Abstract
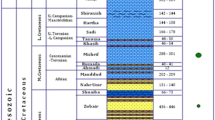
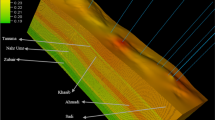
Borehole instability problems have caused non-productive time while drilling operations in the Nahr Umr shale formation. The drilling difficulties, including stuck pipe, caving, and tight holes, have been identified as significant problems in this formation. This study aims to comprehend the causes of wellbore failure and choose the most suitable drilling strategy. In this regard, a mechanical earth model (MEM) was performed using open-hole wireline logging measurements from the offset wells data. Those data included gamma ray, density log, compressional wave velocity, shear wave velocity, neutrons porosity, and image log. Moreover, there were also measured data such as leak-off tests and modular formation dynamics testers that were applied to validate the model’s accuracy.
The analysis exhibited that the leading cause of wellbore instability problems was improper mud weight (10.6 ppg). In addition, inappropriate drilling practices and the heterogeneity of the Nahr Umr formation have magnified the risk of drilling problems. The MEM outcome proved that the mud weight should be 11.6–13.5 ppg to safely drill a vertical well. Thus, this work can be applied as a cost-effective tool when designing future neighboring deviated wells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ b :
-
bulk density of the formation (g/cm3)
- Z :
-
depth
- Δt 𝑛 :
-
shale slowness at a normal trend line
- Δt 0 :
-
shale slowness derived from sonic log
- x :
-
exponent values
- ∆t COMP :
-
compressional slowness of the bulk formation us/ft
- ∆t shear :
-
shear slowness of the bulk formation us/ft
- K dyn :
-
dynamic bulk modulus (Mpsi)
- G dyn :
-
dynamic shear modulus (Mpsi)
- v dyn :
-
unitless Poisson’s ratio
- Vp:
-
compressive sonic wave (ft/ms)
- Vs:
-
shear sonic wave (ft/ms)
- GR:
-
value of gamma ray log
- GRmax:
-
maximum values of gamma ray log
- GRmin:
-
minimum values of gamma ray log
- Ф:
-
porosity from neutron porosity log
- Vshale:
-
shale volume
- (E) :
-
Young’s modulus measured in (Mpsi)
- Esta:
-
static Young’s modulus (Mpsi),
- υsta:
-
static Poisson’s ratio (dimensionless)
- Gsta:
-
static bulk modulus (Mpsi)
- Ksta:
-
static shear modulus (Mpsi)
- α :
-
Biot’s constant
- ε handε H :
-
tectonic strain factors in minimum and maximum horizontal direction, respectively
- E horz :
-
horizontal static Young’s modulus, ex YME_H_VTI_STA Mandatory curve input
- E vert :
-
vertical static Young’s modulus, ex YME_V_VTI_STA Mandatory curve input
- v horz :
-
horizontal compression-horizontal expansion static Poisson ratio, ex PR_HH_VTI_STA mandatory curve input
- v vert :
-
vertical compression-horizontal expansion static Poisson’s ratio, ex PR_VH_VTI_STA mandatory curve input
References
Aadnoy B, Chenevert M (1987) Stability of highly inclined boreholes. SPE Drill Eng 2(04):364–374
Abbas AK, Al-Asadi YM, Alsaba M, Flori RE, Alhussainy S (2018a) Development of a geomechanical model for drilling deviated wells through the Zubair formation in southern Iraq. In: Paper presented at the SPE/IADC Middle East drilling technology conference and exhibition
Abbas AK, Flori RE, Alsaba M (2018b) Estimating rock mechanical properties of the Zubair shale formation using a sonic wireline log and core analysis. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 53:359–369
Abbas AK, Flori RE, Alsaba M, Dahm H, Alkamil EH (2018c) Integrated approach using core analysis and wireline measurement to estimate rock mechanical properties of the Zubair Reservoir, Southern Iraq. J Petroleum Sci Eng 166:406–419
Al-Ajmi A, Zimmerman R (2006) Stability analysis of deviated boreholes using the Mogi-Coulomb failure criterion, with applications to some oil and gas reservoirs. In: Paper presented at the IADC/SPE asia pacific drilling technology conference 2006-meeting the value challenge: performance, deliverability and cost
Alkamil EH, Abbood HR, Flori RE, Eckert A (2017) Wellbore stability evaluation for Mishrif formation. In: Paper presented at the SPE Middle East oil and gas show and conference
Allawi RH (2023) Chemical and mechanical model to analysis wellbore stability. Petroleum Sci Technol:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2023.2183966
Allawi RH (2024a) Fracture pressure predict based on well logs of depleted reservoir in southern Iraqi oilfield. Int J Energy Power Eng 18(1):5–9
Allawi RH (2024b) Geomechanical model of Ratawi shale reservoir. Int J Oil, Gas Coal Technol 35(1):1–16
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS (2021) Wellbore instability management using geomechanical modeling and wellbore stability analysis for Zubair shale formation in Southern Iraq. J Petroleum Explor Prod Technol 11(11):4047–4062
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS (2022a) 4D finite element modeling of stress distribution in depleted reservoir of south Iraq oilfield. J Petroleum Explor Prod Technol 12(3):679–700
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS (2022b) Wellbore stability analysis using shear wave correlation. Arab J Geosci 15(21):1–9
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS (2023a) Prediction of pore and fracture pressure using well logs in Mishrif reservoir in an Iraqi oilfield. In: Paper presented at the AIP conference proceedings
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS (2023b) Wellbore stability analysis and selecting safe mud weight window for Mishrif reservoir in Southern Iraq. Arab J Geosci 16(5):345
Allawi RH, Al-Jawad MS, Alfarge D (2022) New empirical equation to predict the pore pressure in oil reservoirs. Arab J Geosci 15(8):1–16
Alsahlawi Z, Foster H, Hussein M (2017) A geomechanical approach for drilling performance optimization across shales in Safaniya field—Arabian Gulf. In: Saudi Arabia. Paper presented at the SPE Middle East oil & gas show and conference
Barton CA, Moos D, Peska P, Zoback MD (1997) Utilizing wellbore image data to determine the complete stress tensor: application to permeability anisotropy and wellbore stability. The Log Analyst 38(06)
Bell J (2003) Practical methods for estimating in situ stresses for borehole stability applications in sedimentary basins. J Petroleum Sci Eng 38(3-4):111–119
Bradley W (1979) Mathematical concept-stress cloud-can predict borehole failure. Oil Gas J 77(8)
Chang C, Zoback MD, Khaksar A (2006) Empirical relations between rock strength and physical properties in sedimentary rocks. J Petroleum Sci Eng 51(3-4):223–237
Eaton BA (1969) Fracture gradient prediction and its application in oilfield operations. J Petroleum Technol 21(10):1,353–351,360
Gholami R, Moradzadeh A, Rasouli V, Hanachi J (2014) Practical application of failure criteria in determining safe mud weight windows in drilling operations. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(1):13–25
Islam M, Skalle P, Al-Ajmi A, Soreide O (2010) Stability analysis in shale through deviated boreholes using the Mohr and Mogi-Coulomb failure criteria. In: Paper presented at the 44th US rock mechanics symposium and 5th US-Canada rock mechanics symposium
Jaeger J, Cook N, Zimmerman R (2007) Fundamentals of rock mechanics, forth ed. Wiley-Blackwell
Khaksar A, Taylor PG, Fang Z, Kayes TJ, Salazar A, Rahman K (2009) Rock strength from core and logs, where we stand and ways to go. In: Paper presented at the EUROPEC/EAGE conference and exhibition
Mansourizadeh M, Jamshidian M, Bazargan P, Mohammadzadeh O (2016) Wellbore stability analysis and breakout pressure prediction in vertical and deviated boreholes using failure criteria–a case study. J Petroleum Sci Eng 145:482–492
McNally G (1987) Estimation of coal measures rock strength using sonic and neutron logs. Geoexploration 24(4-5):381–395
Morales, R., & Marcinew, R. (1993). Fracturing of high-permeability formations: mechanical properties correlations. Paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition.
Nabaei M, Shahbazi K, Shadravan A, Amani M (2010) Uncertainty analysis in unconfined rock compressive strength prediction. In: Paper presented at the SPE deep gas conference and exhibition
Plumb R (1994) Influence of composition and texture on the failure properties of clastic rocks. In: Paper presented at the rock mechanics in petroleum engineering
Sharland PR, Casey DM, Davies RB, Simmons MD, Sutcliffe OE (2004) Arabian plate sequence stratigraphy–revisions to SP2. GeoArabia 9(1):199–214
Song L (2012) Measurement of minimum horizontal stress from logging and drilling data in unconventional oil and gas. Graduate Studies
Tabaeh HM, Mohammad A (2016) Estimation of in-situ horizontal stresses using the linear poroelastic model and minifrac test results in tectonically active area. Russian J Earth Sci 16(4)
Zhang J (2011) Pore pressure prediction from well logs: methods, modifications, and new approaches. Earth-Sci Rev 108(1-2):50–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Allawi, R.H. Mechanical earth model to mitigate wellbore instability of Nahr Umr formation in Southern Iraq oilfield. Arab J Geosci 17, 218 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-12023-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-12023-1