Abstract
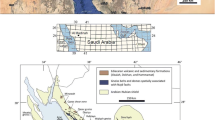
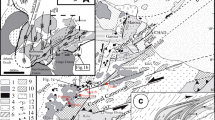
Wall rock alteration products of sheared minerals, micro faults, and quenched glassy matrix in micro faults are the effects of magma ascent under tremendous pressure in both discordant and concordant intrusions. The studied dykes show more shearing effects in wall rock and this magma flow rheology aligned the early-formed plagioclase in dolerite along the contact margins of dyke. The present study covers Salem dolerites, predominantly formed in Attur, Mettur, and Yercaud regions. Salem dolerites imprint the microlevel alteration and changes due to magma flow causing mineral alignment in dolerite, sheared minerals, microfractures, micro faults in wall rock filled by quenched glassy matrix, and recrystallized mineral zones on the contact of the host rock wall. The emphasis of this work is to denote the structural interaction of dolerite dyke with rigid host rock and textural variations from the chilled margin to the centre of the dolerite that changes during the emplacement and cooling process. Petrographically, intersertal and subophitic textures are recognized from the chilled margin and centre of the dolerite dyke, respectively. The present work scrutinizes the nature of the dyke contact with the host rock and whether magma flow alters the host rock wall or not at the micro level in the contact margin. Subsequently, after the emplacement, the study area underwent multiple stages of deformation that changed the pre-existing trend of the dykes. Major faults within the dykes of Attur and Mettur show a different style of deformation. The NNW–SSE dyke in the Attur region deformed dramatically in a sinistral strike-slip brittle manner by a brittle strike-slip fault documented for the time in this region and it is located near the Salem Attur Shear Zone. The ambiguous deformation mechanism of dolerite within the area's high shear sense shows a contradiction to the crustal-scale shear zones of Salem block. This strives the detailed physical and structural work in this region helps to demarcate the deformational process. Mettur dykes deformed as a normal slip toward the foothill of this area. These structural imprints help categorize this region’s mode of deformation and displacement event.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 January 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11193-8
References
Ananth C, Bhadra S, Goswami A (2020) Contrasting kinematics of brittle-shears within the Salem-Attur and Bhavani shear zone, south India: tectonic implications. J Earth Syst Sci 129(1):1–18
Anderson KM, Lisowski SP (2010) Cyclic ground tilt associated with the 2004–2008 eruption of Mount St. Helens. J Geophys Res 115:B11201. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB007102
Baer G, Beyth M, Reches Z (1994) Dikes emplaced into fractured basement, Timna Igneous Complex, Israel. J Geophys Res 99:24
Barker DS (1970) Compositions of granophyre, myrmekite, and graphic granite. Geol Soc Am Bull 81:3339–3350
Beauducel F, Cornet FH, Suhanto E, Duquesnoy T, Kasser M (2000) Constraints on magma flux from displacements data at Merapi volcano, Java, Indonesia. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 105(B4):8193–8203
Behera BM, Waele BD, Thirukumaran V, Sundaralingam K, Narayanan S, Sivalingam B, Biswal TK (2019) Kinematics, strain pattern and geochronology of the Salem-Attur shear zone: tectonic implications for the multiple sheared Salem-Namakkal blocks of the Southern Granulite terrane, India. Precambr Res 324:32–61
Benn K, Allard B (1989) Preferred mineral orientations related to magmatic flow in ophiolite layered gabbros. J Petrol 30(4):925–946
Bhadra BK (2000) Ductile shearing in Attur shear zone and its relation with Moyar shear zone, South India. Gondwana Res 3:361–369
Biswal TK, Thirukumaran V, Ratre K, Bandyapadhaya K, Sundaralingam K, Mondal AK (2010) A study of mylonites from parts of the Salem-Attur shear zone (Tamil Nadu) and its tectonic implications. J Geol Soc India 75(1):128–136
Bouchez JL (1997) Granite is never isotropic: an introduction to AMS studies of granitic rocks. In: Bouchez JL, Hutton DHW, Stephens WE (eds) Granite: from segregation of melt to emplacement fabrics. Petrology and Structural Geology, vol 8. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-1717-5_6
Cañón Tapia E (2004) Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of lava flows and dykes: a historical account. Geol Soc London, Spec Publ 238(1):205–225
Cañón Tapia E, Chávez-Álvarez J (2004) Theoretical aspects of particle movement in flowing magma: implications for the anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of dykes. Geol Soc London, Spec Publ 238(1):227–249
Chadwick WW Jr, Archuleta RJ, Swanson DA (1988) The mechanics of ground deformation precursory to dome-building extrusions at Mount St. Helens 1981–1982. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 93(B5):4351–4366
Chetty TRK, Bhaskar Rao YJ (1998) Behavior of stretching lineation in the Salem-Attur shear belt, Southern Granulite terrane, south India. J Geol Soc India 52:443–448
Chetty TRK, Santosh M (2013) Proterozoic orogens in southern Peninsular India: contiguities and complexities. J Asian Earth Sci 78:39–53
Clark C, Collins AS, Kinny PD, Timms NE, Chetty TRK (2009) SHRIMP U-Pb age constraints on the age of charnockite magmatism and metamorphism in the Salem Block, southern India. Gondwana Res 16:27–36
Clemens JD (2003) S-type granitic magmas-petrogenetic issues, models and evidence. Earth-Sci Rev 61(1):1–18
Collins AS, Clark C, Plavsa D (2014) Peninsular India in Gondwana: the tectonothermal evolution of the Southern Granulite Terrain and its Gondwanan counterparts. Gondwana Res 25:190–203
Cox KG, Bell JD, Pankhurst RJ (1979) The interpretation of igneous rocks. Allen and Unwine, London, p 450
Dash JK, Pradhan SK, Bhutani R, Balakrishnan S, Chandrasekaran G, Basavaiah N (2013) Paleomagnetism of ca. 2.3 Ga mafic dyke swarms in the northeastern Southern Granulite Terrain, India: constraints on the position and extent of Dharwar craton in the Paleoproterozoic. Precambrian Res 228:164–176
Delaney P, Gartner A (1997) Physical processes of shallow mafic dike emplacement near the San Rafael Swell, Utah. Geol Soc Am Bull 109(9):16
Delaney PT, Pollard DD, Ziony JI, McKee EH (1986) Field relations between dikes and joints: emplacement processes and paleostress analysis. J Geophys Res 91:4920–4938
Devaraju TC, Huhma H, Sudhakara TL, Kaukonen RJ, Alapieti TT (2007) Petrology, geochemistry, model Sm-Nd ages and petrogenesis of the granitoids of the northern block of Western Dharwar Craton. J Geol Soc India 70:889–911
D’Mello NG, Zellmer GF, Negrini M, Kereszturi G, Procter J, Stewart R, Prior D, Usuki M, Iizuka Y (2021) Deciphering magma storage and ascent processes of Taranaki, New Zealand, from the complexity of amphibole breakdown textures. Lithos 398:106264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2021.106264
Drury SA (1984) A Proterozoic intracratonic basin, dyke swarms and thermal evolution in south India. J Geol Soc India 25:437–444
Drury SA, Holt RW (1980) The tectonic framework of the south Indian Craton, a reconnaissance involving Land sat imagery. Tectonophysics 65:T1–T15
Eriksson PI, Riishuus MS, Sigmundsson F, Elming SA (2011) Magma flow directions inferred from field evidence and magnetic fabric studies of the Streitishvarf composite dike in east Iceland. J Volcanol Geoth Res 206(1–2):30–45
Ernst R, Baragar W (1992) Evidence from magnetic fabric for the flow pattern of magma in the Mackenzie giant radiating dyke swarm. Nature 356:511–513
Ernst RE, Srivastava RK (2008) India’s place in the Proterozoic world: constraints from the Large Igneous Province (LIP) record. In: Srivastava RK, Sivaji CH, Chalapathi Rao NV (eds) Indian dykes. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 41–56
Ernst RE, Head JW, Parfitt E, Grosfils E, Wilson L (1995) Giant radiating dyke swarms on Earth and Venus. Earth Sci Rev 39:1–58
Fenn PM (1986) On the origin of graphic granite. Am Miner 71(3–4):325–330
Fermor LL (1936) An attempt at the correlation of the ancient schistose formations of peninsular India. Mem Geol Sur India 70:1–52
Frost BR, Frost CD (2008) On charnockites. Gondwana Res 13(1):30–44
Ganguli SS, Pal SK, Sundaralingam K (2021) Kumar P (2021) Insights into the crustal architecture from the analysis of gravity and magnetic data across Salem-Attur Shear Zone (SASZ), Southern Granulite Terrane (SGT), India: an evidence of accretional tectonics. Episodes 44:419–442
Geoffroy L, Callot JP, Aubourg C, Moreira M (2002) Magnetic and plagioclase linear fabric discrepancy in dykes: a new way to define the flow vector using magnetic foliation. Terra Nova 14(3):183190
Geshi N, Kusumoto S, Gudmundsson A (2010) The geometric difference between non-feeders and feeders dikes. Geology 38:195–198
Ghosh JG, Wit MJD, Zartman RE (2004) Age and tectonic evolution of Neoproterozoic ductile shear zones in the Southern Granulite Terrain of India, with implications for Gondwana studies. Tectonics 23:297–319
Green D, Neuberg J, Cayol V (2006) Shear stress along the conduit wall as a plausible source of tilt at Soufrière Hills volcano. Montserrat Geophys Res Lett 33:L10306. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL025890
Gudmundsson A (2006) How local stresses control magma-chamber ruptures, dyke injections, and eruptions in composite volcanoes. Earth Sci Rev 79:1–31
Halls HC, Fahrig WF (1987) Mafic dyke swarms. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 34:1–10
Hautmann S, Gottsmann J, Sparks RSJ, Costa A, Melnik O, Voight B (2009) Modelling ground deformation caused by oscillating overpressure in a dyke conduit at Soufrière Hills Volcano. Montserrat Tectonophysics 471(1–2):87–95
Hoek JD (1995) Dyke propagation and arrest in Proterozoic tholeiitic dyke swarms, Vestfold Hills, East Antarctica. In: Baer G, Heimann A (eds) Physics and chemistry of dykes, pp 79–93
Horsman E, Morgan S, de Saint-Blanquat M, Habert G, Nugent A, Hunter RA, Tikoff B (2009) Emplacement and assembly of shallow intrusions from multiple magma pulses, Henry Mountains, Utah. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 100(1–2):117–132
Hoyer L, Watkeys MK (2017) Using magma flow indicators to infer flow dynamics in sills. J Struct Geol 96:161–175
Huppert HE, Sparks RSJ (1989) Chilled margins in igneous rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 92:397–405
Hutton DH (1988) Granite emplacement mechanisms and tectonic controls: inferences from deformation studies. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 79(2–3):245–255
Jain AK, Singh S, Manickavasagam RM (2003) Intracontinental shear zones in the Southern Granulite Terrain: their kinematics and evolution. Memoirs Geological Society of India 50:225–253
Jayabalan M, Umamaheswaran G, Suresh A (2012) Petrology and geochemistry of dolerite dykes of Dharmapuri and Salem Districts of Tamil Nadu. J Appl Geochem 14(1):52–68
Jolly RJH, Sanderson DJ (1997) A Mohr circle construction for the opening of a pre-existing fracture. J Struct Geol 19(6):887–892
Kavanagh JL, Sparks RSJ (2011) Insights of dyke emplacement mechanics from detailed 3d dyke thickness datasets. J Geol Soc 168(4):965–978
Keir D, Pagli C, Bastow ID, Ayele A (2011) The magma-assisted removal of Arabia in Afar: evidence from dike injection in the Ethiopian rift captured using InSAR and seismicity. Tectonics 30(2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010TC002785
Klamadji MN, Dedzo MG, Tchameni R, Dawaï D (2020) Petrography and geochemical characterization of dolerites from Figuil (Northern Cameroon) and Léré (Southwestern Chad). Int J Geosci 11(7):459–482
Maaløe S (1998) Shape of ascending feeder dikes, and ascent modes of magma. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 81(3–4):207–214
McCaffrey KJW, Miller CF, Karlstrom KE (1999) Synmagmatic deformation patterns in the Old Woman Mountains, SE California. J Struct Geol 21:335–349
Miller CF, Watson EB, Harrison TM (1988) Perspectives on the source, segregation and transport of granitoid magmas. Trans R Soc Edinburgh Earth Sci 79:135–156
Mir AR (2022) Proterozoic newer dolerite dyke swarm magmatism in the Singhbhum Craton, Eastern India. In HM Saleh, & AI Hassan (Eds.), Geochemistry and mineral resources. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.104833
Morgan GB, London D (2012) Process of granophyre crystallization in the Long Mountain Granite, Southern Oklahoma. Bulletin 124(7–8):1251–1261
Murthy NGK (1987) Mafic dyke swarms of the Indian Shield. In: Halls HC, Fahrig WF (eds) Mafic dyke swarms. Geol Assoc Canada Spl Paper 34, pp 393–400
Naha K, Srinivasan R (1996) Nature of the Moyar and Bhavani shear zones, with a note on its implications on the tectonics of the southern Indian Precambrian shield. Proc Indian Acad Sci Earth Planet Sci 105:143–189
Neuberg JW, Collinson AS, Mothes PA, Ruiz MC, Aguaiza S (2018) Understanding cyclic seismicity and ground deformation patterns at volcanoes: intriguing lessons from Tungurahua volcano, Ecuador. Earth Planet Sci Lett 482:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.10.050
Niu J, Song TRA (2021) Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano. Nat Commun 12(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25883-y
Okumura S, Kozono T (2017) Silicic lava effusion controlled by the transition from viscous magma flow to friction-controlled flow. Geophys Res Lett 44:3608–3614. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL072875
Okumura S, Nakamura M, Nakano T, Uesugi K, Tsuchiyama A (2010) Shear deformation experiments on vesicular rhyolite: implications for brittle fracturing, degassing, and compaction of magmas in volcanic conduits. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 115:B06201. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006904
Palmer HC, Ernst RE, Buchan KL (2007) Magnetic fabric studies of the Nipissing sill province and Senneterre dykes, Canadian Shield, and implications for emplacement. Can J Earth Sci 44(4):507–528
Paterson SR, Tobisch OT, Vernon RH (1991) Deformation and pluton emplacement during volcanic arc construction in the Foothills Terrane, central Sierra Nevada, California. Tectonophysics 191:89–110
Paterson SR, Fowler TK Jr, Schmidt KL, Yoshinobu AS, Yuan ES, Miller RB (1998) Interpreting magmatic fabric patterns in plutons. Lithos 44(1–2):53–82
Payacán I, Gutiérrez F, Gelman SE, Bachmann O, Parada MÁ (2014) Comparing magnetic and magmatic fabrics to constrain the magma flow record in La Gloria pluton, central Chile. J Struct Geol 69:32–46
Petrelli M, Zellmer GF (2020) Rates and timescales of magma transfer, storage, emplacement, and eruption. Dynamic Magma Evol 1–41https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119521143.ch1
Pivarunas AF, Meert JG, Pandit MK, Sinha A (2019) Paleomagnetism and geochronology of mafic dykes from the Southern Granulite Terrane, India: Expanding the Dharwar craton southward. Tectonophysics 760:4–22
Pons J, Barbey P, Nachit H, Burg JP (2006) Development of igneous layering during growth of Pluton: The Tarcouate Laccolith (Morocco). Tectonophysics 413(3):271–286
Que M, Allen AR (1996) Sericitization of plagioclase in the Rosses Granite Complex, Co. Donegal, Ireland. Mineral Mag 60(403):927–936. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1996.060.403.07
Radhakrishna T, Joseph M (1996) Proterozoic paleomagnetism of mafic dyke swarms in high grade region of south India. Precamb Res 76:31–46
Radhakrishna T, Krishnendu NR, Balasubramonian G (2013) Palaeoproterozoic Indian shield in the global continental assembly: Evidence from the palaeomagnetism of mafic dyke swarms. Earth Sci Rev 126:370–389
Rasmussen J (1978) Schematic 3-D model of a dyke in the Faeroese basalt plateau. Bull Geol Soc 27:79–84
Rusiecka MK, Baker DR (2021) Growth and textural evolution during crystallization of quartz and feldspar in hydrous, rhyolitic melt. Contrib Miner Petrol 176(7):1–15
Rusiecka MK, Bilodeau M, Baker DR (2020) Quantification of nucleation delay in magmatic systems: experimental and theoretical approach. Contrib Miner Petrol 175(5):1–16
Sajid M (2019) Petrography, geochemistry and physico-mechanical properties of dolerite from Oghi (Mansehra), Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J Himalayan Earth Sci 52(2):185–196
Santosh M, Maruyama S, Sato K (2009) Anatomy of a Cambrian suture in Gondwana: Pacific-type orogeny in southern India? Gondwana Res 16(2):321–341
Santosh M, Yang QY, Shaji E, Tsunogae T, Mohan MR, Satyanarayanan M (2015) An exotic Mesoarchean microcontinent: the Coorg Block, southern India. Gondwana Res 27(1):165–195
Santosh M, Yang QY, Shaji E, Ram Mohan M, Tsunogae T, Satyanarayanan M (2016) Oldest rocks from Peninsular India: Evidence for Hadean to Neoarchean crustal evolution. Gondwana Res 29:105–135
Shelley D (1966) The significance of granophyric and myrmekitic textures in the Lundy granites. Mineral Mag J Mineral Soc 35(273):678–692
Silpa AS, Satish Kumar M (2018) Dyke swarms in the Dharwar craton: a key to understanding the Late Archean to Early Proterozoic cratonic correlations. J Indian Inst Sci 98:365–378
Snoke AW, Tullis J, Todd VR (1998) Fault-related rocks: a photographic atlas. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Srivastava RK, Jayananda M, Gautam GC, Gireesh V, Samal AK (2014) Geochemistry of an ENE–WSW to NE–SW trending∼ 2.37 Ga mafic dyke swarm of the eastern Dharwar craton, India: does it represent a single magmatic event? Geochemistry 74(2):251–265
Srivastava RK, Söderlund U, Ernst RE, Mondal SK, Samal AK (2019) Precambrian mafic dyke swarms in the Singhbhum craton (eastern India) and their links with dyke swarms of the eastern Dharwar craton (southern India). Precambrian Res 329:5–17
Srivastava RK, Söderlund U, Ernst RE, Gautam GC (2021) A ca. 2.25 Ga mafic dyke swarm discovered in the Bastar craton, Central India: implications for a widespread plume-generated Large Igneous Province (LIP) in the Indian shield. Precambrian Res 360:106232
Tauxe L, Gee JS, Staudigel H (1998) Flow directions in dikes from anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility data: the bootstrap way. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 103(B8):17775–17790
Tobisch OT, Cruden AR (1995) Fracture-controlled magma conduits in an obliquely convergent continental magmatic arc. Geology 23:941–944
Tobisch OT, Saleeby JB, Fiske RS (1986) Structural history of volcanic arc rocks, eastern Sierra Nevada, California: a case for extensional tectonics. Tectonics 5:65–94
Twiss RJ, Moores EM (1992) Structural geology. W.H. Freeman, New York
Vachon R, Bazargan M, Hieronymus CF, Ronchin E, Almqvist B (2021) Crystal rotations and alignment in spatially varying magma flows: 2-D examples of common subvolcanic flow geometries. Geophys J Int 226(1):709–727
Valdiya KS (1998) Late quaternary movement and land scape rejuvenation in SE Karnataka and adjoining TN in south Indian shield. J Geol Soc India 51:139–166
Valentine GA, Krogh KEC (2006) Emplacement of shallow dikes and sills beneath a small basaltic volcanic centre - the role of pre-existing structure (Paiute Ridge, southern Nevada, U.S.A.). Earth Planet Sci Lett 246(3):217–230
Venkatesh AS, Rao GP, Rao NP, Bhalla MS (1987) Palaeomagnetic and geochemical studies on dolerite dykes from Tamil Nadu, India. Precambr Res 34:291–310
Vernon R (2000) Review of microstructural evidence of magmatic and solid-state flow. Vis Geosci 5:1–23
Vernon RH, Paterson SR (2006) Mesoscopic structures resulting from crystal accumulation and melt movement in granites, Earth Environ. Sci Trans r Soc Edinburgh 97(4):369–381
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Department of Geology, Periyar University, Salem for providing DST-FIST-sponsored laboratory facilities. The corresponding author would like to acknowledge the support and help of the late Venkat Prasath who is not an author but has provided valuable contributions in preparing fieldwork and sample collection. The authors acknowledge the valuable input and comments from Dr. Syed Haroon Ali for improving this work. The authors acknowledge the reviewers for their critical evaluation, valuable suggestions, comments, and constructive review which help the authors to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: François Roure
The original online version of this article was revised: In the original version of this article, the given and family names of “C. Ramachandran, A. Thirunavukkarasu, R. Ravi” were incorrectly structured.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramachandran, C., Thirunavukkarasu, A. & Ravi, R. Wall rock deformation, chilled margin, textural analysis, and displacement structures of Salem dolerites emplaced within the Southern Granulite Terrane, Tamilnadu, India. Arab J Geosci 16, 52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-11144-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-11144-9