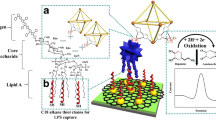
Abstract
We report a facile assay for the rapid visual detection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecules down to the low nanomolar level by taking advantage of the electrostatic interaction between LPS molecules and cysteamine-modified gold nanoparticles (CSH-Au NPs). The large amount of negatively charged groups on the LPS molecules make LPS highly negatively charged. Thus, when modified with cysteamine, the positively charged gold nanoparticles can aggregate in the presence of trace amounts of LPS. The probe is simple, does not require any advanced instrumentation, and the limit of detection (LOD) was determined to be as low as 3.3 × 10−10 mol/L. To the best of our knowledge, it is the most sensitive synthetic LPS sensor reported so far.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seltmann, G.; Holst, O. The Bacterial Cell Wall; Springer: New York, 2002.
Raetz, C. R. H. Biochemistry of Endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 129–170.
US FDA, CDER, CBER, CDRH, CVM. Guideline on validation of the Limulus amebocyte lysate test as an end-product endotoxin test for human and animal parenteral drugs, biological products, and medical devices; CDER, CBER, CDRH, CVM (Eds): Rockville, MD, USA, 20857, 1987.
Zhang, G. H.; Baek, L.; Nielsen, P. E.; Buchardt, O.; Koch, C. Sensitive quantitation of endotoxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibody against Limulus peptide C. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 416–422.
Roslansky, P. F.; Novitsky, T. J. Sensitivity of Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) to LAL-reactive glucans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2477–2483.
Rangin, M.; Basu, A. Lipopolysaccharide identification with functionalized polydiacetylene liposome sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5038–5039.
Voss, S; Fischer, R.; Jung, G.; Wiesmüller, K. -H.; Brock, R. A fluorescence-based synthetic LPS sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 554–561.
Ganesh, V.; Bodewits, K.; Bartholdson, S. J.; Natale, D.; Campopiano, D. J.; Mareque-Rivas J. C. Effective binding and sensing of lipopolysaccharide: Combining complementary pattern recognition receptors. Angew. Chem., Int. Edit. 2009, 48, 356–360.
Zeng, L.; Wu, J.; Dai Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Lee, C. -S. Sensing of bacterial endotoxin in aqueous solution by supramolecular assembly of pyrene derivative. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4014–4017.
Wu, J. C.; Zawistowski, A.; Ehrmann, M.; Yi, T.; Schmuck, C. Peptide functionalized polydiacetylene liposomes act as a fluorescent turn-on sensor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9720–9723.
Ghosh, S. K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: From theory to applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4797–4862.
Sperling, R. A.; Gil, P. R.; Zhang, F.; Zanella, M.; Parak, W. J. Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1896–1908.
Anker, J. N.; Hall, W. P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N. C.; Zhao, J.; Van Duyne, R. P. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442–453.
Nie, Z. H.; Petukhova, A.; Kumacheva, E. Properties and emerging applications of self-assembled structures made from inorganic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 15–25.
Liu, D. B.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. Y. Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1421–1433.
Cai, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. B. One-pot polymerase chain reaction with gold nanoparticles for rapid and ultrasensitive DNA detection. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 557–563.
Elghanian, R.; Storhoff, J. J.; Mucic, R. C.; Letsinger, R. L.; Mirkin, C. A. Selective colorimetric detection of poly-nucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 1997, 277, 1078–1081.
Liu, J. W.; Lu, Y. A colorimetric lead biosensor using DNAzyme-directed assembly of gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6642–6643.
Neely, A.; Perry, C.; Varisli, B.; Singh, A. K.; Arbneshi, T.; Senapati D.; Kalluri, J. R.; Ray, P. C. Ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarker using two-photon Rayleigh scattering properties of gold nanoparticle. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2834–2840.
Sudeep, P. K.; Joseph, S. T. S.; Thomas, K. G. Selective detection of cysteine and glutathione using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6516–6517.
Lee J. -S.; Han, M. S.; Mirkin, C. A. Colorimetric detection of mercuric ion (Hg2+) in aqueous media using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4093–4096.
Darbha, G. K.; Ray, A.; Ray, P. C. Gold nanoparticle-based miniaturized nanomaterial surface energy transfer probe for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of mercury in soil, water, and fish. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 208–214.
Chi, H; Liu, B. H.; Guan, G. J.; Zhang, Z. P.; Han, M. -Y. A simple, reliable and sensitive colorimetric visualization of melamine in milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2010, 135, 1070–1075.
Liu, J. W.; Lu, Y. Fast Colorimetric sensing of adenosine and cocaine based on a general sensor design involving aptamers and nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 90–94.
Zhou, Y; Wang, S. X.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, X. Y. Visual detection of copper(II) by azide- and alkyne-functionalized gold nanoparticles using click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7454–7456.
Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, N.; Lin, Y.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. A simple assay for direct colorimetric visualization of trinitrotoluene at picomolar levels using gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8601–8604.
Ai, K.; Liu, Y. L.; Lu, L. H. Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced color change of gold nanoparticles for visual detection of melamine in raw milk and infant formula. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9496–9497.
Dasary, S. S. R.; Singh, A. K.; Senapati, D.; Yu, H. T.; Ray, P. C. Gold nanoparticle based label-free SERS probe for ultrasensitive and selective detection of trinitrotoluene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13806–13812.
Wang, L. B.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Xu, L. G.; Chen, W.; Kuang, H.; Liu, L. Q.; Agarwal, A.; Xu, C. L.; Kotov, N. A. Side-by-side and end-to-end gold nanorod assemblies for environmental toxin sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5472–5475.
Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y. Q.; Zhu, N. N.; Ma, Y. R.; Mao, L. Q. Colorimetric detection of glucose in rat brain using gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4800–4804.
Kong, B.; Zhu, A. W.; Luo, Y. P.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Y. Y.; Shi, G. Y. Sensitive and selective colorimetric visualization of cerebral dopamine based on double molecular recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1837–1840.
Zhang, J.; Wang, L. H.; Pan, D.; Song, S. P.; Boey, F. Y. C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, C. H. Visual cocaine detection with gold nanoparticles and rationally engineered aptamer structures. Small 2008, 4, 1196–1200.
Qi, W. J.; Wu, D.; Ling, J.; Huang, C. Z. Visual and light scattering spectrometric detections of melamine with polythymine-stabilized gold nanoparticles through specific triple hydrogen-bonding recognition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 4893–4895.
Wu, Z. J.; Zhao, H.; Xue, Y.; Cao, Q.; Yang, J.; He, Y. J.; Li, X. J.; Yuan, Z. B. Colorimetric detection of melamine during the formation of gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2574–2578.
Kuang, H.; Chen, W.; Yan, W. J.; Xu, L. G.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Liu, L. Q.; Chu, H. Q.; Peng, C. F.; Wang, L. B.; Kotov, N. A.; Xu, C. L. Crown ether assembly of gold nanoparticles: Melamine sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2032–2037.
Sun, J. Y.; Ge, J. H.; Liu, W. M.; Fan, Z. Y.; Zhang, H. Y.; Wang, P. F. Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric visualization of streptomycin in raw milk using Au nano-particles supramolecular assembly. Chem. Commun. 2011, 9888–9890.
Shands, J. W. Evidence for a bilayer structure in Gram-negative lipopolysaccharide-Relationship to toxicity. Infect. Immun. 1971, 4, 167–172.
Mayberrycarson, K. J.; Roth, I. L.; Smith, P. F. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharide isolated from thermoplasma-acidophilum. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 121, 700–703.
Niidome, T.; Nakashima, K.; Takahashi, H.; Niidome, Y. Preparation of primary amine-modified gold nanoparticles and their transfection ability into cultivated cells. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1978–1979.
Chan, S.; Horner, S. R.; Fauchet, P. M.; Miller, B. L. Identification of Gram negative bacteria using nanoscale silicon microcavities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11797–11798.
Li, C. H.; Budge, L. P.; Driscoll, C. D.; Willardson, B. M.; Allman, G. W.; Savage P. B. Incremental conversion of outer-membrane permeabilizers into potent antibiotics for gram-negative bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 931–940.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Ge, J., Liu, W. et al. A facile assay for direct colorimetric visualization of lipopolysaccharides at low nanomolar level. Nano Res. 5, 486–493 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0234-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0234-1