biological and Life Sciences 10: 183–190.
Wang, K., Y. Qiao, H. Zhang, S. Yue, H. Li, X. Ji, and L. Liu. 2018. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in earthworms from field contaminated soil in a subtropical area of China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 148: 876–883.
**e, T., M. Wang, W. Chen, and H. Uwizeyimana. 2018. Impacts of urbanization and landscape patterns on the earthworm communities in residential areas in Bei**g. Science of the Total Environment 626: 1261–1269.
Yu, Y., X. Li, G. Yang, Y. Wang, X. Wang, L. Cai, and X. Liu. 2019. Joint toxic effects of cadmium and four pesticides on the earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 227: 489–495.
Yvan, C., S. Stéphane, C. Stéphane, B. Pierre, R. Guy, and B. Hubert. 2012. Role of earthworms in regenerating soil structure after compaction in reduced tillage systems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 55: 93–103.
Zhang, C., J. Dai, X. Chen, H. Li, and P. Lavelle. 2020. Effects of a native earthworm species (Amynthas morrisi) and Eisenia fetida on metal fractions in a multi-metal polluted soil from South China. Acta Oecologica 102: 103503.
Zhou, H., T. Zhang, J. Zhuang, M. Xu, X. Liu, Q. Shi, and D. Zhou. 2020. Study on the regulation of earthworm physiological function under cadmium stress based on a compound mathematical model. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 80: 103499.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, GOI, New Delhi for financial assistance in the form of a Major research project letter No SR/SO/AS-030/2013. We are also thankful to Dr. J. M. Julka (Ex Scientist, Zoological Survey of India), Shoolini University, Solan (Himachal Pradesh, India) for confirmation of identified earthworm species.
Funding
Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi (Project Letter No SR/SO/AS-030/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Singh, J. & Vig, A.P. Earthworm Community Structures in Three Wetland Ecosystems with Reference to Soil Physicochemical Properties. Proc Zool Soc 75, 231–241 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-022-00436-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-022-00436-3