Abstract
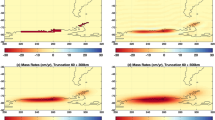
The possible seismo-ionospheric anomalies of the recent Mw 6.0 and Mw 6.4 twin earthquakes of 14 November 2021 in southern Iran were studied through Global Positioning System (GPS) and ground ionosonde observations. GPS measured total electron content observations, and ionosonde measured NmF2 and hmF2, showing ionospheric anomalies in the pre-seismic and co-seismic phases of the earthquakes. A positive increase in ΔTEC was observed at near-field stations ~ 2–7 days before the twin earthquakes. Our observations also show an increase in the estimated values of NmF2 and hmF2 in the pre-seismic phase compared to their mean values. As the “Kp” and “Dst” indices were quiet during the observation period, these anomalies are apparently generated by seismic activity. The observation of sudden co-seismic ionospheric disturbances at near-field stations immediately after the earthquakes explains the mechanism of co-seismic energy propagation through the lithosphere-atmosphere–ionosphere coupling. The estimated differential NmF2 values show a dip in the peak electron density of − 2.84 × 1011 e/m3 during the time of earthquakes. Our results also show anomalous pre-seismic enhancements in all the three parameters used in this study—TEC, NmF2, and hmF2—an indication of precursory signatures of the twin events. In addition, these parameters also show similar changes in their co-seismic phases. Thus, the observed pre- and co-seismic ionospheric anomalies reveal the characteristic signatures of the preparation processes and the co-seismic energy propagation of the twin earthquakes.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
GPS data of the SCAS station and the ground ionosonde data used in this study were provided by the Sharjah Academy for Astronomy, Space Sciences and Technology (SAASST). The GPS data of DRS6 and DRS9 stations were provided by Dubai municipality. The solar and geomagnetic indices were obtained from the NOAA National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) (https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/geomag/indices.html). The GPS RINEX data of the IGS stations were obtained from the International GNSS service (IGS) (https://igs.org). The earthquake data used in this study were obtained from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) (https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/search/).
References
Afraimovich EL, Astafyeva EI (2008) TEC anomalies - local TEC changes prior to earthquakes or TEC response to solar and geomagnetic activity changes? Earth, Planets and Space 60(9):961–966. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352851
Afraimovich EL, Perevalova NP, Plotnikov AV, Uralov AM (2001) The shock-acoustic waves generated by earthquakes. Ann Geophys 19(4):395–409. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-19-395-2001
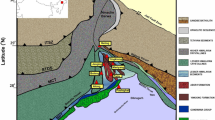
Alavi M (1994) Tectonics of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran: new data and interpretations. Tectonophysics 229(3):211–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(94)90030-2
Astafyeva EI, Afraimovich EL (2006) Long-distance traveling ionospheric disturbances caused by the great Sumatra-Andaman earthquake on 26 December 2004. Earth Planets Space 58:1025–1031. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352607
Astafyeva E, Shalimov S, Olshanskaya E, Lognonne P (2013) Ionospheric response to earthquakes of different magnitudes: larger quakes perturb the ionosphere stronger and longer. Geophys Res Lett 40(9):1675–1681
Astiz L, Kanamori H (1984) An earthquake doublet in Ometepec, Guerrero, Mexico. Phys Earth Planet Inter 34(1–2):24–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201(84)90082-7
Blaunstein N, and Hayakawa M (2009) Short-term ionospheric precursors of earthquakes using vertical and oblique ionosondes. Physics and Chem Earth, 34(6–7), 496–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2008.07.002
Bolt BA (1964) Seismic air waves from the great 1964 Alaskan earthquake. Nature 202:1094–1095
Cahyadi MN, Arisa D, Muafiry IN, Muslim B, Rahayu RW, Putra ME, Wulansari M, Setiadi B, Arisal A, Razi P et al (2022) Directivity of coseismic ionospheric disturbances propagation following the 2016 West Sumatra earthquake using three-dimensional tomography GNSS-TEC. Atmosphere 13:1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091532
Chen H, Han P, Hattori K (2022) Recent advances and challenges in the seismo-electromagnetic study: a brief review. Remote Sensing 14:5893. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225893
De Santis A, Balasis G, Pavón-Carrasco FJ, Cianchini G, Mandea M (2017) Potential earthquake precursory pattern from space: the 2015 Nepal event as seen by magnetic Swarm satellites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 461:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.12.037
De Santis A, Perrone L, Calcara M, Campuzano SA, Cianchini G, D’Arcangelo S, Di Mauro D, Marchetti D, Nardi A, Orlando M et al (2022) A comprehensive multiparametric and multilayer approach to study the preparation phase of large earthquakes from ground to space: the case study of the June 15 2019, M7.2 Kermadec Islands (New Zealand) earthquake. Remote Sens Environ 283:113325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2022.113325
Depuev V, Zelenova T (1996) Electron density profile changes in a per-earthquake period. Adv Space Res 18(6):115–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1177(95)00911-6
Dobrovolsky IP, Zubkov SI, Miachkin VI (1979) Estimation of the size of earthquake preparation zones. Pure Appl Geophys 117(5):1025–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876083
Dohn WL, Posmetier ES (1964) Ground-coupled air waves from the great Alaskan earthquake. J Geophys Res 69:5357–5361
Fan M, Zhu K, De Santis A, Marchetti D, Cianchini G, Piscini A, He X, Wen J, Wang T, Zhang Y et al (2022) Analysis of Swarm satellite magnetic field data for the 2015 Mw 78 Nepal earthquake based on nonnegative tensor decomposition. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote sens 60:2006119
Fathian A, Atzori S, Svigkas N, Tolomei C, Shugar DH, Reicherter K (2022) Source characteristics of the Fin doublet earthquakes of 14 November 2021 (Mw 6.2 and 6.3) utilizing InSAR data. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2022:2119–2122. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883591
Freund F (2011) Pre-earthquake signals: underlying physical processes. J Asian Earth Sci 41:383–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.009
Freund F, Ouillon G, Scoville J, Sornette D (2021) Earthquake precursors in the light of peroxy defects theory: critical review of systematic observations. Eur Phys J Spec Top 230:7–46
Gautam PK, Chauhan V, Sathyaseelan R, Kumar N, Pappachen JP (2018) Co-seismic ionospheric GPS-TEC disturbances from different source characteristic earthquakes in the Himalaya and the adjoining regions. NRIAG J Astron Geophys 7(2):237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrjag.2018.05.009
Goda K, Kiyota T, Pokhrel RM, Chiaro G, Katagiri T, Sharma K, Wilkinson S (2015) The 2015 Gorkha Nepal earthquake: insights from earthquake damage survey. Front Built Environ 1(May):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2015.00008
Gupta S, Upadhayaya AK (2017) Preearthquake anomalous ionospheric signatures observed at low-mid latitude Indian station, Delhi, during the year 2015 to early 2016: preliminary results. J Geophys Res Space Physics 122(8):8694–8719. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JA024192
He L, Heki K (2016) Three dimensional distribution of ionospheric anomalies prior to three large earthquakes in Chile. Geophys Res Lett 43:7287–7293. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL069863
He L, Heki K (2017) Ionospheric anomalies immediately before M(w)7.0–8.0 earthquakes. J Geophys Res Space Physics 122:8659–8678. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JA024012
Heki K (2011) Ionospheric electron enhancement preceding the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake. Geophys Res Lett 38(17):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047908
Hessami K, Nilforoushan F, Talbot CJ (2006) Active deformation within the Zagros Mountains deduced from GPS measurements. J Geol Soc 163(1):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-764905-031
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H, Collins J (1992) GPS theory and practice, Springer -Verlag Wien. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6199-9
Hoshiba M, Iwakiri K, Hayashimoto N, Shimoyama T, Hirano K, Yamada Y, Ishigaki Y, Kikuta H (2011) Outline of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake (M w 9.0) -earthquake early warning and observed seismic intensity. Earth, Planets and Space 63(7):547–551. https://doi.org/10.5047/eps.2011.05.031
Huang CS, Foster JC, Goncharenko LP, Sofko GJ, Borovsky JE, Rich FJ (2003) Midlatitude ionospheric disturbances during magnetic storms and substorms. J Geophys Res Space Physics 108(A6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JA009608
Ippolito A, Perrone L, De Santis A, Sabbagh D (2020) Ionosonde data analysis in relation to the 2016 Central Italian earthquakes. Geosciences 10:354. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090354
Jahani S, Callot JP, Letouzey J, Frizon de Lamotte D (2009) The eastern termination of the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, Iran: structures, evolution, and relationships between salt plugs, folding, and faulting. Tectonics 28(6):TC6004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008TC002418
** S (2018) Two-mode ionospheric disturbances following the 2005 Northern California offshore earthquake from GPS measurements. J Geophys Res Space Physics 123:8587–8598. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JA025001
Kim VP, Khegai VV, Illich-Svitych PV (1994) On one possible ionospheric precursor of earthquakes. Phys Solid Earth 30:223–226
Kon S, Nishihashi M, Hattori K (2011) Ionospheric anomalies possibly associated with M ≥ 6.0 earthquakes in the Japan area during1998–2010: case studies and statistical study. J Asian Earth Sci 41:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.10.005
Kuo CL, Lee LC, Huba JD (2014) An improved coupling model for the lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere system. J Geophys Res: Space Physics 119:3189–3205. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JA019392
Liu JY, Chuo YJ, Shan SJ, Tsai YB, Chen YI, Pulinets SA, Yu SB (2004) Pre-earthquake ionospheric anomalies registered by continuous GPS TEC measurements. Ann Geophys 22(5):1585–1593. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-22-1585-2004
Manea VC, Armaş I, Manea M, Gheorghe M (2021) InSAR surface deformation and numeric modeling unravel an active salt diapir in southern Romania. Sci Rep 11(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91517-4
Martin SS (2005) Intensity distribution from the 2004 M 90 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake. Seismol Res Lett 76(3):321–330. https://doi.org/10.1785/gssrl.76.3.321
Ni J, Barazangi M (1986) Seismotectonics of the Zagros continental collision zone and a comparison with the Himalayas. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 91:8205–8218
Nissen E, Tatar M, Jackson JA, Allen MB (2011) New views on earthquake faulting in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt of Iran. Geophys J Int 186(3):928–944. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05119.x
Oikonomou C, Haralambous H, Pulinets S, Khadka A, Paudel SR, Barta V, Muslim B, Kourtidis K, Karagioras A, İnyurt S (2021) Investigation of pre-earthquake ionospheric and atmospheric disturbances for three large earthquakes in Mexico. Geosci (switzerland) 11(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11010016
Ouzounov D, Pulinets S, Davidenko D, Rozhnoi A, Solovieva M, Fedun V, Dwivedi BN, Rybin A, Kafatos M, Taylor P (2021) Transient effects in atmosphere and ionosphere preceding the 2015 M7.8 and M7.3 Gorkha-Nepal earthquakes. Front Earth Sci 9:757358. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.757358
Perrone L, De Santis A, Abbattista C, Alfonsi L, Amoruso L, Carbone M, Cesaroni C, Cianchini G, De Franceschi G, De Santis A et al (2018) Ionospheric anomalies detected by ionosonde and possibly related to crustal earthquakes in Greece. Ann Geophys 36:361–371
Pilia S, Jackson JA, Hawkins R, Kaviani A, Ali MY (2020) The Southern Zagros collisional orogen: new insights from transdimensional trees inversion of seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 47:e2019GL086258. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL086258
Pulinets S, Ouzounov D (2011) Lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling (LAIC) model - an unified concept for earthquake precursors validation. J Asian Earth Sci 41(4–5):371–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.005
Pulinets SA, Khegai VV, Boyarchuk KA, Lomonosov AM (1998) Atmospheric electric field as a source of ionospheric variability. Phys Usp 41:515–522
Pulinets SA, Ouzounov D, Ciraolo L, Singh R, Cervone G, Leyva A, Dunajecka M, Karelin AV, Boyarchuk KA, Kotsarenko A (2006) Thermal, atmospheric and ionospheric anomalies around the time of the Colima M7.8 earthquake of 21 January 2003. Annales Geophysicae 24(3):835–849. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-24-835-2006
Pulinets S, Krankowski A, Hernandez-Pajares M, Marra S, Cherniak I, Zakharenkova I, Rothkaehl H, Kotulak K, Davidenko D, Blaszkiewicz L, Fron A, Flisek P, Rigo AG, Budnikov P (2021) Ionosphere sounding for pre-seismic anomalies identification (INSPIRE): results of the project and perspectives for the short-term earthquake forecast. Front Earth Sci 9(April):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.610193
Pulinets SA, Boyarchuk (2003) Ionospheric precursors of earthquakes. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/b137616
Riga G, Balocchi P (2018) Double earthquakes classification and seismic precursors. Open Journal of Earthquake Research 07(01):1–27. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojer.2018.71001
Rikitake T (1968) Geomagnetism and earthquake prediction. Tectonophysics 6(1):59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(68)90026-7
Roeloffs EA (1988) Hydrologic precursors to earthquakes: a review. Pure Appl Geophys 126(2–4):177–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878996
Rolland LM, Occhipinti G, Lognonné P, Loevenbruck A (2010) Ionospheric gravity waves detected offshore Hawaii after tsunamis. Geophys Res Lett 37:L17101. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044479
Rolland LM, Lognonné P, Munekane H (2011) Detection and modeling of Rayleigh wave induced patterns in the ionosphere. J Geophys Res Space Physics 116:A05320. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JA016060
Shah M, Ahmed A, Ehsan M, Khan M, Tariq MA, Calabia A, and Rahman Z ur (2020) Total electron content anomalies associated with earthquakes occurred during 1998–2019. Acta Astronautica, 175(June), 268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.06.005
Shah M, ** S (2015) Statistical characteristics of seismo-ionospheric GPS TEC disturbances prior to global Mw≥5.0 earthquakes (1998–2014). J Geodyn 92:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2015.10.002
Skelton A, Liljedahl-Claesson L, Wästeby N, Andrén M, Stockmann G, Sturkell E, Mörth CM, Stefansson A, Tollefsen E, Siegmund H, Keller N, Kjartansdóttir R, Hjartarson H, Kockum I (2019) Hydrochemical changes before and after earthquakes based on long-term measurements of multiple parameters at two sites in Northern Iceland—a review. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 124(3):2702–2720. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB016757
Stampfli G, Mosar J, Favre P, Pillevuit A, Vannay JC (2001) Permo-Mesozoic evolution of the western Tethys realm: the Neo-Tethys East Mediterranean Basin connection, in Peri-Tethyan Rift/Wrench Basins and Passive Margins, Peri-Tethys Mem., vol. 6, edited by P. A. Ziegler et al. Mem Mus Natl Hist Nat 186:51–108
Takin M (1972) Iranian geology and continental drift in the Middle East. Nature 235:147–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/235147a0
Talebian M, Jackson J (2004) A reappraisal of earthquake focal mechanisms and active shortening in the Zagros mountains of Iran. Geophys J Int 156(3):506–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02092.x
Vernant P, Nilforoushan F, Hatzfeld D, Abbassi MR, Vigny C, Masson F, Nankali H, Martinod J, Ashtiani A, Bayer R, Tavakoli F, Chéry J (2004) Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophys J Int 157(1):381–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02222.x
Walpersdorf A, Hatzfeld D, Nankali H, Tavakoli F, Nilforoushan F, Tatar M, Vernant P, Chéry J, Masson F (2006) Difference in the GPS deformation pattern of North and Central Zagros (Iran). Geophys J Int 167(3):1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03147.x
Yang Y-H, Li X, Hu J-C, Song J, Zhao J, Yassaghi A et al (2023) The 2022 Hormozgan doublet earthquake: two blind thrusts-related folding in Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, southeast Iran. Geophys Res Lett 50:e2022GL101902. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GL101902
Zakharenkova IE, Shagimuratov II, Krankowski A, Lagovsky AF (2007) Precursory phenomena observed in the total electron content measurements before great Hokkaido earthquake of September 25, 2003 (M = 8.3). Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica 51(2):267–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-007-0014-7
Zhang Y, Wang T, Chen W, Zhu K, Marchetti D, Cheng Y, Fan M, Wang S, Wen J, Zhang D, Zhang H (2023) Are there one or more geophysical coupling mechanisms before earthquakes? The case study of Lushan (China) 2013. Remote Sens 15:1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061521
Zhao B, Wang M, Yu T, Wan W, Lei J, Liu L, Ning B (2008) Is an unusual large enhancement of ionosphericelectron density linked with the 2008 great Wenchuan earthquake? J Geophys Res Space Physics 113:A11304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013613
Zhou Z, Tian L, Zhao J, Wang H, Liu J (2020) Stress-related pre-seismic water radon concentration variations in the Pan** Observation Well, China (1994–2020). Front Earth Sci 8(November):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.596283
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank and acknowledge the Director of Sharjah Academy for Astronomy, Space Sciences and Technology (SAASST) for the GPS and ionosonde data. Our sincere thanks and acknowledgment to the survey department of the Dubai Municipality (Eng. Eman AL Falasi and Eng. Osama S. A Mohamed) for their collaboration in providing the data of two GPS stations (DRS6 and DRS9). Author RS would also like to thank the Director of Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehradun, India, for providing the facilities to carry out this work. We thank Abd Elmahmoud Elgaili for his help with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JPP conceived the problem, carried out data analysis, interpreted the results, and drafted the text. HAH and RS participated in the scientific discussions, interpreted the results, and co-drafted the text. AMD carried out the ionosonde data processing, and AS reviewed the results and provided useful suggestions during the preparation of the manuscript. All the authors actively discussed the results and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Longjun Dong
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pappachen, J.P., Hamdan, H.A., Sathiyaseelan, R. et al. Possible seismo-ionospheric anomalies of Mw 6.0 and 6.4 south Iran twin earthquakes on 14 November 2021 from GPS and ionosonde observations. Arab J Geosci 17, 201 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-12005-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-12005-3