Abstract
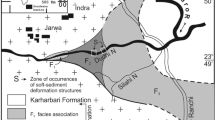
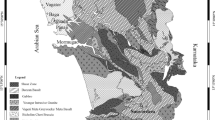
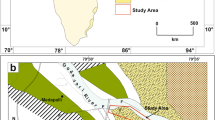
A particular type of soft-sediment deformation structure, similar to imbricate structure, is developed in the Jurassic strata at Honggouzi, western Qaidam Basin, China. We refer to this structure as a duplex-like deformation structure, because it is inferred to have been formed by the action of fast-moving, submarine gravity current sediments gliding across a pre-existing semiconsolidated sedimentary layer. The layers of duplex-like structure crop out in the southeastern limb of the core of a medium-sized anticline. The average dip direction of the duplex-like structure is 301.2° and the average dip angle is 54.7°. Duplex-like deformed laminations are composed mainly of weakly metamorphosed, extremely poorly sorted, feldspathic lithic graywacke. Sericite can be observed along bedding planes. The duplex-like structure occurs within a sequence of river-channel fine conglomerate, interchannel carbonaceous mudstone (shale), shallow-water delta sand-shale, shallow-lake calcareous mudstone, olistostromes, and a turbidite. At the bottom of the sequence, we found brownish-red shallow-lake calcareous mudstone and carbonaceous mudstone and at the top olistostromes whose genesis is related to the slip and drag of a slumped body of submarine sediment. In combination with other symbiotic and associated structures, it is considered that the duplex-like structure was formed by the slum** and subsequent movement and traction of delta-front semiconsolidated sediments over the bottom sediments of a shore or shallow-lake sedimentary environment, probably triggered by an earthquake. The attitude of the duplex-like structure indicates that the direction of gliding was from NW301.2° toward SE121°, which is consistent with the current location of the Altun Mountains, indicating that the Altun Mountains existed in the Jurassic. The orogenesis of these mountains likely involved seismic activity, and an earthquake was the triggering factor in the formation of the duplex-like structure by causing the slum**/gliding of the olistostrome sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Calibe, K. T., Ibrahim, T., 2009. Analysis of Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in Neogene Fluvio-Lacustrine Deposits of Çaybagi Formation. Eastern Turkey Sedimentary Geology, 15(1–4): 16–30
Du, Y. S., Shi, G., Guo, Y. M., et al., 2007. Permian Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures Related to Earthquake in the Southern Sydney Basin, Eastern Australia. Acta Geological Sinica, 81(4): 511–518 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Emiliano, M., Roberto, T., Giovanni, B., et al., 2003. Deltaic, Mixed and Turbidite Sedimentation of Ancient Foreland Basins. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 20: 733–755
Hao, X., Da, Z. T., Jun, F. Z., et al., 2011. Formation Mechanism of Underpressured Reservoir in Huatugou Oilfield of Qaidam Basin. Journal of Earth Science, 22(5): 632–639. doi: 10.1007/s12583-011-0214-5
Jeffrey, G. M., Peter, A. H., Shanmugam, G., et al., 2001. Experiments on Subaqueous Sandy Gravity Flows: The Role of Clay and Water Content in Flow Dynamics and Depositional Structures. GSA Bulletin, 113(11): 1377–1386
Juan, P. R., Nieves, M., Ana, R. S., et al., 2007. Lateral Variability of Ancient Seismites Related to Differences in Sedimentary Facies (the Synrift Escucha Formation, Mid-Cretaceous, Eastern Spain). Sedimentary Geology, 201: 461–484
Lu, H. B., Wang, J., Zhang, H. C., 2011. The Discovery and Regional Tectonic Implication of the Late Mesozoic Slump Sedimentary Layer in Lingshan Island, Shandong. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(6): 938–946 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Meng, Q. R., Fang, X., 2008. Cenozoic Tectonic Development of the Qaidam Basin in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 444: 1–24
Moiola, R. J., Shanmugam, G., 1984a. Facies Analysis of Upper Jackfork Formation (Pennsyvanian), DeGray Dam. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 68: 509
Morris, R. C., and Sutherland, P. K., 1984, The Mississippian-Pennsylvanian Boundary in the Ouachita Mountains, Arbuckle Mountains and Ardmore Basin, Arkansas and Oklahoma. In: Sutherland, P. K., Manger, W. L., eds., Biostratigraphy: 9th International Congress on Carbonifereous Stratigraphy and Geology. 2: 357–368
Morris, R. C., Shanmugam, G., 1985. Slope and Axial Fan Systems in Carboniferous Rock, Frontal Ouachita Mountains; Oklahoma and Arkansas. In: Morris, R. C., Mullen, E. D., eds., Alkalic Rocks and Carboniferous Sandstones, Ouachita Mountains. New Perspectives (Geological Sociaty of America South-Central Section Guidebook). Fayetteville, University of Arkansas. 1–33
Morris, R. C., 1973. Flyschfacies of the Quachita Trough-with Examples From the Splillway at Degray Dam, Arkansas. In: Stone, C. G., Haley, B. R., Viele, G. W., et al., eds., A Guidebook to the Geology of the Quachita Mountains. Little Rock, Arkansas Geological Commission. 158–168
Pei, J. L., Sun, Z. M., Wang, X. S., et al., 2009. Evidence for Tibetan Plateau Uplift in Qaidam Basin before Eocene-Oligocene Boundary and Its Climatic Implications. Journal of Earth Science, 20(2): 430–437. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0035-y
Qiao, X. F., Guo, X. P., 2011. Research on Lower Jurassic Soft-Sediment Deformation of Southwest Tianshan Mountains, Sinkiang. Geological Review, 57(6): 761–769 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Rodríguez-Pascua, M. A., Calvo, J. P., Gómez-Gras, D., et al., 2000. Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures Interpreted as Seismites in Lacustrine Sediments of the Prebetic Zone, SE Spain, and Their Potential Use as Indicators of Earthquake Magnitudes during the Late Miocene. Sedimentary Geology, 135: 117–135
Royden, L. H., Burchfiel, B. C., King, R. W., et al., 1997. Surface Deformation and Lower Crustal Flow in Easter Tibet. Science, 276: 788–790
Shanmugam, G., Moiola, R. J., Sales, J. K., 1988. Duplex-Like Structures in Submarine Fan Channels, Ouachita Mountains, Arkansas. Geology, 16: 229–232
Song, T. G., Wang, X. P., 1993. Structural Styles and Stratigraphic Patterns of Syndepositional Faults in a Contractional Setting.. Geologists Bulletin, 77: 102–117
Visser, N. J., Collison, W. P., Terblanche, J. C., 1984. The Origin of Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in Permo-Carboniferous Glacial and Proglacial Beds, South Africa. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 54(4): 1183–1196
Wan, T. F., Zhu, H., 2002. Tectonics and Environment Change of Meso-Cenozoic in China Continent and Its Adjacent Areas. Geoscience, 16: 107–120 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, H. A., Zhong, J. H., Chen, X., et al., 2008. Characteristics of Cretaceous Seismite in the Tamuch Age Depression Mongolia, and Its Significance. Acta Geological Sinica, 82(6): 1088–1094 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhong, J. H., Xu, S. H., Wang, Z. K., et al., 2008. Study On the Quarternary Glacial-Ploughed Deformation Beddings in Seven Springs Area, Western Qaidam Basin. Geological Review, 54(2): 207–215 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhong, J. H., Yin, C. M., Duan, H. L., et al., 2007. Mesozoic Paleocurrent Properties in the Southern Edge of Altun Mountain in the Western Qaidam Bain. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 27(2): 20–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ni, L. T., Zhong, J. H., Shao, Z. F., et al., 2015. Characteristics, Genesis, and Sedimentary Environment of Duplex-Like Structures in the Jurassic Sediments of Western Qaidam Basin, China. Journal of Earth Science, 26(5): 677–689. doi:10.1007/s12583-015-0578-2. http://en.earth-science.net
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, L., Zhong, J., Shao, Z. et al. Characteristics, Genesis, and Sedimentary Environment of Duplex-Like Structures in the Jurassic Sediments of Western Qaidam Basin, China. J. Earth Sci. 26, 677–689 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0578-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0578-2