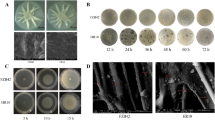
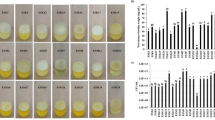
Abstract
Biofilm formation is an effective survival strategy of plant-associated microorganisms in hostile environments, so the application of biofilm-forming and exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing beneficial microbes to plants has received more attention in recent years. This study examined the ability of biofilm and EPS production of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus thuringiensis strains under different NaCl concentrations (0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 mmol/L), pH values (5.5, 6.5, 7.5, and 8.5), and phosphate levels (0, 25, 50, and 100 mmol/L at 0 and 400 mmol/L NaCl). B. subtilis BS2 and B. thuringiensis BS6/BS7 strains significantly increased biofilm formation in a similar pattern to EPS production under salt stress. B. subtilis BS2/BS3 enhanced biofilm production at slightly acidic pH with a lower EPS production but the other strains formed considerably more amount of biofilm and EPS at alkaline pH. Interestingly, higher levels of phosphate substantially decreased biofilm and EPS production at 0 mmol/L NaCl but increased biofilm formation at 400 mmol/L salt concentration. Overall, contrary to phosphate, salt and pH differently influenced biofilm and EPS production by Bacillus strains. EPS production contributed to biofilm formation to some extent under all the conditions tested. Some Bacillus strains produced more abundant biofilm under salt and pH stress, indicating their potential to form in vivo biofilms in rhizosphere and on plants, particularly under unfavorable conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ansari FA, Ahmad I, Pichtel J (2019) Growth stimulation and alleviation of salinity stress to wheat by the biofilm forming Bacillus pumilus strain FAB10. Appl Soil Ecol 143:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.05.023
Bhatia R, Ruppel S, Narula N (2008) Diversity studies of Azotobacter spp. from cotton-wheat crop** systems of India. J Basic Microbiol 48:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200800059
Çam S, Bicek S (2023) The effects of temperature, salt, and phosphate on biofilm and exopolysaccharide production by Azotobacter spp. Arch Microbiol 205:87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03428-9
Çam S, Brinkmeyer R (2020a) The effects of temperature, pH, and iron on biofilm formation by clinical versus environmental strains of Vibrio vulnificus. Folia Microbiol 65:557–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00761-9
Çam S, Brinkmeyer R (2020b) Differential expression of vvhA and CPS operon allele 1 genes in Vibrio vulnificus under biofilm and planktonic conditions. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 113:1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01452-z
Çam S, Brinkmeyer R, Schwarz JR (2019) Quantitative PCR enumeration of vcgC and 16S rRNA type A and B genes as virulence indicators for environmental and clinical strains of Vibrio vulnificus in Galveston Bay oysters. Can J Microbiol 65:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2018-0399
Çam S, Küçük Ç, Almaca A (2023) Bacillus strains exhibit various plant growth promoting traits and their biofilm-forming capability correlates to their salt stress alleviation effect on maize seedlings. J Biotechnol 369:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2023.05.004
Çam S, Küçük Ç, Cevheri C (2022) The effect of salinity-resistant biofilm-forming Azotobacter spp. on salt tolerance in maize growth. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 109:349–358. https://doi.org/10.13080/z-a.2022.109.045
Danhorn T, Hentzer M, Givskov M, Parsek MR, Fuqua C (2004) Phosphorus limitation enhances biofilm formation of the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens through the PhoR-PhoB regulatory system. J Bacteriol 186:4492–4501. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.14.4492-4501.2004
Desmond P, Best JP, Morgenroth E, Derlon N (2018) Linking composition of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the physical structure and hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms. Water Res 132:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.058
Fessia A, Barra P, Barros G, Nesci A (2022) Could Bacillus biofilms enhance the effectivity of biocontrol strategies in the phyllosphere? J Appl Microbiol 133:2148–2166. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15596
Fitzpatrick F, Humphreys H, Smyth E, Kennedy CA, O’Gara JP (2002) Environmental regulation of biofilm formation in intensive care unit isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Hosp Infect 52:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhin.2002.1309
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2415
Gao T, Foulston L, Chai Y, Wang Q, Losick R (2015) Alternative modes of biofilm formation by plant-associated Bacillus cereus. Microbiol Open 4:452–464
Hamadi F, Latrache H, Mabrrouki M, Elghmari A, Outzourhit A, Ellouali M, Chtaini A (2005) Effect of pH on distribution and adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to glass. J Adhes Sci Technol 19:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1163/1568561053066891
Haque MM, Biswas MS, Mosharaf MK, Haque MA, Islam MS, Nahar K, Islam MM, Shozib HB, Islam MM, Elahi FE (2022) Halotolerant biofilm-producing rhizobacteria mitigate seawater-induced salt stress and promote growth of tomato. Sci Rep 12(1):5599. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09519-9
Haque MM, Khatun M, Mosharaf MK, Rahman A, Haque MA, Nahar K (2023) Biofilm producing probiotic bacteria enhance productivity and bioactive compounds in tomato. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 50:102673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102673
Haque MM, Mosharaf MK, Khatun M, Haque MA, Biswas MS, Islam MS, Islam MM, Shozib HB, Miah MMU, Molla AH, Siddiquee MA (2020) Biofilm producing rhizobacteria with multiple plant growth-promoting traits promote growth of tomato under water-deficit stress. Front Microbiol 11:542053. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.542053
Haque MM, Oliver MMH, Nahar K, Alam MZ, Hirata H, Tsuyumu S (2017) CytR homolog of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum controls air-liquid biofilm formation by regulating multiple genes involved in cellulose production, c-di-GMP signaling, motility, and type III secretion system in response to nutritional and environmental signals. Front Microbiol 8:972. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00972
Harjai K, Khandwaha RK, Mittal R, Yadav V, Gupta V, Sharma S (2005) Effect of pH on production of virulence factors by biofilm cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Folia Microbiol 50:99–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931455
Hentzer M, Teitzel Gail M, Balzer Grant J, Heydorn A, Molin S, Givskov M, Parsek Matthew R (2001) Alginate overproduction affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm structure and function. J Bacteriol 183:5395–5401. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.18.5395-5401.2001
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (eds) (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Hoštacká A, Čižnár I, Štefkovičová M (2010) Temperature and pH affect the production of bacterial biofilm. Folia Microbiol 55:75–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0012-y
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) Mrbayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Jefferson KK (2004) What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol Lett 236:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.06.005
Kasim WA, Gaafar RM, Abou-Ali RM, Omar MN, Hewait HM (2016) Effect of biofilm forming plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on salinity tolerance in barley. Ann Agric Sci 61:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2016.07.003
Mendrygal KE, González JE (2000) Environmental regulation of exopolysaccharide production in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 182:599–606. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.182.3.599-606.2000
Monds RD, Silby MW, Mahanty HK (2001) Expression of the Pho regulon negatively regulates biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aureofaciens PA147-2. Mol Microbiol 42:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02641.x
Morcillo RJL, Manzanera M (2021) The effects of plant-associated bacterial exopolysaccharides on plant abiotic stress tolerance. Metabolites 11:337. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060337
Nostro A, Cellini L, Di Giulio M, D’Arrigo M, Marino A, Blanco AR, Favaloro A, Cutroneo G, Bisignano G (2012) Effect of alkaline pH on staphylococcal biofilm formation. APMIS 120:733–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0463.2012.02900.x
Prasanna R, Triveni S, Bidyarani N, Babu S, Yadav K, Adak A, Khetarpal S, Pal M, Shivay YS, Saxena AK (2014) Evaluating the efficacy of cyanobacterial formulations and biofilmed inoculants for leguminous crops. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60:349–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2013.792407
Rinaudi LV, Giordano W (2010) An integrated view of biofilm formation in rhizobia. FEMS Microbiol Lett 304:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01840.x
Seneviratne G, Thilakaratne R, Jayasekara A, Seneviratne K, Padmathilake KRE, De Silva M (2009) Develo** beneficial microbial biofilms on roots of non legumes: A novel biofertilizing technique. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Musarrat J (eds) Microbial strategies for crop improvement. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 51–62
Sharipova M, Rudakova N, Mardanova A, Evtugyn V, Akosah Y, Danilova I, Suleimanova A (2023) Biofilm formation by mutant strains of bacilli under different stress conditions. Microorganisms 11:1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061486
Stepanović S, Vuković D, Hola V, Bonaventura GD, Djukić S, Ćirković I, Ruzicka F (2007) Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS 115:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0463.2007.apm_630.x
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040023
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Velmourougane K, Prasanna R, Saxena AK (2017) Agriculturally important microbial biofilms: Present status and future prospects. J Basic Microbiol 57:548–573. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201700046
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991
Yasmeen T, Ahmad A, Arif MS, Mubin M, Rehman K, Shahzad SM, Iqbal S, Rizwan M, Ali S, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2020) Biofilm forming rhizobacteria enhance growth and salt tolerance in sunflower plants by stimulating antioxidant enzymes activity. Plant Physiol Biochem 156:242–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.09.016
Funding
This study was granted by Harran University-Scientific Research Projects (#22230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SÇ; methodology: SÇ and İB; formal analysis and investigation: SÇ and İB; writing — original draft preparation: SÇ; writing — review and editing: SÇ; funding acquisition: İB; resources: SÇ; supervision: SÇ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
All authors participated voluntarily in the research.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript and agree with the submission of this work to Folia Microbiologica.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çam, S., Badıllı, İ. The effect of NaCl, pH, and phosphate on biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide production by high biofilm producers of Bacillus strains. Folia Microbiol 69, 613–624 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-023-01101-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-023-01101-8