Abstract
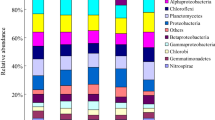
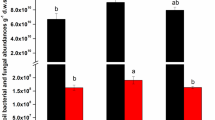
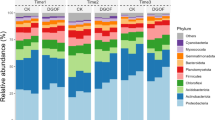
Tobacco-rice rotation is a common farming system in south China, and many tillage practices such as straw mulching, dolomite dust, and quicklime application have been adopted to improve crop production. These agricultural management practices alter soil physical and chemical properties and affect microbial life environment and community composition. In this research, six tillage practices including no tobacco and rice straw mulching (CK), tobacco and rice straw mulching (TrSr), rice straw returning fire (TrSc), tobacco and rice straw mulching with dolomite dust (TSD), rice straw returning fire and quicklime (TSQ), and rice straw returning fire, quicklime and reduced fertilizer (TSQf) were conducted to detect changes in soil bacterial diversity and composition using Illumina sequencing. The results showed that the total number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) from the six treatments was 2030, and the number of mutual OTUs among all samples was 550. The TrSc treatment had the highest diversity and richness, while TSQf had the lowest. Soil physio-chemical properties and microbial diversity can influence each other. Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria had the greatest proportion in all treatments. The abundance of Nitrospirae was the highest in the TrSc treatment. The TSQf treatment had the highest abundance of Firmicutes. The abundance of Nitrospira in the TrSc treatment was 2.29-fold over CK. Streptomyces affiliated with Firmicutes improved by 37.33% in TSQf compared to TSQ. TSQf treatment was considered to be the most important factor in determining the relative abundance at the genus level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asiloglu, R., Honjo, H., Saka, N., Asakawa, S., and Murase, J. 2015. Community structure of microeukaryotes in a rice rhizosphere revealed by DNA-based PCR-DGGE. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 61, 761–768.
Bapteste, É., Brochier, C., and Boucher, Y. 2005. Higher-level classification of the Archaea: evolution of methanogenesis and methanogens. Archaea 1, 353–363.
Bastida, F., Zsolnay, A., Hernández, T., and García, C. 2008. Past, present and future of soil quality indices: a biological perspective. Geoderma 147, 159–171.
Beales, N. 2004. Adaptation of microorganisms to cold temperatures, weak acid preservatives, low pH, and osmotic stress: a review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 3, 1–20.
Bergmann, G.T., Bates, S.T., Eilers, K.G., Lauber, C.L., Caporaso, J.G., Walters, W.A., Knight, R., and Fierer, N. 2011. The under-recognized dominance of Verrucomicrobia in soil bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 1450–1455.
Bumunang, E.W., Jordaan, K., Barros, E., Bezuidenhout, C., and Babalola, O.O. 2015. Analysis of rhizobacterial community in field grown GM and non-GM maize soil samples using PCR-DGGE. J. Agricul. Technol. 11, 1109–1117.
Cappa, F., Suciu, N., Trevisan, M., Ferrari, S., Puglisi, E., and Cocconcelli, P.S. 2014. Bacterial diversity in a contaminated Alpine glacier as determined by culture-based and molecular approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 497, 50–59.
Chang, E.H., Chen, T.H., Tian, G., and Chiu, C.Y. 2016. The effect of altitudinal gradient on soil microbial community activity and structure in moso bamboo plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 98, 213–220.
Chen, J., Liu, X., Zheng, J., Zhang, B., Lu, H., Chi, Z., Pan, G., Li, L., Zheng, J., and Zhang, X. 2013. Biochar soil amendment increased bacterial but decreased fungal gene abundance with shifts in community structure in a slightly acid rice paddy from Southwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 71, 33–44.
Da Cheng Hao, S.M.S., Mu, J., Hu, W.L., and **ao, P.G. 2016. Unearthing microbial diversity of Taxus rhizosphere via MiSeq highthroughput amplicon sequencing and isolate characterization. Sci. Reports 6, 22006.
Dilworth, M., Howieson, J., Reeve, W., Tiwari, R., and Glenn, A. 2001. Acid tolerance in legume root nodule bacteria and selecting for it. Ani. Prod. Sci. 41, 435–446.
Dorr de Quadros, P., Zhalnina, K., Davis-Richardson, A., Fagen, J.R., Drew, J., Bayer, C., Camargo, F.A., and Triplett, E.W. 2012. The effect of tillage system and crop rotation on soil microbial diversity and composition in a subtropical acrisol. Diversity 4, 375–395.
Drenovsky, R.E., Elliott, G.N., Graham, K.J., and Scow, K.M. 2004. Comparison of phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) and total soil fatty acid methyl esters (TSFAME) for characterizing soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 36, 1793–1800.
Edgar, R.C., Haas, B.J., Clemente, J.C., Quince, C., and Knight, R. 2011. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27, 2194–2200.
Faccin, G.L., Miotto, L.A., do Nascimento Vieira, L., Barreto, P.L.M., and Amante, E.R. 2009. Chemical, sensorial and rheological properties of a new organic rice bran beverage. Rice Science 16, 226–234.
Fierer, N., Bradford, M.A., and Jackson, R.B. 2007. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88, 1354–1364.
Fierer, N., Lauber, C.L., Ramirez, K.S., Zaneveld, J., Bradford, M.A., and Knight, R. 2012. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 6, 1007–1017.
Gribaldo, S. and Brochier-Armanet, C. 2006. The origin and evolution of Archaea: a state of the art. Philos. Trans R Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 361, 1007–1022.
Haynes, R. 2005. Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: an overview. Adv. Agron. 85, 221–268.
Hirsch, P.R., Mauchline, T.H., and Clark, I.M. 2010. Culture-independent molecular techniques for soil microbial ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42, 878–887.
Janssen, P.H. 2006. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 1719–1728.
Kemmitt, S., Lanyon, C., Waite, I., Wen, Q., Addiscott, T., Bird, N.R., O’donnell, A., and Brookes, P. 2008. Mineralization of native soil organic matter is not regulated by the size, activity or composition of the soil microbial biomass–a new perspective. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40, 61–73.
Kolton, M., Harel, Y.M., Pasternak, Z., Graber, E.R., Elad, Y., and Cytryn, E. 2011. Impact of biochar application to soil on the rootassociated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 4924–4930.
Lauber, C.L., Strickland, M.S., Bradford, M.A., and Fierer, N. 2008. The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40, 2407–2415.
Lehmann, J., Rillig, M.C., Thies, J., Masiello, C.A., Hockaday, W.C., and Crowley, D. 2011. Biochar effects on soil biota–a review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 1812–1836.
Li, W. and Godzik, A. 2006. Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22, 1658–1659.
Li, J., Lu, J., Li, X., Ren, T., Cong, R., and Zhou, L. 2014. Dynamics of potassium release and adsorption on rice straw residue. PLoS One 9, e90440.
Liao, Y., Zheng, S., Jun, N., Jian, X., Lu, Y., and Qin, X. 2013. Longterm effect of fertilizer and rice straw on mineral composition and potassium adsorption in a reddish paddy soil. J. Integr. Agr. 12, 694–710.
Lu, R. 1999. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method. Chinese Agriculture and Sciences Press, Bei**g, P.R. China.
Lu, P., Lin, Y.H., Yang, Z.Q., Xu, Y.P., Tan, F., Jia, X.D., Wang, M., Xu, D.R., and Wang, X.Z. 2015. Effects of application of corn straw on soil microbial community structure during the maize growing season. J. Basic Microbiol. 55, 22–32.
Ma, J., Wang, Z., Yang, Y., Mei, X., and Wu, Z. 2013. Correlating microbial community structure and composition with aeration intensity in submerged membrane bioreactors by 454 high-throughput pyrosequencing. Water Res. 47, 859–869.
Marschner, P., Kandeler, E., and Marschner, B. 2003. Structure and function of the soil microbial community in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 35, 453–461.
Pan, F., Li, Y., Chapman, S.J., and Yao, H. 2015. Effect of rice straw application on microbial community and activity in paddy soil under different water status. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 5941–5948.
Ramirez, K.S., Craine, J.M., and Fierer, N. 2012. Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Global Change Biol. 18, 1918–1927.
Ramirez, K.S., Lauber, C.L., Knight, R., Bradford, M.A., and Fierer, N. 2010. Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in contrasting systems. Ecology 91, 3463–3470.
Reali, V. and Fiuza, L. 2012. Ecology of Bacillus sp. and Lysinibacillus sp. in rice field soils from Southern Brazil, pp. 89–93. Microbes in Applied Research, World Scientific.
Rivero, C., Chirenje, T., Ma, L., and Martinez, G. 2004. Influence of compost on soil organic matter quality under tropical conditions. Geoderma 123, 355–361.
Roesch, L.F., Fulthorpe, R.R., Riva, A., Casella, G., Hadwin, A.K., Kent, A.D., Daroub, S.H., Camargo, F.A., Farmerie, W.G., and Triplett, E.W. 2007. Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J. 1, 283–290.
Schloss, P.D., Westcott, S.L., Ryabin, T., Hall, J.R., Hartmann, M., Hollister, E.B., Lesniewski, R.A., Oakley, B.B., Parks, D.H., and Robinson, C.J. 2009. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 7537–7541.
Sessitsch, A., Hardoim, P., Dö ring, J., Weilharter, A., Krause, A., Woyke, T., Mitter, B., Hauberg-Lotte, L., Friedrich, F., and Rahalkar, M. 2012. Functional characteristics of an endophyte community colonizing rice roots as revealed by metagenomic analysis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 25, 28–36.
Sinclair, L., Osman, O.A., Bertilsson, S., and Eiler, A. 2015. Microbial community composition and diversity via 16S rRNA gene amplicons: evaluating the Illumina platform. PLoS One 10, e0116955.
Tang, Y., Lian, B., Dong, H., Liu, D., and Hou, W. 2012. Endolithic bacterial communities in dolomite and limestone rocks from the Nanjiang Canyon in Guizhou karst area (China). Geomicrobiol. J. 29, 213–225.
Wang, Q., Garrity, G.M., Tiedje, J.M., and Cole, J.R. 2007. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5261–5267.
Wang, Y., Sheng, H.F., He, Y., Wu, J.Y., Jiang, Y.X., Tam, N.F.Y., and Zhou, H.W. 2012. Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 8264–8271.
Weber, S., Stubner, S., and Conrad, R. 2001. Bacterial populations colonizing and degrading rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 1318–1327.
**ong, X., Frank, D.N., Robertson, C.E., Hung, S.S., Markle, J., Canty, A.J., McCoy, K.D., Macpherson, A.J., Poussier, P., and Danska, J.S. 2012. Generation and analysis of a mouse intestinal metatranscriptome through Illumina based RNA-sequencing. PLoS One 7, e36009.
Zhang, X., Qu, Y., Ma, Q., Zhang, Z., Li, D., Wang, J., Shen, W., Shen, E., and Zhou, J. 2015. Illumina MiSeq sequencing reveals diverse microbial communities of activated sludge systems stimulated by different aromatics for indigo biosynthesis from indole. PLoS One 10, e0125732.
Zhao, S., Li, K., Zhou, W., Qiu, S., Huang, S., and He, P. 2016. Changes in soil microbial community, enzyme activities and organic matter fractions under long-term straw return in north-central China. Agricul. Ecosyst. Environ. 216, 82–88.
Zhong, W., Gu, T., Wang, W., Zhang, B., Lin, X., Huang, Q., and Shen, W. 2010. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 326, 511–522.