Abstract
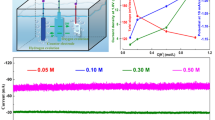
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to valuable formate as liquid fuel is a promising way to alleviate the greenhouse effect. The edge active sites in bismuth (Bi) nanosheets play a critical role in the electrochemical reduction of CO2 into formate, which enable the operation of CO2 reduction with high cathodic energy efficiency, especially under large current densities of ≥ 200 mA/cm2. However, the undesirable reconstruction of small Bi nanosheets into large nanosheets leads to the decreasing of edge active sites during electrocatalysis. Here we report stable isolated ultrasmall bismuth nanosheets-synthesized by in-situ electrochemical transformation of ligands covered bismuth vanadate-on silver nanowires as an efficient electrocatalyst for CO2-to-formate reduction. The cooperative electrocatalyst achieves a formate current density of 186 mA/cm2 and a cathodic energy efficiency of 75% for formate, which is the only best compared to the literature results. Operando Raman and morphologic measurements demonstrate that the excellent energy utilization of the electrocatalyst is originated from the rich edge active sites with Bi-O species of the ultrasmall Bi nanosheets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serna, L.; Fenoll, C. Co** with human CO2 emissions. Nature 2000, 408, 656–657.
Lue, S. J.; Liu, N. Y.; Rajesh Kumar, S.; Tseng, K. C. Y.; Wang, B. Y.; Leung, C. H. Experimental and one-dimensional mathematical modeling of different operating parameters in direct formic acid fuel cells. Energies 2017, 10, 1972.
Wang, W. H.; Himeda, Y.; Muckerman, J. T.; Manbeck, G. F.; Fujita, E. CO2 hydrogenation to formate and methanol as an alternative to photo- and electrochemical CO2 reduction. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12936–12973.
Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, L. J.; Wang, J. The evolution of catalytically active calcium catalyst during steam gasification of lignite char. Carbon 2021, 172, 162–173.
**a, C.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Liang, W. T.; Stavitski, E.; Alshareef, H. N.; Wang, H. T. Continuous production of pure liquid fuel solutions via electrocatalytic CO2 reduction using solid-electrolyte devices. Nat. Energy. 2019, 4, 776–785.
Ren, W. H.; Zhao, C. Paths towards enhanced electrochemical CO2 reduction. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 7–9.
Zheng, X. L.; De Luna, P.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Zhang, B.; Becknell, N.; Ross, M. B.; Li, Y. F.; Banis, M. N.; Li, Y. Z.; Liu, M. et al. Sulfur-modulated tin sites enable highly selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate. Joule 2017, 1, 794–805.
Sun, S. N.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Ji, W. X.; Dong, L. Z.; Wang, Y. R.; Lan, Y. Q. Identification of the activity source of CO2 electroreduction by strategic catalytic site distribution in stable supramolecular structure system. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa195.
Shang, H. S.; Wang, T.; Pei, J. J.; Jiang, Z. L.; Zhou, D. N.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. J.; Dong, J. C.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Chen, W. X. et al. Design of a single-atom indiumδ+-N4 interface for efficient electroreduction of CO2 to formate. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22465–22469.
Shi, Y. M.; Ji, Y.; Long, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y. F.; **ao, J. P.; Zhang, B. Unveiling hydrocerussite as an electrochemically stable active phase for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to formate. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3415.
Yang, W. F.; Chen, S.; Ren, W. H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X. J.; Jia, C.; Liu, J. N.; Zhao, C. Nanostructured amalgams with tuneable silver-mercury bonding sites for selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide into formate and carbon monoxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15907–15912.
Zhang, Z. R.; Ahmad, F.; Zhao, W. H.; Yan, W. S.; Zhang, W. H.; Huang, H. W.; Ma, C.; Zeng, J. Enhanced electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 via chemical coupling between indium oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4029–4034.
Pang, R. C.; Tian, P. F.; Jiang, H. L.; Zhu, M. H.; Su, X. Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. L.; Zhu, Y. H.; Song, L.; Li, C. Z. Tracking structural evolution: Operando regenerative CeOx/Bi interface structure for high-performance CO2 electroreduction. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, nwaa187, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa187.
Yang, F.; Elnabawy, A. O.; Schimmenti, R.; Song, P.; Wang, J. W.; Peng, Z. Q.; Yao, S.; Deng, R. P.; Song, S. Y.; Lin, Y. et al. Bismuthene for highly efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction reaction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1088.
Yang, J.; Wang, X. L.; Qu, Y. T.; Wang, X.; Huo, H.; Fan, Q. K.; Wang, J.; Yang, L. M.; Wu, Y. E. Bi-based metal-organic framework derived leafy bismuth nanosheets for carbon dioxide electroreduction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001709.
Li, L. Q.; Tang, C.; **a, B. Q.; **, H. Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Two-dimensional mosaic bismuth nanosheets for highly selective ambient electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2902–2908.
Yao, D. Z.; Tang, C.; Li, L. Q.; **a, B. Q.; Vasileff, A.; **, H. Y.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Qiao, S. Z. In situ fragmented bismuth nanoparticles for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001289.
Zhang, L.; Chen, D. R.; Jiao, X. L. Monoclinic structured BiVO4 nanosheets: Hydrothermal preparation, formation mechanism, and coloristic and photocatalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2668–2673.
Koh, J. H.; Won, D. H.; Eom, T.; Kim, N. K.; Jung, K. D.; Kim, H.; Hwang, Y. J.; Min, B. K. Facile CO2 electro-reduction to formate via oxygen bidentate intermediate stabilized by high-index planes of Bi dendrite catalyst. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5071–5077.
Zhu, D. D.; Liu, J. L.; Qiao, S. Z. Recent advances in inorganic heterogeneous electrocatalysts for reduction of carbon dioxide. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3423–3452.
Lu, P. L.; Gao, D. L.; He, H. Y.; Wang, Q. X.; Liu, Z. J.; Dipazir, S.; Yuan, M. L.; Zu, W. Y.; Zhang, G. J. Facile synthesis of a bismuth nanostructure with enhanced selectivity for electrochemical conversion of CO2 to formate. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7805–7812.
Zhou, J. H.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Y.; Luo, M. Y.; Guo, X. Y.; Meng, Q. Y.; Zhang, Y. W. Boosting electrochemical reduction of CO2 at a low overpotential by amorphous Ag-Bi-S-O decorated Bi0 nanocrystals. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14197–14201.
Voiry, D.; Shin, H. S.; Loh, K. P.; Chhowalla, M. Low-dimensional catalysts for hydrogen evolution and CO2 reduction. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0105.
He, S. S.; Ni, F. L.; Ji, Y. J.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y. Z.; Bai, H. P.; Liu, G. J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Y.; Zhang, B. et al. The p-orbital delocalization of main-group metals to boost CO2 electroreduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16114–16119.
Zhong, H. X.; Qiu, Y. L.; Zhang, T. T.; Li, X. F.; Zhang, H. M.; Chen, X. B. Bismuth nanodendrites as a high performance electrocatalyst for selective conversion of CO2 to formate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13746–13753.
Cao, C. S.; Ma, D. D.; Gu, J. F.; **e, X. Y.; Zeng, G.; Li, X. F.; Han, S. G.; Zhu, Q. L.; Wu, X. T.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic layers leading to atomically thin bismuthene for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15014–15020.
Ma, D. D.; Han, S. G.; Cao, C. S.; Li, X.; Wu, X. T.; Zhu, Q. L. Remarkable electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with ultrahigh CO/H2 ratio over single-molecularly immobilized pyrrolidinonyl nickel phthalocyanine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 264, 118530.
Ma, W. X.; Bu, J.; Liu, Z. P.; Yan, C.; Yao, Y.; Chang, N. H.; Zhang, H. P.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J. Monoclinic scheelite bismuth vanadate derived bismuthene nanosheets with rapid kinetics for electrochemically reducing carbon dioxide to formate. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006704.
Fan, L.; **a, C.; Zhu, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. T. Electrochemical CO2 reduction to high-concentration pure formic acid solutions in an all-solid-state reactor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3633.
Gong, Q. F.; Ding, P.; Xu, M. Q.; Zhu, X. R.; Wang, M. Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, Q.; Han, N.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, J. et al. Structural defects on converted bismuth oxide nanotubes enable highly active electrocatalysis of carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2807.
Wang, Y. T.; Li, Y. H.; Liu, J. Z.; Dong, C. X.; **ao, C. Q.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, H. L.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Z. BiPO4-derived 2D nanosheets for efficient electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to liquid fuel. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7687–7685.
Deng, P. L.; Wang, H. M.; Qi, R. J.; Zhu, J. X.; Chen, S. H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, L.; Qi, K.; Liu, H. F.; **a, B. Y. Bismuth oxides with enhanced bismuth-oxygen structure for efficient electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 743–750.
Yi, L. C.; Chen, J. X.; Shao, P.; Huang, J. H.; Peng, X. X.; Li, J. W.; Wang, G. X.; Zhang, C.; Wen, Z. H. Molten-salt-assisted synthesis of bismuth nanosheets for long-term continuous electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to formate. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20112–20119.
Xu, X. S.; Xu, Y. X.; Xu, F.; Jiang, G.; Jian, J. S.; Yu, H. W.; Zhang, E. M.; Shchukin, D.; Kaskel, S.; Wang, H. Q. Black BiVO4: Size tailored synthesis, rich oxygen vacancies, and sodium storage performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 1636–1645.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21808061, 21838003, 91834301, and 22008069), the Shanghai Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (Nos. 18JC1410500 and 19JC1410400), the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (No. 222201718002), and the Shanghai Sailing Program (No. 20YF1410200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Isolated ultrasmall Bi nanosheets for efficient CO2-to-formate electroreduction. Nano Res. 15, 1409–1414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3677-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3677-4