Abstract
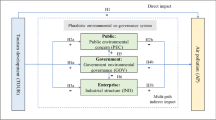
The purpose of this paper is to analyze the diffusion and interaction of air pollutants in different cities, and point out a method to evaluate the efficient correlation between air pollutants in the data of cities and nearby areas, so as to establish the air pollution information of surrounding towns. In addition, this paper analyzes the weather forecast according to the mobile migration and the impact of rural green tourism. Tourism is increasingly becoming a tool for achieving sustainable development, especially from the perspective of poverty reduction. The number of overseas travel receipts increases and can be recognized as the easiest way to reduce poverty. Strategic research aims to use tourism to alleviate poverty a significant amount, but there is little understanding of macro levels of poverty alleviation, especially at different levels of poverty. Mature tourist objections require a consistently expanding assortment of items and markets. To be effective, this system requires a point by point comprehension of the degree of likely sightseers and utilization designs. Experimental examinations on the travel industry burning through the will, in general, utilize standard least-squares relapse for this reason. Most important of this technology, however, is that it is higher, has significant limitations, and is unable to distinguish below average tourists. Intra-digit regression also considers exploration of the overall conditional distribution of a given predictor response variable, thus producing a more comprehensive map of significant predictors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 November 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09132-6
28 September 2021
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08471-8
References
Aptoula E, Ozdemir MC, Yanikoglu B (2016) Deep learning with attribute profiles for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13:1970–1974
Babiker M, Gudmundsson A (2004) The effects of dykes and faults on groundwater flow in an arid land: the Red Sea Hills, Sudan. J Hydrol 297:256–273
Cao X, Chen J, Imura H, Higashi O (2009) A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens Environ 113:2205–2209
Deng Z, Sun H, Zhou S, Zhao J, Lei L, Zou H (2018) Multi-scale object detection in remote sensing imagery with convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 145:3–22
Fauvel M, Tarabalka Y, Bendiktsson JA, Chanussot J, & Tilton J (2013). Advances in spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proceedings of the IEEE, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 101, 652-675
Huang B, Zhao B, Song Y (2018) Urban land-use map** using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens Environ 214:73–86
Li W, Fu H, Yu L, Gong P, Feng D, Li C, Clinton N (2016) Stacked autoencoder-based deep learning for remote-sensing image classification: a case study of African land-cover map**. Int J Remote Sens 37:5632–5646
Li Y, **e W, Li H (2017) Hyperspectral image reconstruction by deep convolutional neural network for classification. Pattern Recogn 63:371–383
Mathur A, Foody GM (2008) Multiclass and binary SVM classification: implications for training and classification users. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 5:241–245
Mou L, Ghamisi P, Zhu XX (2018) Unsupervised Spectral–spatial feature learning via deep residual Conv–Deconv network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56:391–406
Othman E, Bazi Y, Alajlan N, Alhichri H, Melgani F (2016) Using convolutional features and a sparse autoencoder for land-use scene classification. Int J Remote Sens 37:2149–2167
Pacifici F, Chini M, Emery WJ (2009) A neural network approach using multi-scale textural metrics from very high-resolution panchromatic imagery for urban land-use classification. Remote Sens Environ 113:1276–1292
Pal M, Foody GM (2010) Feature selection for classification of hyperspectral data by SVM. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48:2297–2307
Singh PK, Gaur ML, Mishra SK, Rawat SS (2010) An updated hydrological review on recent advancements in soil conservation service-curve number technique. J Water Clim Chang 1(2):118–134
Song X, Fan G, Rao M (2008) SVM-based data editing for enhanced one-class classification of remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 5:189–193
**ng C, Ma L, Yang X (2016) Stacked denoise autoencoder based feature extraction and classification for hyperspectral images. J Sensors 2016:1–10
Yang X, Ye Y, Li X, Lau RYK, Zhang X, Huang X (2018) Hyperspectral image classification with deep learning models. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens:1–16
Zhang P, Gong M, Su L, Liu J, Li Z (2016) Change detection based on deep feature representation and map** transformation for multi-spatial-resolution remote sensing images. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 116:24–41
Acknowledgements
This paper is the production of Scientific research projects in Inner Mongolia colleges and universities in 2021 (project number: NJSY21131), Chifeng University - Scientific Research Serve for the Local Project (project number: cfxyfc201825), and also the production of “East Mongolian Tourism and Cultural Industry Research Innovation Team” of Chifeng University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sheldon Williamson
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Environment and Low Carbon Transportation
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09132-6
About this article
Cite this article
Lili, Z. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Prediction of air pollutants and rural green tourism factors based on dynamic migration. Arab J Geosci 14, 1777 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08061-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08061-8