Abstract
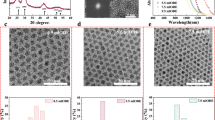
As promising optoelectronic materials, lead sulfide quantum dots (PbS QDs) have attracted great attention. However, their applications are substantially limited by the QD quality and/or complicated synthesis. Herein, a facile new synthesis is developed for highly monodisperse and halide passivated PbS QDs. The new synthesis is based on a heterogeneous system containing a PbCl2−Pb(OA)2 solid-liquid precursor solution. The solid PbCl2 inhibits the diffusion of monomers and maintains a high oversaturation condition for the growth of PbS QDs, resulting in high monodispersities. In addition, the PbCl2 gives rise to halide passivation on the PbS QDs, showing excellent stability in air. The high monodispersity and good passivation endow these PbS QDs with outstanding optoelectronic properties, demonstrated by a 9.43% power conversion efficiency of PbS QD solar cells with a bandgap of ∼ 0.95 eV (1,300 nm). We believe that this heterogeneous strategy opens up a new avenue optimizing for the synthesis and applications of QDs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreels, I.; Justo, Y.; De Geyter, B.; Haustraete, K.; Martins, J. C.; Hens, Z. Size-tunable, bright, and stable PbS quantum dots: A surface chemistry study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2004–2012.
Zhang, J. B.; Crisp, R. W.; Gao, J. B.; Kroupa, D. M.; Beard, M. C.; Luther, J. M. Synthetic conditions for high-accuracy size control of PbS quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1830–1833.
Giansante, C.; Infante, I.; Fabiano, E.; Grisorio, R.; Suranna, G. P.; Gigli, G. “Darker-than-Black” PbS quantum dots:Enhancing optical absorption of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals via short conjugated ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1875–1886.
Chuang, C. H. M.; Brown, P. R.; Bulović, V.; Bawendi, M. G. Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 796–801.
Liu, M. X.; Voznyy, O.; Sabatini, R.; De Arquer, F. P. G.; Munir, R.; Balawi, A. H.; Lan, X. Z.; Fan, F. J.; Walters, G.; Kirmani, A. R. et al. Hybrid organic-inorganic inks flatten the energy landscape in colloidal quantum dot solids. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 258–263.
Mcdonald, S. A.; Konstantatos, G.; Zhang, S. G.; Cyr, P. W.; Klem, E. J. D.; Levina, L.; Sargent, E. H. Solution-processed PbS quantum dot infrared photodetectors and photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 138–142.
De Arquer, F. P. G.; Armin, A.; Meredith, P.; Sargent, E. H. Solution-processed semiconductors for next-generation photodetectors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16100.
Choi, M. J.; De Arquer, F. P. G.; Proppe, A. H.; Seifitokaldani, A.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Baek, S. W.; Liu, M. X.; Sun, B.; Biondi, M. et al. Cascade surface modification of colloidal quantum dot inks enables efficient bulk homojunction photovoltaics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 103.
Yin, X. T.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y. X.; Yang, Y. W.; **ng, Y. L.; Que, W. X. PbS QD-based photodetectors: Future-oriented near-infrared detection technology. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 417–438.
Saran, R.; Curry, R. J. Lead sulphide nanocrystal photodetector technologies. Nat. Photon. 2016, 10, 81–92.
Pradhan, S.; Stavrinadis, A.; Gupta, S.; Christodoulou, S.; Konstantatos, G. Breaking the open-circuit voltage deficit floor in PbS quantum dot solar cells through synergistic ligand and architecture engineering. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1444–1449.
Wang, Y. J.; Lu, K. Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Z. K.; Shi, G. Z.; Fang, H. H.; Chen, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, F.; Gu, M. F. et al. In situ passivation for efficient PbS quantum dot solar cells by precursor engineering. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704871.
Green, P. B.; Villanueva, F. Y.; Demmans, K. Z.; Imperiale, C. J.; Hasham, M.; Nikbin, E.; Howe, J. Y.; Burns, D. C.; Wilson, M. W. B. PbS nanocrystals made using excess lead chloride have a halide-perovskite-like surface. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 9270–9284.
Hines, M. A.; Scholes, G. D. Colloidal PbS nanocrystals with size-tunable near-infrared emission: Observation of post-synthesis self-narrowing of the particle size distribution. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1844–1849.
Ning, Z. J.; Voznyy, O.; Pan, J.; Hoogland, S.; Adinolfi, V.; Xu, J. X.; Li, M.; Kirmani, A. R.; Sun, J. P.; Minor, J. et al. Air-stable n-type colloidal quantum dot solids. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 822–828.
Wu, M. F.; Congreve, D. N.; Wilson, M. W. B.; Jean, J.; Geva, N.; Welborn, M.; Van Voorhis, T.; Bulović, V.; Bawendi, M. G.; Baldo, M. A. Solid-state infrared-to-visible upconversion sensitized by colloidal nanocrystals. Nat. Photon. 2016, 10, 31–34.
Kirkwood, N.; Monchen, J. O. V.; Crisp, R. W.; Grimaldi, G.; Bergstein, H. A. C.; Du Fossé, I.; Van Der Stam, W.; Infante, I.; Houtepen, A. J. Finding and fixing traps in II–VI and III–V colloidal quantum dots: The importance of Z-type ligand passivation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15712–15723.
Ning, Z. J.; Ren, Y.; Hoogland, S.; Voznyy, O.; Levina, L.; Stadler, P.; Lan, X. Z.; Zhitomirsky, D.; Sargent, E. H. All-inorganic colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics employing solution-phase halide passivation. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6295–6299.
Sun, B.; Vafaie, M.; Levina, L.; Wei, M. Y.; Dong, Y. T.; Gao, Y. J.; Kung, H. T.; Biondi, M.; Proppe, A. H.; Chen, B. et al. Ligand-assisted reconstruction of colloidal quantum dots decreases trap state density. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3694–3702.
Anderson, N. C.; Hendricks, M. P.; Choi, J. J.; Owen, J. S. Ligand exchange and the stoichiometry of metal chalcogenide nanocrystals: Spectroscopic observation of facile metal-carboxylate displacement and binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18536–18548.
Weidman, M. C.; Beck, M. E.; Hoffman, R. S.; Prins, F.; Tisdale, W. A. Monodisperse, air-stable PbS nanocrystals via precursor stoichiometry control. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6363–6371.
Green, P. B.; Li, Z. Q.; Wilson, M. W. B. PbS nanocrystals made with excess PbCl2 have an intrinsic shell that reduces their stokes shift. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5897–5901.
Winslow, S. W.; Liu, Y.; Swan, J. W.; Tisdale, W. A. Quantification of a PbClx. shell on the surface of PbS nanocrystals. ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 209–216.
Colbert, A. E.; Placencia, D.; Ratcliff, E. L.; Boercker, J. E.; Lee, P.; Aifer, E. H.; Tischler, J. G. Enhanced infrared photodiodes based on PbS/PbClx. core/shell nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 58916–58926.
Zhang, C. W.; **a, Y.; Zhang, Z. M.; Huang, Z.; Lian, L. Y.; Miao, X. S.; Zhang, D. L.; Beard, M. C.; Zhang, J. B. Combination of cation exchange and quantized Ostwald ripening for controlling size distribution of lead chalcogenide quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3615–3622.
**a, Y.; Liu, S. S.; Wang, K.; Yang, X. K.; Lian, L. Y.; Zhang, Z. M.; He, J. G.; Liang, G. J.; Wang, S.; Tan, M. L. et al. Cation-exchange synthesis of highly monodisperse PbS quantum dots from ZnS nanorods for efficient infrared solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907379.
Zhao, Y. M.; Peng, Y. L.; Shan, C.; Lu, Z.; Wojtas, L.; Zhang, Z. J.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Y. Q.; Ma, S. Q. Metallocorrole-based porous organic polymers as a heterogeneous catalytic nanoplatform for efficient carbon dioxide conversion. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1145–1152.
Zhang, N. Q.; Ye, C. L.; Yan, H.; Li, L. C.; He, H.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom site catalysts for environmental catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3165–3182.
Wei, Y. C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C. P.; Wang, Z. Y.; Jiang, F. L.; Liu, Y. S.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, D. P.; Hong, M. C. Constructing all-inorganic perovskite/fluoride nanocomposites for efficient and ultra-stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106386.
Suh, Y. H.; Lee, S.; Jung, S. M.; Bang, S. Y.; Yang, J. J.; Fan, X. B.; Zhan, S. J.; Samarakoon, C.; Jo, J. W.; Kim, Y. et al. Engineering core size of InP quantum dot with incipient ZnS for blue emission. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102372.
Li, M. Y.; Chen, S. W.; Zhao, X. Z.; **ong, K.; Wang, B.; Shah, U. A.; Gao, L.; Lan, X. Z.; Zhang, J. B.; Hsu, H. Y. et al. Matching charge extraction contact for infrared PbS colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Small 2022, 18, 2105495.
Zhang, J. B.; Chernomordik, B. D.; Crisp, R. W.; Kroupa, D. M.; Luther, J. M.; Miller, E. M.; Gao, J. B.; Beard, M. C. Preparation of Cd/Pb chalcogenide heterostructured janus particles via controllable cation exchange. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7151–7163.
Liu, X. Y.; Liu, Y. X.; Xu, S.; Geng, C.; **e, Y. Y.; Zhang, Z. H.; Zhang, Y. H.; Bi, W. G. Formation of “steady size” state for accurate size control of CdSe and CdS quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3576–3580.
Ng, T. W.; Chan, C. Y.; Lo, M. F.; Guan, Z. Q.; Lee, C. S. Formation chemistry of perovskites with mixed iodide/chloride content and the implications on charge transport properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9081–9085.
Fan, J. Z.; Andersen, N. T.; Biondi, M.; Todorović, P.; Sun, B.; Ouellette, O.; Abed, J.; Sagar, L. K.; Choi, M. J.; Hoogland, S. et al. Mixed lead halide passivation of quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904304.
Yuan, L.; Patterson, R.; Cao, W. K.; Zhang, Z. W.; Zhang, Z. L.; Stride, J. A.; Reece, P.; Conibeer, G.; Huang, S. J. Air-stable PbS quantum dots synthesized with slow reaction kinetics via a PbBr2 precursor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68579–68586.
Woo, J. Y.; Ko, J. H.; Song, J. H.; Kim, K.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y. H.; Lee, D. C.; Jeong, S. Ultrastable PbSe nanocrystal quantum dots via in situ formation of atomically thin halide adlayers on PbSe(100). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8883–8886.
Elleman, A. J.; Wilman, H. The structure and epitaxy of lead chloride deposits formed from lead sulphide and sodium chloride. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. A 1949, 62, 344–355.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2021YFA0715502 and 2021YFA0715500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61974052 and 61904065), the Innovation Project of Optics Valley Laboratory (No. OVL2021BG009), and the Fund from Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (No. GJHZ20210705142540010), the Key R&D Program of Hubei Province (No. 2021BAA014), and the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Hubei Province (No. 2021EHB010). The authors thank the Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Li, M., Liu, Y. et al. Heterogeneous system synthesis of high quality PbS quantum dots for efficient infrared solar cells. Nano Res. 16, 5750–5755 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5251-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5251-0