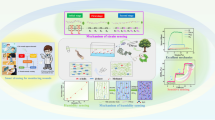
Abstract
Facing the ubiquitous corrosion threat, the great significance of develo** high-performance protective materials with the dual function of self-healing defects and self-warning damage is extremely challenging. Herein, inspired by the biological skin and pearls, we proposed that the biological polyurethanes (PU) embedded with multiple dynamic bonds (reversible hydrogen bonds and aromatic disulfide bonds) were combined with polydopamine (PDA)/1,10-phenanthroline (Phen)/graphene oxide (GO) (PPG) nanosheets (PDA encapsulated GO with Phen) to obtain a versatile nacre structure polymer with the interface hydrogen bond between PPG and PU matrix. The biomimetic polymer not only guarantees ultrahigh toughness (116.1 MJ·m−3) and abnormal elongation (2320%) but shows satisfactory repair performance (81% under 25 °C for 3 h), and the coating can accelerate damage recovery (87%) under near-infrared light (NIR) irradiation for 1 h due to the photothermal properties of PPG. The warning of damages in the coating can be enabled through the Phen chelation Fe2+ ions that bring in the corrosion reaction to produce a conspicuous red color, thereby achieving the active warning function of the bionic coating on defects for the first time. In addition, the electrochemical tests exhibit that the repair performance and protection effect of the biomimetic coating in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution are also trustworthy, and this highly reliable bio-based bionic coating brings a revolutionary program to inaugurate multifunctional and high-performance intelligent materials under harsh environments.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Q.; Zhang, X. D.; Ben, S.; Zhao, Z. H.; Ning, Y. Z.; Liu, K. S.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired superhydrophobic magnesium alloy surfaces with active anti-corrosion and self-healing properties. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 3312–3319.
Liu, C. B.; Wu, H.; Qiang, Y. J.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Design of smart protective coatings with autonomous self-healing and early corrosion reporting properties. Corros. Sci. 2021, 184, 109355.
Yimyai, T.; Thiramanas, R.; Phakkeeree, T.; Iamsaard, S.; Crespy, D. Adaptive coatings with anticorrosion and antibiofouling properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102568.
Akbarzadeh, S.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Bahlakeh, G. A green assisted route for the fabrication of a high-efficiency self-healing anti-corrosion coating through graphene oxide nanoplatform reduction by Tamarindus indiaca extract. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122147.
Cho, S. H.; White, S. R.; Braun, P. V. Self-healing polymer coatings. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 645–649.
Wu, H.; Li, J. W.; Zhang, W. Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, F. C.; Han, E. H. Supramolecular engineering of nacre-inspired bio-based nanocomposite coatings with exceptional ductility and high-efficient self-repair ability. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135405.
Zhu, X. B.; Zheng, W. R.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Non-covalent assembly of a super-tough, highly stretchable and environmentally adaptable self-healing material inspired by nacre. J. Mate. Chem. A 2021, 9, 20737–20747.
Wang, J.; Zhang, X. W.; Zhang, S.; Kang, J. Y.; Guo, Z. C.; Feng, B. Y.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Z.; Yu, J.; Song, W. L. et al. Semi-convertible hydrogel enabled photoresponsive lubrication. Matter 2021, 4, 675–687.
Yoshida, S.; Ejima, H.; Yoshie, N. Tough elastomers with superior self-recoverability induced by bioinspired multiphase design. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1701670.
Feng, H. M.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Hou, J.; Chen, S. G. Preparation of dynamic polyurethane networks with UV-triggered photothermal self-healing properties based on hydrogen and ion bonds for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 89–101.
Qu, Q. Q.; He, J.; Da, Y. S.; Zhu, M. H.; Liu, Y. Y.; Li, X. X.; Tian, X. Y.; Wang, H. High toughness polyurethane toward artificial muscles, tuned by mixing dynamic hard domains. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 8243–8254.
Yao, W. J.; Tian, Q. Y.; Shi, J. Q.; Luo, C. S.; Wu, W. Printable, down/up-conversion triple-mode fluorescence responsive and colorless self-healing elastomers with superior toughness. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100211.
Nellepalli, P.; Patel, T.; Oh, J. K. Dynamic covalent polyurethane network materials: Synthesis and self-healability. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100391.
Wang, J. W.; Zheng, Y. P.; Qiu, S. L.; Song, L. Ethanol inducing self-assembly of poly-(thioctic acid)/graphene supramolecular ionomers for healable, flame-retardant, shape-memory electronic devices. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 908–915.
Patrick, J. F.; Robb, M. J.; Sottos, N. R.; Moore, J. S.; White, S. R. Polymers with autonomous life-cycle control. Nature 2016, 540, 363–370.
Kang, S.; Qiao, S. Y.; Cao, Y. T.; Hu, Z. M.; Li, N.; Yu, J. R.; Wang, Y. Multifunctional tubular carbon nanofibers/polyurethane electromagnetic wave absorber with room-temperature self-healing and recyclable performance. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 33–44.
Chen, K.; Ding, J.; Li, L. D.; Shang, G. Y.; Yue, Y. H.; Guo, L. Amorphous alumina nanosheets/polylactic acid artificial nacre. Matter 2019, 1, 1385–1398.
Ghazlan, A.; Ngo, T.; Tan, P.; **e, Y. M.; Tran, P.; Donough, M. Inspiration from nature’s body armours—A review of biological and bioinspired composites. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2021, 205, 108513.
Zhang, Y. Y.; Peng, J. S.; Li, M. Z.; Saiz, E.; Wolf, S. E.; Cheng, Q. F. Bioinspired supertough graphene fiber through sequential interfacial interactions. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8901–8908.
Diesendruck, C. E.; Sottos, N. R.; Moore, J. S.; White, S. R. Biomimetic self-healing. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10428–10447.
Gong, S. S.; Ni, H.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, Q. F. Learning from nature: Constructing high performance graphene-based nanocomposites. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 210–219.
Huang, C. J.; Peng, J. S.; Wan, S. J.; Du, Y.; Dou, S. X.; Wagner, H. D.; Tomsia, A. P.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, Q. F. Ultra-tough inverse artificial nacre based on epoxy-graphene by freeze-casting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7636–7640.
Restrepo, V.; Martinez, R. V. Bioinspired fabrication of reconfigurable elastomeric cementitious structures using self-healing mechanical adhesives interfaces. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109691.
Zhang, K. R.; Gao, H. L.; Pan, X. F.; Zhou, P.; **ng, X.; Xu, R.; Pan, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y. M.; Hu, B. et al. Multifunctional bilayer nanocomposite guided bone regeneration membrane. Matter 2019, 1, 770–781.
Owuor, P. S.; Tsafack, T.; Schara, S.; Hwang, H.; Jung, S.; Salvatierra, R. V.; Li, T.; Susarla, S.; Ren, M. Q.; Wei, B. Q. et al. Achieving self-stiffening and laser healing by interconnecting graphene oxide sheets with amine-functionalized ovalbumin. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800932.
Wang, J. W.; Zheng, Y. P.; Ren, W.; Ang, E. H.; Song, L.; Zhu, J. X.; Hu, Y. Intrinsic ionic confinement dynamic engineering of ionomers with low dielectric-k, high healing and stretchability for electronic device reconfiguration. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139837.
Yanagisawa, Y.; Nan, Y. L.; Okuro, K.; Aida, T. Mechanically robust, readily repairable polymers via tailored noncovalent cross-linking. Science 2018, 359, 72–76.
Kushner, A. M.; Guan, Z. B. Modular design in natural and biomimetic soft materials. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9026–9057.
Kong, W. B.; Yang, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. J.; Cheng, H. F.; Yan, P. Y.; Huang, L.; Ning, J. Y.; Zeng, F. H.; Cai, X. F.; Wang, M. An ultralow hysteresis, self-healing and stretchable conductor based on dynamic disulfide covalent adaptable networks. J. Mate. Chem. A 2022, 10, 2012–2020.
Fu, X.; Tian, L.; Fan, Y.; Ye, W.; Qiao, Z. A.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L.; Ming, W. Stimuli-responsive self-healing anticorrosion coatings: From single triggering behavior to synergetic multiple protections. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100575.
Qiu, Z. J.; Zhao, W. J.; Cao, M. K.; Wang, Y. Q.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, B. Z. Dynamic visualization of stress/strain distribution and fatigue crack propagation by an organic mechanoresponsive AIE luminogen. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803924.
Liu, C. B.; **, Z. Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Synthesis of nanosensors for autonomous warning of damage and self-repairing in polymeric coatings. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 3194–3204.
Wang, J. K.; Ma, L. W.; Guo, X.; Wu, S. H.; Liu, T.; Yang, J. Z.; Ren, C. H.; Li, S. S.; Zhang, D. W. Two birds with one stone: Nanocontainers with synergetic inhibition and corrosion sensing abilities towards intelligent self-healing and self-reporting coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134515.
Liu, T.; Zhang, D. W.; Ma, L. W.; Huang, Y.; Hao, X. P.; Terryn, H.; Mol, A.; Li, X. G. Smart protective coatings with self-sensing and active corrosion protection dual functionality from pH-sensitive calcium carbonate microcontainers. Corros. Sci. 2022, 200, 110254.
Cao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, Q. Y.; Chen, S. G. Synthesis of smart nanofiber coatings with autonomous self-warning and self-healing functions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 27168–27176.
Li, W. L.; Matthews, C. C.; Yang, K.; Odarczenko, M. T.; White, S. R.; Sottos, N. R. Autonomous indication of mechanical damage in polymeric coatings. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2189–2194.
Cheng, L.; Liu, C. B.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Photothermal-triggered shape memory coatings with active repairing and corrosion sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 22509–22521.
Liu, C. B.; Cheng, L.; Qian, B.; Cui, L. Y.; Zeng, R. C. Corrosion self-warning and repair tracking of polymeric coatings based on stimulus responsive nanosensors. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 8429–8440.
Patel, C. J.; Mannari, V. Air-drying bio-based polyurethane dispersion from cardanol: Synthesis and characterization of coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 997–1006.
Bhunia, H. P.; Nando, G. B.; Chaki, T. K.; Basak, A.; Lenka, S.; Nayak, P. L. Synthesis and characterization of polymers from cashewnut shell liquid (CNSL), a renewable resource II. Synthesis of polyurethanes. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 1381–1391.
Wu, H.; Cheng, L.; Liu, C. B.; Lan, X. J.; Zhao, H. C. Engineering the interface in graphene oxide/epoxy composites using bio-based epoxy-graphene oxide nanomaterial to achieve superior anticorrosion performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 755–766.
Zhou, S. F.; Yan, J.; Chen, J. L.; Yan, H. M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, G. Z.; Zhang, Q. X.; Liu, Y. Q. Polydopamine/polyethyleneimine co-crosslinked graphene oxide for the enhanced tribological performance of epoxy resin coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 13–20.
Müeller, M.; Keßler, B. Deposition from dopamine solutions at Ge substrates: An in situ ATR-FTIR study. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12499–12505.
Lee, W.; Lee, J. U.; Jung, B. M.; Byun, J. H.; Yi, J. W.; Lee, S. B.; Kim, B. S. Simultaneous enhancement of mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of graphene oxide paper by embedding dopamine. Carbon 2013, 65, 296–304.
Zheng, C.; Ren, H. J.; Cui, Z. F.; Chen, F. H.; Hong, G. Y. Synthesis and characterization of nano-scale Terbium(III)-trimesic acid (TMA)-1, 10-phenanthroline(phen) luminescent complex. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 333–336.
Davoodian, N.; Nakhaei Pour, A.; Izadyar, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Salimi, A.; Kamali Shahri, S. M. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-7 and ZIF-8)-supported cobalt catalysts. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5747.
Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Polydopamine modified ultrathin hydroxyapatite nanosheets for anti-corrosion reinforcement in polymeric coatings. Corros. Sci. 2021, 178, 109064.
Rella, S.; Mazzotta, E.; Caroli, A.; De Luca, M.; Bucci, C.; Malitesta, C. Investigation of polydopamine coatings by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy as an effective tool for improving biomolecule conjugation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 31–39.
Cheng, L.; Liu, C. B.; Wu, H.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. A two-dimensional nanocontainer based on mesoporous polydopamine coated lamellar hydroxyapatite towards anticorrosion reinforcement of waterborne epoxy coatings. Corros. Sci. 2021, 193, 109891.
Zangmeister, R. A.; Morris, T. A.; Tarlov, M. J. Characterization of polydopamine thin films deposited at short times by autoxidation of dopamine. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8619–8628.
Tong, Z. M.; Song, L. N.; Chen, S. F.; Hu, J. K.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Y. Y.; Zhan, X. L.; Zhang, Q. H. Hagfish-inspired smart SLIPS marine antifouling coating based on supramolecular: Lubrication modes responsively switching and self-healing properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201290.
Xun, X. C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Ouyang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. Tough and degradable self-healing elastomer from synergistic soft-hard segments design for biomechano-robust artificial skin. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20656–20665.
Nawaz, H.; Tian, W. G.; Zhang, J. M.; Jia, R. N.; Chen, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. Cellulose-based sensor containing phenanthroline for the highly selective and rapid detection of Fe2+ ions with naked eye and fluorescent dual modes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2114–2121.
Rehman, H. U.; Chen, Y. J.; Hedenqvist, M. S.; Li, H.; Xue, W. C.; Guo, Y. L.; Guo, Y. P.; Duan, H. N.; Liu, H. Z. Self-healing shape memory PUPCL copolymer with high cycle life. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704109.
Chen, Y. L.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Q. F.; Pan, F.; Cui, C. J.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Liu, B. Advances in mechanics of hierarchical composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 214, 108970.
Min, Y. J.; Kang, K. H.; Kim, D. E. Development of polyimide films reinforced with boron nitride and boron nitride nanosheets for transparent flexible device applications. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2366–2378.
Wang, D.; Ren, S. Y.; Chen, J. Y.; Li, Y. K.; Wang, Z. F.; Xu, J. H.; Jia, X.; Fu, J. J. Healable, highly thermal conductive, flexible polymer composite with excellent mechanical properties and multiple functionalities. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133163.
Kim, S. M.; Jeon, H.; Shin, S. H.; Park, S. A.; Jegal, J.; Hwang, S. Y.; Oh, D. X.; Park, J. Superior toughness and fast self-healing at room temperature engineered by transparent elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705145.
Liu, M. C.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z. J.; Rong, J. C.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. Y.; Shen, L.; Gao, F.; Huang, X. L.; He, H. F. A high stiffness and self-healable polyurethane based on disulfide bonds and hydrogen bonding. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 124, 109475.
Miwa, Y.; Kurachi, J.; Kohbara, Y.; Kutsumizu, S. Dynamic ionic crosslinks enable high strength and ultrastretchability in a single elastomer. Commun. Chem. 2018, 1, 5.
Xu, J.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhang, X. R.; Zhang, Y. M.; Yang, Z. H.; Li, S.; Tao, L. M.; Wang, Q. H.; Wang, T. M. Room-temperature self-healing supramolecular polyurethanes based on the synergistic strengthening of biomimetic hierarchical hydrogen-bonding interactions and coordination bonds. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138673.
Hœrlé, S.; Mazaudier, F.; Dillmann, Santarini, G. Advances in understanding atmospheric corrosion of iron. II. Mechanistic modelling of wet-dry cycles. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1431–1465.
Zhu, X. B.; Yan, Q. Q.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, H. C.; Wang, L. P. Self-alignment of cationic graphene oxide nanosheets for anticorrosive reinforcement of epoxy coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124435.
Ding, J. H.; Zhao, H. R.; Zhou, M.; Liu, P. L.; Yu, H. B. Super-anticorrosive inverse nacre-like graphene-epoxy composite coating. Carbon 2021, 181, 204–211.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the LingChuang Research Project of China National Nuclear Corporation (No. E041F212Z1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5544_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
The biomimetic design provides efficient self-healing of ultrahightough and damage-warning bio-based elastomer for protective clothing of metals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Zhu, Z., Gao, N. et al. The biomimetic design provides efficient self-healing of ultrahigh-tough and damage-warning bio-based elastomer for protective clothing of metals. Nano Res. 16, 10587–10596 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5544-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5544-y