Abstract
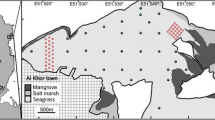
Anthropogenic nutrient loading has led to declines in the function and productivity of some tropical coastal ecosystems. We use the seagrass Thalassia testudinum as a sentinel for tracing nutrient inputs and movements in Ambergris Caye Lagoon, Belize, a region heavily dependent on ecotourism and in the process of expanding its network of marine protected areas. Seagrass samples were collected at stations distributed along a 24-km section of the lagoon, with stations bracketing the urban center of San Pedro. Leaf tissue carbon/nitrogen (C:N) stoichiometry, stable isotope composition (δ13C, δ15N), and epiphyte load (mg cm−2) were analyzed relative to spatial location and proximate land use conditions. Seagrass tissues showed a modal pattern in δ15N composition along the north–south axis of the lagoon, with maximum average values (1.5 ± 1.1 ‰ [SD]), occurring adjacent to or slightly down-current of the most urbanized areas of San Pedro (range = −3.0–3.7 ‰). Offshore seagrasses were enriched in δ13C relative to inshore areas, but there was no consistent relationship with adjacent land use. Tissue C:N and epiphyte load (mg cm−2) decreased monotonically from south to north, declining from average values of 25.3 to 19.2 (C:N) and from 4.2 to 0.8 mg cm−2 (epiphyte load). Impervious surface cover adjacent to lagoon sites was positively related to δ15N values (parameter estimate ± SE = 0.80 ± 0.36) but negatively related to tissue C:N (−2.78 ± 0.65) and epiphyte load (−1.04 ± 0.33). Isoscapes of spatially interpolated isotope values highlighted the location and potential sources of nutrient input to the lagoon, some of which occurred within marine protected areas. These results support the application of seagrass tissue stable isotope composition analysis as a low-cost and time-integrated means of tracing nutrient inputs in some naturally oligotrophic ecosystems. Spatially explicit information on nutrient inputs is vital for natural resource managers and land-use planners to identify, mitigate, and control sources of anthropogenic eutrophication in tropical coastal ecosystems such as Ambergris Caye Lagoon.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, M.J., and S.V. Smith. 1983. C:N:P ratios of benthic marine plants. Limnology and Oceanography 28: 568–574.
Anderson, W.T., and J.W. Fourqurean. 2003. Intra-and interannual variability in seagrass carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes from south Florida a preliminary study. Organic Geochemistry 34: 185–194.
Ashikin, C.N., M. Rozaimi, N. Arina, M. Fairoz, and N. Hidayah. 2020. Nitrogen dynamics within an estuarine seagrass meadow under heavy anthropogenic influence. Marine Pollution Bulletin 150: 110628.
Bellwood, D.R., T.P. Hughes, C. Folke, and M. Nystrom. 2004. Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 429: 827–833.
Blersch, D.M., and P.C. Kangas. 2013. A modeling analysis of the sustainability of ecotourism in Belize. Environment Development and Sustainability 15: 67–80.
Bologna, P.A., and K.L. Heck. 2002. Impact of habitat edges on density and secondary production of seagrass-associated fauna. Estuaries 25: 1033–1044.
Boo, E. 1990. Ecotourism: The potentials and pitfalls: Country case studies. Washington: WWF.
Borowitzka, M.A., P.S. Lavery, and M. van Keulen. 2007. Epiphytes of seagrasses. In Seagrasses: Biology Ecology and Conservation, ed. A.W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 441–461. Dordrecht: Springer.
Brodie, J.E., M. Devlin, D. Haynes, and J. Waterhouse. 2011. Assessment of the eutrophication status of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon (Australia). Biogeochemistry 106: 281–302.
Burkholder, D.A., M.R. Heithaus, and J.W. Fourqurean. 2012. Feeding preferences of herbivores in a relatively pristine subtropical seagrass ecosystem. Marine and Freshwater Research 63: 1051–1058.
Campbell, J.E., and J.W. Fourqurean. 2009. Interspecific variation in the elemental and stable isotope content of seagrasses in South Florida. Marine Ecology Progress Series 387: 109–123.
Cardona, M., and K. Cardona. 2009. Revised master development plan for Ambergris Caye. Ambergris Caye: Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute.
Carruthers, T., B. Van Tussenbroek, and W. Dennison. 2005. Influence of submarine springs and wastewater on nutrient dynamics of Caribbean seagrass meadows. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 64: 191–199.
Ceballos-Lascurain, H. 1996. Tourism ecotourism and protected areas: The state of nature-based tourism around the world and guidelines for its development. Gland: IUCN.
Cherrington, E.A., E. Ek, P. Cho, B.F. Howell, B.E. Hernandez, E.R. Anderson, A.I. Flores, B.C. Garcia, E. Sempris, D.E. Irwin, and D.E. 2010. Forest cover and deforestation in Belize: 1980–2010. Cathalac: SERVIR.
Convention on Biological Diversity. 2014. Fifth national report to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity. Belmopan: Ministry of Forestry Fisheries and Sustainable Development.
Cook, P.L.M., V. Evrard, and R.J. Woodland. 2015. Factors controlling nitrogen fixation in temperate seagrass beds. Marine Ecology Progress Series 525: 41–51.
Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute (CZMAI). 2016. Belize Integrated Coastal Zone Management Plan. Belize City: CZMAI.
Danovaro, R., E. Nepote, M.L., Martire, L. Carugati, Z. Da Ros, F. Torsani, A. Dell'Anno, and C. Corinaldesi. 2020. Multiple declines and recoveries of Adriatic seagrass meadows over forty years of investigation. Marine Pollution Bulletin 161: 111804.
Deegan, L.A., A. Wright, S.G. Ayvazian, J.T. Finn, H. Golden, R.R. Merson, and J. Harrison. 2002. Nitrogen loading alters seagrass ecosystem structure and support of higher trophic levels. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 12: 193–212.
De Boeck, H.J., J.M. Bloor, J. Kreyling, J.C. Ransijn, I. Nijs, A. Jentsch, and M. Zeiter. 2018. Patterns and drivers of biodiversity–stability relationships under climate extremes. Journal of Ecology 106: 890–902.
Doody, J.P. 2004. ‘Coastal squeeze’–an historical perspective. Journal of Coastal Conservation 10: 129–138.
Duarte, C.M. 1990. Seagrass nutrient content. Marine Ecology Progress Series 6: 201–207.
Duarte, C.M., I.J. Losada, I.E. Hendriks, I. Mazarrasa, and N. Marbà. 2013. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nature Climate Change 3: 961–968.
Duarte, C.M., A. Delgado-Huertas, A. Anton, P. Carrillo-de-Albornoz, D.C. López-Sandoval, S. Agustí, H. Almahasheer, N. Marbá, I.E. Hendriks, and D. Krause-Jensen. 2018. Stable isotope (δ13C, δ15N, δ18O, δD) composition and nutrient concentration of Red Sea primary producers. Frontiers in Marine Science 5: 298.
Dumont, E., J.A. Harrison, C. Kroeze, E.J. Bakker, and S.P. Seitzinger. 2005. Global distribution and sources of dissolved inorganic nitrogen export to the coastal zone: results from a spatially explicit global model. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 19: GB4S02.
Durako, M.J., and M.O. Hall. 1992. Effects of light on the stable carbon isotope composition of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Marine Ecology Progress Series 86: 99–101.
Evans, S.M., K.J. Griffin, R.A. Blick, A.G. Poore, and A. Vergés. 2018. Seagrass on the brink: decline of threatened seagrass Posidonia australis continues following protection. Plos one 13: e0190370.
Espel, D., N.J. Diepens, O. Boutron, E. Buffan-Dubau, Y. Chérain, E. Coulet, P. Grillas, A. Probst, J. Silvestre, and A. Elger. 2019. Dynamics of the seagrass Zostera noltei in a shallow Mediterranean lagoon exposed to chemical contamination and other stressors. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 222: 1–12.
Fourqurean, J.W., and J.C. Zieman. 2002. Nutrient content of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum reveals regional patterns of relative availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in the Florida Keys USA. Biogeochemistry 61: 229–245.
Fourqurean, J.W., S.P. Escorcia, W.T. Anderson, and J.C. Zieman. 2005. Spatial and seasonal variability in elemental content, δ13C and δ15N of Thalassia testudinum from South Florida and its implications for ecosystem studies. Estuaries 28: 447–461.
Fourqurean, J.W., M.F. Muth, and J.N. Boyer. 2010. Epiphyte loads on seagrasses and microphytobenthos abundance are not reliable indicators of nutrient availability in oligotrophic coastal ecosystems. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60: 971–983.
Fourqurean, J.W., S.A. Manuel, K.A. Coates, W.J. Kenworthy, and J.N. Boyer. 2015. Water quality, isoscapes and stoichioscapes of seagrasses indicate general P limitation and unique N cycling in shallow water benthos of Bermuda. Biogeosciences 12: 6235–6249.
Fry, B. 2006. Stable isotope ecology. New York: Springer.
Furman, B.T., M. Merello, C.P. Shea, W.J. Kenworthy, and M.O. Hall. 2019. Monitoring of physically restored seagrass meadows reveals a slow rate of recovery for Thalassia testudinum. Restoration Ecology 27: 421–430.
Garcés-Cuartas, N., C.A. Niño-Torres, D.N. Castelblanco-Martínez, A. Delgado-Huertas, N.P. Cetz-Navarro, R. Ortiz-Pulido, and J. Cuevas. 2021. Isotopic composition of aquatic and semiaquatic plants from the Mexican Caribbean: a baseline for regional ecological studies. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 260: 107489.
Gossling, S. 2000. Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation 27: 223–224.
Grau, J., M. del Rosario Navia, A. Rihm, J. Ducci, D. Martin, and T. Kuratomi. 2013. Water and sanitation in Belize. Belize: Inter-American Development Bank.
Halpern, B.S., K.A. Selkoe, F. Micheli, and C.V. Kappel. 2007. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conservation Biology 21: 1301–1315.
Hastie, T., and R. Tibshirani. 1990. Generalized additive models, 335. London: Chapman and Hall.
Hauxwell, J., and I. Valiela. 2004. Effects of nutrient loading on shallow seagrass-dominated coastal systems: Patterns and processes. In Estuarine Nutrient Cycling: The influence of primary producers, ed. S.L. Nielsen, G.T. Banta, and M.F. Pedersen, 59–92. Dordrecht: Springer.
Hauxwell, J., J. Cebrián, and I. Valiela. 2003. Eelgrass Zostera marina loss in temperate estuaries: Relationship to land-derived nitrogen loads and effect of light limitation imposed by algae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 247: 59–73.
Heck, K.L., and J.F. Valentine. 2007. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 371–381.
Heijs, F.M. 1984. Annual biomass and production of epiphytes in three monospecific seagrass communities of Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb.) Aschers. Aquatic Botany 20: 195–218.
Hemminga, M.A. 1998. The root/rhizome system of seagrasses: An asset and a burden. Journal of Sea Research 39: 183–196.
Hu, X., D.J. Burdige, and R.C. Zimmerman. 2012. δ13C is a signature of light availability and photosynthesis in seagrass. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 441–448.
Hughes, A.R., K.J. Bando, L.F. Rodriguez, and S.L. Williams. 2004. Relative effects of grazers and nutrients on seagrasses: A meta-analysis approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 282: 87–99.
Jones, B.L., L.C. Cullen-Unsworth, and R.K. Unsworth. 2018. Tracking nitrogen source using δ15N reveals human and agricultural drivers of seagrass degradation across the British Isles. Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 133.
Kitting, C.L., B. Fry, and M.D. Morgan. 1984. Detection of inconspicuous epiphytic algae supporting food webs in seagrass meadows. Oecologia 62: 145–149.
Lapointe, B.E., P.J. Barile, and W.R. Matzie. 2004. Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment of seagrass and coral reef communities in the Lower Florida Keys: Discrimination of local versus regional nitrogen sources. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 308: 23–58.
Lee, K.S., and K.H. Dunton. 2000. Effects of nitrogen enrichment on biomass allocation growth and leaf morphology of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Marine Ecology Progress Series 196: 39–48.
Louime, C., J. Fortune, and G. Gervais. 2017. Sargassum invasion of coastal environments: A growing concern. American Journal of Environmental Sciences 13: 58–64.
McClelland, J.W., I. Valiela, and R.H. Michener. 1997. Nitrogen-stable isotope signatures in estuarine food webs: A record of increasing urbanization in coastal watersheds. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 930–937.
McClelland, J.W., and I. Valiela. 1998. Changes in food web structure under the influence of increased anthropogenic nitrogen inputs to estuaries. Marine Ecology Progress Series 168: 259–271.
McGlathery, K.J., K. Sundback, and I.C. Anderson. 2007. Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: The role of plants in the coastal filter. Marine Ecology Progress Series 348: 1–18.
McMinn, S. 1997. The challenge of sustainable tourism. The Environmentalist 17: 135–141.
Meerman, J., W. Sabido. 2001. Central American Ecosystems: Belize. Programme for Belize, Belize City. 2 volumes 50 + 88 pp.
Moreno, P.S. 2005. Ecotourism along the Meso-American Caribbean reef: The impacts of foreign investment. Human Ecology 33: 217–244.
Naeem, S., and S. Li. 1997. Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability. Nature 390: 507–509.
Nagelkerken, I., S.J.M. Blaber, S. Bouillon, P. Green, M. Haywood, L.G. Kirton, J.O. Meynecke, J. Pawlik, H.M. Penrose, A. Sasekumar, and P.J. Somerfield. 2008. The habitat function of mangroves for terrestrial and marine fauna: A review. Aquatic Botany 89: 155–185.
Nagelkerken, I. 2009. Ecological connectivity among tropical coastal ecosystems, 615. Dordrecht: Springer.
Nelson, W. 2007. Development of an epiphyte indicator of nutrient enrichment: Threshold values for seagrass epiphyte load. Ecological Indicators 74: 343–356.
Nelson, W.G. 2017. Development of an epiphyte indicator of nutrient enrichment: threshold values for seagrass epiphyte load. Ecological indicators 74: 343-356.
Nixon, S.W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition social causes and future concerns. Ophelia 41: 199–219.
NTCE. 2015. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): North Ambergris Caye water system & sewage collection and treatment for Belize Water Services Limited (BWSL). Belize: Tunich Nah Consultancy (NTCE).
Nuenninghoff, S., M.H. Lemay, C. Rogers, and D. Martin. 2014. Sustainable tourism in Belize. Washington DC: Inter-American Development Bank.
Orth, R.J., T.J.B. Carruthers, W.C. Dennison, C.M. Duarte, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck, R.A. Hughes, G.A. Kendrick, J.W. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F.T. Short, M. Waycott, and S.L. Williams. 2006. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 56: 987–996.
Peterson, B.J., T.A. Frankovich, and J.C. Zieman. 2007. Response of seagrass epiphyte loading to field manipulations of fertilization, gastropod grazing and leaf turnover rates. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 349: 61–72.
Prado, P., and K.L. Heck. 2011. Seagrass selection by omnivorous and herbivorous consumers: Determining factors. Marine Ecology Progress Series 429: 45–55.
R Core Team. 2020. R: a language and environment for statistical computing, version 3.5.3. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. www.R-project.org/. Accessed Mar 2019.
Rettig, J.E., and G.R. Smith. 2021. Relative strength of top-down effects of an invasive fish and bottom-up effects of nutrient addition in a simple aquatic food web. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 28: 5845–5853.
RStudio Team. 2016. RStudio: integrated development for R, version 1.1.463. Boston: RStudio. http://www.rstudio.com/. Accessed Jan 2020.
Rudon, M. 2014. Welcome to San Mateo…San Pedro Subdivision Turned Slum…. Channel 5 News Belize: Great Belize Productions Ltd.
Ruiz, J.M., C. Marco-Méndez, and J.L. Sánchez-Lizaso. 2010. Remote influence of off-shore fish farm waste on Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows. Marine Environmental Research 69: 118–126.
Ruiz-Frau, A., S. Gelcich, I.E. Hendriks, C.M. Duarte, and N. Marbà. 2017. Current state of seagrass ecosystem services: Research and policy integration. Ocean & Coastal Management 149: 107–115.
Savage, C., P.R. Leavitt, and R. Elmgren. 2010. Effects of land use, urbanization, and climate variability on coastal eutrophication in the Baltic Sea. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1033–1046.
Spivak, A.C., E.A. Canuel, J.E. Duffy, and J.P. Richardson. 2009. Nutrient enrichment and food web composition affect ecosystem metabolism in an experimental seagrass habitat. PLoS One 4: e7473.
Statistical Institute of Belize (SIB). 2017. Population and housing census. Belmopan: SIB.
Steinberg, M.K. 2015. A nationwide assessment of threats to bonefish, tarpon and permit stocks and habitat in Belize. Environmental Biology of Fishes 98: 2277–2285.
Sweetman, B.M., J.R. Cissell, S. Rhine, and M.K. Steinberg. 2019a. Land cover changes on Ambergris Caye, Belize: A case study of unregulated tourism development. The Professional Geographer 71: 123–134.
Sweetman, B.M., J.R. Foley, and M.K. Steinberg. 2019b. A baseline analysis of coastal water quality of the port Honduras marine reserve, Belize: A critical habitat for sport fisheries. Environmental Biology of Fishes 102: 429–442.
Szmant, A.M. 2002. Nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: Is it a major cause of coral reef decline? Estuaries 25: 743–766.
Tang, L.Q., J.Y. Sheng, B.G. Hatcher, and P.F. Sale. 2006. Numerical study of circulation, dispersion, and hydrodynamic connectivity of surface waters on the Belize shelf. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans 111: C01003.
Teichberg, M., S.E. Fox, Y.S. Olsen, I. Valiela, P. Martinetto, O. Iribarne, E.Y. Muto, M.A.V. Petti, T.N. Corbisier, M. Soto-Jimenez, F. Paez-Osuna, P. Castro, H. Freitas, A. Zitelli, M. Cardinaletti, and D. Tagliapietra. 2010. Eutrophication and macroalgal blooms in temperate and tropical coastal waters: Nutrient enrichment experiments with Ulva spp. Global Change Biology 16: 2624–2637.
Torio, D.D., and G.L. Chmura. 2013. Assessing coastal squeeze of tidal wetlands. Journal of Coastal Research 29: 1049–1061.
van Tussenbroek, B.I., H.A.H. Arana, R.E. Rodríguez-Martínez, J. Espinoza-Avalos, H.M. Canizales-Flores, C.E. González-Godoy, M.G. Barba-Santos, A. Vega-Zepeda, and L. Collado-Vides. 2017. Severe impacts of brown tides caused by Sargassum spp on near-shore Caribbean seagrass communities. Marine Pollution Bulletin 122: 272–281.
Wang, F., P. Cheng, N. Chen, and Y.M. Kuo. 2020. Tidal driven nutrient exchange between mangroves and estuary reveals a dynamic source-sink pattern. Chemosphere 270: 128665.
Waycott, M., C.M. Duarte, T.J. Carruthers, R.J. Orth, W.C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck, A.R. Hughes, and G.A. Kendrick. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 12377–12381.
Welsh, D.T. 2000. Nitrogen fixation in seagrass meadows: Regulation plant-bacteria interactions and significance to primary productivity. Ecology Letters 3: 58–71.
Wood, S. 2021. mgcv: Mixed GAM computation vehicle with automatic smoothness estimation. R package version 1.8–34.
Woodland, R.J., J.R. Thomson, R. Mac-Nally, P. Reich, V. Evrard, F.Y. Wary, J.P. Walker, and P.L.M. Cook. 2015. Nitrogen loads explain primary productivity in estuaries at the ecosystem scale. Limnology and Oceanography 60: 1751–1762.
Xue, D., J. Botte, B. De Baets, F. Accoe, A. Nestler, P. Taylor, O. Van Cleemput, M. Berglund, and P. Boeckx. 2009. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface-and groundwater. Water Research 43: 1159–1170.
Young, E.H. 2003. Balancing conservation with development in marine-dependent communities. In Political Ecology, ed. K.S. Zimmerer and T.J. Bassett, 29–49. New York: Guilford Press.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Britany Clark, Maureen Mattes, Gail Hatfield, Herb Moore, Gabriela Zabel, Carolin McManus, Zachary Mattes, Cameron Allen, and Cedric Magen for their assistance with logistics, field collections, and stable isotope analysis.
Funding
RJW was partially funded by the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (UMCES) Chesapeake Biological Laboratory and the College of Southern Maryland (CSM). TM and DMQ received travel awards from CSM. This is the UMCES contribution # 6114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ken Dunton
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, T.E., Molina, J.T., Quill, D.M. et al. Seagrass Stable Isotope Composition Provides Seascape-Scale Tracking of Anthropogenic Nitrogen Inputs in a Tropical Marine Lagoon. Estuaries and Coasts 45, 1999–2011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-022-01058-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-022-01058-w