Abstract
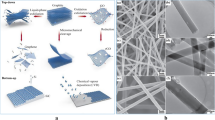
Paper-based biosensing platforms are the leading area of research today. In this work, a platform for biosensing applications with improved detection capability has been prepared using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) incorporated in electrospun nanofibers. The computational study results demonstrated that the addition of AuNPs brings about better stability to the polymer complex, and the energy band gap was found to be lowered for the PVA-AuNPs (Eg = 3.57 eV) compared to PVA (Eg = 8.82 eV). Based on this data, AuNPs were incorporated into the polymer matrix by immersion and dispersion techniques. Different ratios of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to AuNPs have been prepared, and the optical, thermal, morphological, and structural properties of the substrates were evaluated to prepare a matrix with better biosensing capabilities. Improved photoluminescence emission intensity of the order of 2.5 times higher was observed for PVA-AuNPs (7:3) nanofibers compared to bare PVA nanofibers. The improved photoluminescence emission intensity of the polymer matrix can be used as a quantitative parameter for the diagnosis of several diseases. The field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) analysis shows the successful encapsulation of AuNPs within the nanofibers with an average fiber diameter of 101 ± 21 nm and particle size of around 4.24 nm of Au NPs. The prepared PVA-AuNPs nanofibers showed stable luminescence properties (less than 10% variation) even after two months of storage at room temperature. The bioconjugation studies showed better photoluminescence emission intensity for the proposed substrate than the conventional nitrocellulose (NC) membrane. The functional performance of the modified NC membrane with electrospun nanofibers showed a three times higher response than the bare NC membrane. The present study may give new insight to use the gold-incorporated nanofibers as an additive element to the conventional NC membrane in order to bring out better bioconjugation competency with improved sensing properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an on-going study.
References
T. Dikid, S.K. Jain, A. Sharma, A. Kumar, J.P. Narain, Emerging & re-emerging infections in India: an overview. Indian J. Med. Res. 138, 19–31 (2013)
R.S. Mani, V. Ravi, A. Desai, S.N. Madhusudana, Emerging viral infections in India. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 82, 5–21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-011-0001-1
N. Sarma, Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases in South East Asia. Indian J. Dermatol. 62, 451–455 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/ijd.IJD_389_17
M. Ciotti, M. Ciccozzi, A. Terrinoni, W.-C. Jiang, C.-B. Wang, S. Bernardini, The COVID-19 pandemic. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 57, 365–388 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2020.1783198
S. Li, B.-K. Lee, Formation of locally aligned nanofibers by electrospinning on preplaced dielectric particles. Mater. Res. Express 5, 095031 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad920
Y. Li, J. Zhu, P. Zhu, C. Yan, H. Jia, Y. Kiyak, J. Zang, J. He, M. Dirican, X. Zhang, Glass fiber separator coated by porous carbon nanofiber derived from immiscible PAN/PMMA for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 552, 31–42 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.01.062
J.T. Jung, J.F. Kim, H.H. Wang, E. Di Nicolo, E. Drioli, Y.M. Lee, Understanding the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 514, 250–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.04.069
D. Jao, V.Z. Beachley, Continuous dual-track fabrication of polymer micro-/nanofibers based on direct drawing. ACS Macro Lett. 8, 588–595 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00167
J. Yan, Y. Han, S. **a, X. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Yu, B. Ding, Polymer template synthesis of flexible BaTiO3 crystal nanofibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1907919 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201907919
W. Zhang, X. Yu, Y. Li, Z. Su, K.D. Jandt, G. Wei, Protein-mimetic peptide nanofibers: motif design, self-assembly synthesis, and sequence-specific biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 80, 94–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.12.001
H.M. Ibrahim, M.M. Reda, A. Klingner, Preparation and characterization of green carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS)—polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) electrospun nanofibers containing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and its potential use as biomaterials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 821–829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.174
J.S. Algethami, T. Amna, L.S. Alqarni, A.A. Alshahrani, M.A.M. Alhamami, A.F. Seliem, B.H.A. Al-Dhuwayin, M.S. Hassan, Production of ceramics/metal oxide nanofibers via electrospinning: new insights into the photocatalytic and bactericidal mechanisms. Materials 16, 5148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145148
X. Yang, Y. Chen, C. Zhang, G. Duan, S. Jiang, Electrospun carbon nanofibers and their reinforced composites: preparation, modification, applications, and perspectives. Compos. Part B Eng. 249, 110386 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110386
S.T. Aruna, L.S. Balaji, S.S. Kumar, B.S. Prakash, Electrospinning in solid oxide fuel cells—a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 67, 673–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.003
J. Hu, H. Wei, Q. Wu, X. Zhao, K. Chen, J. Sun, Z. Cui, C. Wang, Preparation and characterization of luminescent polyimide/glass composite fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 18, 4329–4339 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.04.101
G. El-Fawal, Polymer nanofibers electrospinning: a review. Egypt. J. Chem. (2019). https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2019.14837.1898
Y. Yan, X. Liu, J. Yan, C. Guan, J. Wang, Electrospun nanofibers for new generation flexible energy storage. Energy Environ. Mater. 4, 502–521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12146
M.M. Abdul-Hameed, S.A.P. Mohamed-Khan, B.M. Thamer, N. Rajkumar, H. El-Hamshary, M. El-Newehy, Electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery applications: methods and mechanism. Polym. Adv. Technol. 34, 6–23 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5884
Y. Bian, C. Zhang, H. Wang, Q. Cao, Degradable nanofiber for eco-friendly air filtration: progress and perspectives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 306, 122642 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122642
J. Zhou, L. Wang, W. Gong, B. Wang, D.-G. Yu, Y. Zhu, Integrating Chinese herbs and western medicine for new wound dressings through handheld electrospinning. Biomedicines 11, 2146 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146
K. Halicka, J. Cabaj, Electrospun nanofibers for sensing and biosensing applications—a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126357
G. Zhang, X. Zhao, J. Hu, Y. Li, H. Ma, Z. Cui, Preparation and adsorption performance of cellulose acetate fiber-chitosan/titanium dioxide surface layers composite membranes prepared based on a sol-gel method. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 61, 1248–1260 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2022.2159619
C. Huang, L. Xu, X. Xu, L. Ma, H. Bao, J. Liao, J. Wang, J. Han, G. Xu, D. Huang, B. Ye, H. Zhang, M. Wu, X. Zhao, H. Ma, Highly amidoxime utilization ratio of porous poly(cyclic imide dioxime) nanofiber for effective uranium extraction from seawater. Chem. Eng. J. 443, 136312 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136312
G. Ren, D. Lu, Y. Zhang, Z. Cui, Z. Li, H. Yu, J. He, Poly(methyl methacrylate) embedded fluorine-free polyurethane electrospun nanofiber membranes with enhanced waterproof and breathable performance. Compos. Commun. 43, 101698 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2023.101698
F. Ebrahimi, S.R. Nabavi, A. Omrani, Fabrication of hydrophilic hierarchical PAN/SiO2 nanofibers by electrospray assisted electrospinning for efficient removal of cationic dyes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 25, 102258 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102258
M.N. Uddin, Md. Mohebbullah, S.M. Islam, M.A. Uddin, Md. Jobaer, Nigella/honey/garlic/olive oil co-loaded PVA electrospun nanofibers for potential biomedical applications. Prog. Biomater. 11, 431–446 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-022-00207-5
L. Yang, C. Niu, X. Cao, Y. Wang, Z. Zhu, H. Sun, W. Liang, J. Li, A. Li, Mechanically robust conjugated microporous polymer membranes prepared using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) electrospun nanofibers as a template for efficient PM capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 637, 305–316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.01.059
O. Mitxelena-Iribarren, M. Riera-Pons, S. Pereira, F.J. Calero-Castro, J.M. Castillo-Tuñón, J. Padillo-Ruiz, M. Mujika, S. Arana, Drug-loaded PCL electrospun nanofibers as anti-pancreatic cancer drug delivery systems. Polym. Bull. 80, 7763–7778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04425-6
M.I. Baker, S.P. Walsh, Z. Schwartz, B.D. Boyan, A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 100B, 1451–1457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.32694
G. Swift, Directions for environmentally biodegradable polymer research. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 105–110 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1021/ar00027a005
W.R. Gombotz, D.K. Pettit, Biodegradable polymers for protein and peptide drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 6, 332–351 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1021/bc00034a002
S. Ram, T.K. Mandal, Photoluminescence in small isotactic, atactic and syndiotactic PVA polymer molecules in water. Chem. Phys. 303, 121–128 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2004.05.006
D. Sharma, B.K. Satapathy, Polymer substrate-based transition metal modified electrospun nanofibrous materials: current trends in functional applications and challenges. Polym. Rev. 62, 439–484 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2021.1972006
M. Baghali, W.A.D.M. Jayathilaka, S. Ramakrishna, The role of electrospun nanomaterials in the future of energy and environment. Materials 14, 558 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030558
G. Wang, D. Yu, A.D. Kelkar, L. Zhang, Electrospun nanofiber: emerging reinforcing filler in polymer matrix composite materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 75, 73–107 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.08.002
M.A. Teixeira, M.C. Paiva, M.T.P. Amorim, H.P. Felgueiras, Electrospun nanocomposites containing cellulose and its derivatives modified with specialized biomolecules for an enhanced wound healing. Nanomaterials 10, 557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030557
T. Patil, R. Gambhir, A. Vibhute, A.P. Tiwari, Gold nanoparticles: synthesis methods, functionalization and biological applications. J. Clust. Sci. 34, 705–725 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02287-6
J. Najeeb, U. Farwa, F. Ishaque, H. Munir, A. Rahdar, M.F. Nazar, M.N. Zafar, Surfactant stabilized gold nanomaterials for environmental sensing applications—a review. Environ. Res. 208, 112644 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112644
S. Ali, X. Chen, W. Shi, G. Huang, L. Yuan, L. Meng, S. Chen, X. Zhonghao, X. Chen, Recent advances in silver and gold nanoparticles-based colorimetric sensors for heavy metal ions detection: a review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 53, 718–750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2021.1973886
J.P. Oliveira, A.R. Prado, W.J. Keijok, M.R.N. Ribeiro, M.J. Pontes, B.V. Nogueira, M.C.C. Guimarães, A helpful method for controlled synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles through response surface modeling. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 216–226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.04.003
D. Quesada-González, C. Stefani, I. González, A. De La Escosura-Muñiz, N. Domingo, P. Mutjé, A. Merkoçi, Signal enhancement on gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow tests using cellulose nanofibers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111407
M J Frisch, G W Trucks, H B Schlegel, G E Scuseria, M A Robb, J R Cheeseman, G Scalmani, V Barone, B Mennucci, G A Peterson, H Nakatsuji, M Caricato, X Li, H P Hratchian, A F Izmaylov, J Blonio, G Zheng, J L Sonnenberg, M Hada, M Ehara, K Toyota, R Fukuda, J Hasegawa, M Ishida, T Nakajima, Y Honda, O Kitao, H Nakai, T Vreven, J A Montogomery Jr., J E Peralta, F Ogliaro, M Bearpark, J J Heyd, E Brothers, K N Kudin, V N Staroverov, R Kobayashi, J Normand, K Raghavachari, A Rendell, J C Burant, S S Iyengar, J Tomasi, M Cossi, N Rega, J M Millam, M Klene, J E Knox, J B Cross, V Bakken, C Adamo, J Jaramillo, R R Gomperts, R E Stratmann, O Yazyev, A J Austin, R Cammi, C Pomelli, J W Ochterski, R L Martin, K Morokuma, V G Zakrzewski, G A Voth, P Salvador, J J Dannenberg, S Dapprich, A D Daniels, O Farkas, J B Foresman, J V Ortiz, J Cioslowski, D J Fox, Gaussian ‘16W, Rev. C.01, (2019)
E.D. Glendening, F. Weinhold, Natural resonance theory: II. Natural bond order and valency. Wiley Online Libr. 19, 610–627 (1998)
P.K. Jain, M.A. El-Sayed, Plasmonic coupling in noble metal nanostructures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 487, 153–164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2010.01.062
M.R. Tchalala, D.H. Anjum, S. Chaieb, Effect of ionic liquid (emim BF 4) on the dispersion of gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 758, 012020 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/758/1/012020
J. Zheng, C. Zhou, M. Yu, J. Liu, Different sized luminescent gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 4, 4073 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr31192e
M. Pattabi, R.M. Pattabi, Photoluminescence from gold and silver nanoparticles. Nano Hybrids 6, 1–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/NH.6.1
J.P. Wilcoxon, J.E. Martin, F. Parsapour, B. Wiedenman, D.F. Kelley, Photoluminescence from nanosize gold clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 108, 9137–9143 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.476360
C. Fernández-Ponce, J.P. Muñoz-Miranda, D.M. De Los-Santos, E. Aguado, F. García-Cozar, R. Litrán, Influence of size and surface cap** on photoluminescence and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 20, 305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4406-0
H.A. Alluhaybi, S.K. Ghoshal, B.O. Alsobhi, W.N. Wan-Shamsuri, Visible photoluminescence from gold nanoparticles: a basic insight. Optik 192, 162936 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.162936
W. Wang, X. Ding, Q. Xu, J. Wang, L. Wang, X. Lou, Zeta-potential data reliability of gold nanoparticle biomolecular conjugates and its application in sensitive quantification of surface absorbed protein. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 148, 541–548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.09.021
T.P. Mthethwa, M.J. Moloto, A. De Vries, K.P. Matabola, Properties of electrospun CdS and CdSe filled poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) nanofibres. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 569–575 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.12.022
N.D. Luong, J. Oh, Y. Lee, J.H. Yeon, J. Hur, J.J. Park, J.M. Kim, J. Nam, Immobilization of gold nanoparticles on poly(methyl methacrylate) electrospun fibers exhibiting solid-state surface plasmon effect. Surf. Interface Anal. 44, 318–321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.3804
O.A. Ghazy, M.M. Shehata, H.M. Hosni, H.H. Saleh, Z.I. Ali, In situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles within poly (vinyl alcohol) matrix under electron accelerator radiation: photoluminescence, thermal and electrical properties. Opt. Quantum Electron. 53, 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02727-5
H. Lu, L. Zou, Y. Xu, H. Sun, Y.V. Li, Preparation and study of poly vinyl alcohol/hyperbranched polylysine fluorescence fibers via wet spinning. Mater. Res. Express 5, 025102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaaedc
S.D. Borse, S.S. Joshi, Optical and structural properties of PVA capped gold nanoparticles and their antibacterial efficacy. Adv. Chem. Lett. 1, 15–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1166/acl.2013.1007
A. Sillen, Y. Engelborghs, The correct use of “average” fluorescence parameters. Photochem. Photobiol. 67, 475–486 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1998.tb09082.x
B. Smith, Infrared spectral interpretation a systematic approach (CRC Press LLC, Florida, 2000)
I. Jipa, A. Stoica, M. Stroescu, L.-M. Dobre, T. Dobre, S. **ga, C. Tardei, Potassium sorbate release from poly(vinyl alcohol)-bacterial cellulose films. Chem. Pap. (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0068-4
G. Aruldhas, Molecular structure and spectroscopy, 2nd edn. (PHI Learning Private Limited, 2008)
H. Zhu, M. Du, M. Zhang, P. Wang, S. Bao, M. Zou, Y. Fu, J. Yao, Self-assembly of various Au nanocrystals on functionalized water-stable PVA/PEI nanofibers: a highly efficient surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates with high density of “hot” spots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 54, 91–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.047
C. Sun, R. Qu, C. Ji, Y. Meng, C. Wang, Y. Sun, L. Qi, Preparation and property of polyvinyl alcohol-based film embedded with gold nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 11, 1005–1010 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9552-3
L.H. Gaabour, Spectroscopic and thermal analysis of polyacrylamide/chitosan (PAM/CS) blend loaded by gold nanoparticles. Results Phys. 7, 2153–2158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.06.027
E.D. Boland, B.D. Coleman, C.P. Barnes, D.G. Simpson, G.E. Wnek, G.L. Bowlin, Electrospinning polydioxanone for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 1, 115–123 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2004.09.003
J. Rnjak-Kovacina, S.G. Wise, Z. Li, P.K.M. Maitz, C.J. Young, Y. Wang, A.S. Weiss, Tailoring the porosity and pore size of electrospun synthetic human elastin scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering. Biomaterials 32, 6729–6736 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.05.065
S. H. G. Neubert, Controllability of electrospinning and electrospraying-advances and application, National University of Singapore, (2010). https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/48636297.pdf
P.K. Khanna, R. Gokhale, V.V.V.S. Subbarao, A.K. Vishwanath, B.K. Das, C.V.V. Satyanarayana, PVA stabilized gold nanoparticles by use of unexplored albeit conventional reducing agent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 92, 229–233 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.01.016
M.S.S. Bharathi, C. Byram, D. Banerjee, D. Sarma, B. Barkakaty, V.R. Soma, Gold nanoparticle nanofibres as SERS substrate for detection of methylene blue and a chemical warfare simulant (methyl salicylate). Bull. Mater. Sci. 44, 103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02402-9
A.A. Al-Shamari, A.M. Abdelghany, H. Alnattar, A.H. Oraby, Structural and optical properties of PEO/CMC polymer blend modified with gold nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12, 1597–1605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.050
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India, under the CRG scheme (No- CRG/2020/001529). The authors acknowledge HLL Lifecare Limited, Trivandrum, Kerala, India, for providing necessary facilities and support. The authors acknowledge the technical support provided by Ms. Alice Noble A, Research Scholar, Department of Physics, University of Kerala (Computational studies), and Ms. Arya R S, Research Intern, CRDC (Bioconjugation studies). The authors would also like to thank COE-AMGT, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore for FESEM–EDAX analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ms. Sujitha A S literature survey, performing experiments for the study, manuscript writing—original draft, graph plotting and analysis. R. Saikant: performing experiments for the lateral flow assay kits, part of manuscript writing. Dr. Lakshminarayanan Ragupathy: visualization, formal analysis, review and editing. Dr. Hubert Joe conceptualization, methodology, theoretical studies, formal analysis, review and editing. Dr. Diksha Painuly: conceptualization, methodology, resources, validation, formal analysis, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this research work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sujitha, A.S., Saikant, R., Ragupathy, L. et al. Gold Nanoparticles-Incorporated Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for Optical Biosensing Applications: An Experimental and Computational Approach. Fibers Polym 25, 1193–1210 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-024-00511-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-024-00511-w