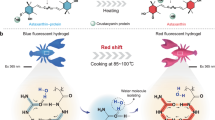
Abstract
Fluorescent hydrogels with fast and reversible responses have attracted extensive attention, and it remains a challenge to design multistimuli-responsive fluorescent hydrogel through a facile and versatile method. Meanwhile, the segmental motion in hydrogels is of significance for the various functions of hydrogels such as chemical reactivity, self-healing, and mechanical strength, etc., however, it is difficult and complicated to in situ investigate the segmental motion under different conditions. In this work, a multistimuli-responsive fluorescent hydrogel was designed and fabricated by introducing a tetraphenylethylene (TPE) derivative as a nonaggregated crosslinker in the gel network. Since the intermolecular rotation of TPE at the crosslinking point was directly integrated with the dynamic conformational transition of the macromolecular network, the mobility of macromolecular segments can be monitored by the fluorescence intensity of the hydrogel. The prepared hydrogel has promising fluorescence responses to temperature, pH, metal ions, and hydrogen bonding agents, and characterization of the fluorescence and the chain segmental motion showed that the weaker the mobility of the network macromolecular chain is, the stronger the fluorescence intensity is. Furthermore, due to the multistimuli-responsive fluorescence of the hydrogel, such fluorescent hydrogels can be designed as reversible patterning displays and biomimetic color/shape adjustable actuators, with various potential applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei, S. X.; Li, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. W.; Chen, T.; Tang, B. Z. Multicolor fluorescent polymeric hydrogels. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8608–8624.
Li, Z.; Ji, X. F.; **e, H. L.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregation-induced emission-active gels: Fabrications, functions, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100021.
Yang, C. H.; Suo, Z. G. Hydrogel ionotronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 125–142.
Zhao, X. H.; Chen, X. Y.; Yuk, H.; Lin, S. T.; Liu, X. Y.; Parada, G. Soft materials by design: Unconventional polymer networks give extreme properties. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4309–4372.
Yang, J.; Li, K.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z. Z.; Fan, J. H.; Qin, G.; Cui, W.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Q. Recent progress in double network elastomers: One plus one is greater than two. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110244.
Weng, G. S.; Thanneeru, S.; He, J. Dynamic coordination of Euiminodiacetate to control fluorochromic response of polymer hydrogels to multistimuli. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706526.
Deng, J. W.; Wu, H. R.; **e, W. D.; Jia, H. Y.; **a, Z. G.; Wang, H. L. Metal cation-responsive and excitation-dependent nontraditional multicolor fluorescent hydrogels for multidimensional information encryption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 39967–39975.
Hai, J.; Li, T. R.; Su, J. X.; Liu, W. S.; Ju, Y. M.; Wang, B. D.; Hou, Y. L. Reversible response of luminescent terbium(III)-nanocellulose hydrogels to anions for latent fingerprint detection and encryption. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6786–6790.
Li, M.; Li, W. J.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X. J.; Wang, Z. H.; Street, J.; Ong, W. J.; **a, Z. H.; Xu, Q. A self-healing hydrogel with pressure sensitive photoluminescence for remote force measurement and healing assessment. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 703–710.
Zhu, Q. D.; van Vliet, K.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Miserez, A. A double-layer mechanochromic hydrogel with multidirectional force sensing and encryption capability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808191.
Ji, X. F.; Wu, R. T.; Long, L. L.; Ke, X. S.; Guo, C. X.; Ghang, Y. J.; Lynch, V. M.; Huang, F. H.; Sessler, J. L. Encoding, reading, and transforming information using multifluorescent supramolecular polymeric hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705480.
Le, X. X.; Shang, H.; Yan, H. Z.; Zhang, J. W.; Lu, W.; Liu, M. J.; Wang, L. P.; Lu, G. M.; Xue, Q. J.; Chen, T. A urease-containing fluorescent hydrogel for transient information storage. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3640–3646.
Li, Z. Q.; Chen, H. Z.; Li, B.; **e, Y. M.; Gong, X. L.; Liu, X.; Li, H. R.; Zhao, Y. L. Photoresponsive luminescent polymeric hydrogels for reversible information encryption and decryption. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901529.
Zhu, C. N.; Bai, T. W.; Wang, H.; Ling, J.; Huang, F. H.; Hong, W.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z. L. Dual-encryption in a shape-memory hydrogel with tunable fluorescence and reconfigurable architecture. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102023.
Liu, J. Z.; Guo, Q. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Gai, J. G.; Zhang, C. H. Multistage responsive materials for real-time, reversible, and sustainable light-writing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106673.
Yao, Y.; Yin, C. Z.; Hong, S. K.; Chen, H. H.; Shi, Q. K.; Wang, J.; Lu, X. Y.; Zhou, N. J. Lanthanide-ion-coordinated supramolecular hydrogel inks for 3D printed full-color luminescence and opacitytuning soft actuators. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8868–8876.
Lan, R. C.; Gao, Y. Z.; Shen, C.; Huang, R.; Bao, J. Y.; Zhang, Z. P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Y.; Yang, H. Humidity-responsive liquid crystalline network actuator showing synergistic fluorescence color change enabled by aggregation induced emission luminogen. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010578.
Zhu, C. N.; Bai, T. W.; Wang, H.; Bai, W.; Ling, J.; Sun, J. Z.; Huang, F. H.; Wu, Z. L.; Zheng, Q. Single chromophore-based white-light-emitting hydrogel with tunable fluorescence and patternability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39343–39352.
Li, Z. Q.; Wang, G. N.; Wang, Y. G.; Li, H. R. Reversible phase transition of robust luminescent hybrid hydrogels. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 2216–2220.
Wei, S. X.; Lu, W.; Le, X. X.; Ma, C. X.; Lin, H.; Wu, B. Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Theato, P.; Chen, T. Bioinspired synergistic fluorescence-color-switchable polymeric hydrogel actuators. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 16389–16397.
Zhang, Y. C.; Le, X. X.; Jian, Y. K.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J. W.; Chen, T. 3D fluorescent hydrogel origami for multistage data security protection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905514.
Wei, S. X.; Qiu, H. Y.; Shi, H. H.; Lu, W.; Liu, H.; Yan, H. Z.; Zhang, D. C.; Zhang, J. W.; Theato, P.; Wei, Y. et al. Promotion of color-changing luminescent hydrogels from thermo to electrical responsiveness toward biomimetic skin applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 10415–10427.
Le, X. X.; Shang, H.; Wu, S. S.; Zhang, J. W.; Liu, M. J.; Zheng, Y. F.; Chen, T. Heterogeneous fluorescent organohydrogel enables dynamic anti-counterfeiting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2108365.
Ma, C. X.; Lu, W.; Yang, X. X.; He, J.; Le, X. X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. W.; Serpe, M. J.; Huang, Y. J.; Chen, T. Bioinspired anisotropic hydrogel actuators with on-off switchable and color-tunable fluorescence behaviors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704568.
Wang, Z. J.; Jiang, J. L.; Mu, Q. F.; Maeda, S.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J. P. Azo-crosslinked double-network hydrogels enabling highly efficient mechanoradical generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3154–3161.
He, G. X.; Lei, H.; Sun, W. X.; Gu, J.; Yu, W. T.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H. Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, M.; Xue, B. et al. Strong and reversible covalent double network hydrogel based on force-coupled enzymatic reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201765.
Cui, W.; Zhu, R. J.; Zheng, Y.; Mu, Q. F.; Pi, M. H.; Chen, Q.; Ran, R. Transforming non-adhesive hydrogels to reversible tough adhesives via mixed-solvent-induced phase separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 9706–9718.
Dai, X. Y.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Gao, L. N.; Bai, T.; Wang, W.; Cui, Y. L.; Liu, W. G. A mechanically strong, highly stable, thermoplastic, and self-healable supramolecular polymer hydrogel. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3566–3571.
Xu, J. J.; Wang, G. Y.; Wu, Y. F.; Ren, X. Y.; Gao, G. H. Ultrastretchable wearable strain and pressure sensors based on adhesive, tough, and self-healing hydrogels for human motion monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25613–25623.
Takahashi, R.; Ikai, T.; Kurokawa, T.; King, D. R.; Gong, J. P. Double network hydrogels based on semi-rigid polyelectrolyte physical networks. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6347–6354.
Liu, C.; Morimoto, N.; Jiang, L.; Kawahara, S.; Noritomi, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Mayumi, K.; Ito, K. Tough hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement. Science 2021, 372, 1078–1081.
Desando, M. A.; Lahajnar, G.; Sepe, A. Proton magnetic relaxation and the aggregation of n-octylammonium n-octadecanoate surfactant in deuterochloroform solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 338–345.
Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Duan, L. J.; Gao, G. H. Nucleotide-driven skin-attachable hydrogels toward visual human-machine interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 4515–4523.
Shi, L. Y.; Carstensen, H.; Hölzl, K.; Lunzer, M.; Li, H.; Hilborn, J.; Ovsianikov, A.; Ossipov, D. A. Dynamic coordination chemistry enables free directional printing of biopolymer hydrogel. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5816–5823.
Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregation-induced emission: New vistas at the aggregate level. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9888–9907.
Li, J.; Wang, J. X.; Li, H. X.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Supramolecular materials based on AIE luminogens (AIEgens): Construction and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1144–1172.
Li, B. T.; Zhang, Y. C.; Wang, J.; Yan, B.; Liang, J. D.; Dong, Y. P.; Zhou, Q. Fast and reversibly humidity-responsive fluorescence based on AIEgen proton transfer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49119–49127.
Liu, H.; Wei, S. X.; Qiu, H. Y.; Zhan, B. B.; Liu, Q. Q.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J. W.; Ngai, T.; Chen, T. Naphthalimide-based aggregation-induced emissive polymeric hydrogels for fluorescent pattern switch and biomimetic actuators. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000123.
Hu, Y. B.; Barbier, L.; Li, Z.; Ji, X. F.; Le Blay, H.; Hourdet, D.; Sanson, N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Marcellan, A.; Tang, B. Z. Hydrophilicity-hydrophobicity transformation, thermoresponsive morphomechanics, and crack multifurcation revealed by AIEgens in mechanically strong hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101500.
Wang, X. M.; Xu, K. Y.; Yao, H. C.; Chang, L. M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. J.; Zhao, Y. L.; Qin, J. L. Temperature-regulated aggregation-induced emissive self-healable hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 5002–5013.
Xue, J. Q.; Bai, W.; Duan, H. Y.; Nie, J. J.; Du, B. Y.; Sun, J. Z.; Tang, B. Z. Tetraphenylethene cross-linked thermosensitive microgels via acylhydrazone bonds: Aggregation-induced emission in nanoconfined environments and the cononsolvency effect. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5762–5772.
Mei, J.; Hong, Y. N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, Y. H.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregation-induced emission: The whole is more brilliant than the parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479.
Wang, Z. K.; Nie, J. Y.; Qin, W.; Hu, Q. L.; Tang, B. Z. Gelation process visualized by aggregation-induced emission fluorogens. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12033.
Makrocka-Rydzyk, M.; Woźniak-Braszak, A.; Jurga, K.; Jurga, S. Local motions in poly (ethylene-co-norbornene) studied by 1H NMR relaxometry. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2015, 71, 67–72.
Yu, H. C.; Zheng, S. Y.; Fang, L. T.; Ying, Z. M.; Du, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, K. F.; Wu, Z. L.; Zheng, Q. Reversibly transforming a highly swollen polyelectrolyte hydrogel to an extremely tough one and its application as a tubular grasper. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005171.
Yu, H. C.; Hao, X. P.; Zhang, C. W.; Zheng, S. Y.; Du, M.; Liang, S. M.; Wu, Z. L.; Zheng, Q. Engineering tough metallosupramolecular hydrogel films with kirigami structures for compliant soft electronics. Small 2021, 17, 2103836.
Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Hua, L. Q.; Lu, J. L.; Wang, K. J.; Zhao, C. Z. Biomimetic self-deformation of polymer interpenetrating network with stretch-induced anisotropicity. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 8351–8359.
Steck, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, J. W.; Hassan, S.; Suo, Z. G. Topological adhesion. I. Rapid and strong topohesives. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2020, 39, 100803.
Acknowledgement
This work was funded from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51903250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Yan, B., Wang, J. et al. A multistimuli-responsive fluorescent hydrogel based on a fluorescence response to macromolecular segmental motion. Nano Res. 16, 12098–12105 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5361-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5361-8