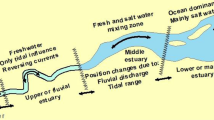
Abstract
For the stable securing of water resources for farming and residential purposes, the embankment, preventing the tidal action and intrusion of seawater into the river, have been constructed in the mouth of many major rivers in Korea. The Seom** River is one of the major rivers without embankment in their mouth and had been famous for the biodiversity and overall environmental health. However, the brackish water zone in the Seom** River has been gradually extending upstream due to the factors such as extracting aggregate and dredging in the channel, reclamation of the river mouth, and the depletion of runoff discharge from watershed. The saltwater intrusion extended upstream has resulted in the problems such as abrupt changes in ecosystems and environmental conditions over the brackish water areas. In this study, the extent of salinity intrusion has been estimated with Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC) model for the total reach of the Seom** River with the length of 78 km (from Gurye Gauging Station to Yeosu Tide Station, including the endpoint of the Seom** River). The antecedent rainfall events has been applied to the established model for calibration and verification of the model. In order to consider the effect of the dam construction and resulting changes in runoff characteristics of watershed, the flow duration analyses have been conducted for the cases of before and after the construction of Juam Dam. The results show that the construction of dam and conveying water over the basins result in the depletion of the streamflow, and the depletion of discharge from watershed extend the range of salinity intrusion about 1 km upstream.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JM, Cha KU, Ryoo KS, Lyu S (2011) Study of the lower duration curve characteristic by reservoir and weir couple-operating system in Geum River basin. Journal of Korea Water Resources Association 44(4):285–293, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3741/JKWRA.2011.44.4.285
Ahn JM, Hur YT, Lyu S (2013) Coupling simulation with multidimensional models for river flow. Journal of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers 33(1):1–10, DOI: https://doi.org/10.12652/KSCE.2013.33.1.137 (in Korean)
Ahn JM, Lyu S (2012) Development of GUI system for coupling of multi-dimensional hydraulic models. Journal of Korean Wetlands Society 14(3):353–363, DOI: https://doi.org/10.17663/JWR.2012.14.3.353
Ahn JM, Lyu S, Kim JC (2012) Study of operation rules for flood control to Seom** River dam using HEC-ResSim. Journal of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers 32(2b):93–101, DOI: https://doi.org/10.12652/KSCE.2012.32.2B.093 (in Korean)
Ahn JM, Park IH (2012) An assessment on the hydraulic characteristics of a multi-dimensional model in response to measurement resolution and spatial interpolation methods. Journal of the Korean Society for GeoSpatial Information System 20(1):43–51, DOI: https://doi.org/10.7319/kogsis.2012.20.1.043
Ahn JM, Park IH, Lyu S, Hur YT (2012) Evaluation of optimal grid resolution for hydrodynamic proper simulation. Journal of the Korean Society for GeoSpatial Information System 20(1):109–116, DOI: https://doi.org/10.7319/kogsis.2012.20.1.109
Buschman FA, Hoitink AJF, Van Der Vegt M, Hoekstra P (2010) Subtidal flow division at a shallow tidal junction. Water Resources Research 46(12):1–12, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2010WR009266
Chen L, Yang Z, Liu H (2016) Assessing the eutrophication risk of the Danjiangkou Reservoir based on the EFDC model. Ecological Engineering 96:117–127, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.02.021
Des M, deCastro M, Sousa MC, Dias JM, Gómez-Gesteira M (2019) Hydrodynamics of river plume intrusion into an adjacent estuary: The Minho River and Ria de Vigo. Journal of Marine Systems 189: 87–97, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2018.10.003
Dunlop G, Palanichamy J, Kokkat A, James EJ, Palani S (2019) Simulation of saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifer of Nagapattinam in the lower cauvery basin using SEAWAT. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 8:294–301
Easton AK (1977) Selected programs for tide analysis and prediction. The Flinders Institute for Atmospheric and Marine Science, South Australia, 1–77
Galperin B, Kantha LH, Hassid S, Rosati A (1988) A quasi-equilibrium turbulent energy model for geophysical flows. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences 45(1):55–62, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1988)045<0055:AQETEM>2.0.CO;2
Gong W, Shen J, Jia L (2013) Salt intrusion during the dry season in the Huangmaohai Estuary, Pearl River Delta, China. Journal of Marine Systems 111–112:235–252, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.11.006
Hamrick JM (1992) A three-dimensional environmental fluid dynamics computer code: Theoretical and computational aspects. Special Report No. 317, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg, VA, USA, DOI: https://doi.org/10.21220/V5TT6C
Hamrick JM, Wu TS (1997) Computational design and optimization of the EFDC/HEM3D surface water hydrodynamic and eutrophication models. Next generation environmental models and computational methods. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 143–161
Huang F, Ye C, Wen X, Yan J, Zhang N (1994) Characteristics of salinity and active range of saline wedge in the Huangmaohai Estuary. Marine Science Bulletin 23(2):33–39 (in Chinese)
Hur YT, Ryoo KS, Cha KU (2010) Introduce of the orthogonal curves grid generation technique considering moving boundary conditions. Proc. of the KSCE Annual Conference and Civil Exposition, October 20–22, Incheon, Korea (in Korean)
Jeong S, Yeon K, Hur Y, Oh K (2010) Salinity intrusion characteristics analysis using EFDC model in the downstream of Geum River. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22(6):934–939, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60201-1
Jung K (2010) Estimation of salt distribution in the downstream of Seom** River. MSc Thesis, Honam University, Gwangju, Korea
Kwak G (2008) Temporal and spatial mixing characteristics of Seom** River discharges using a three-dimensional numerical model. MSc Thesis, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea
Lee J, Kim Y (2011) Analysis of flow duration characteristics due to environmental change in Korea river basin. Journal of Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation 11(1):67–75, DOI: https://doi.org/10.9798/kosham.2011.11.1.067
Lee JW, Kim HS, Woo HS (1993) An analysis of the effect of damming on flow duration characteristics of five major rivers in Korea. Journal of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers 13(3):79–91 (in Korean)
Liu S, Tang Z, Gao M, Hou G (2017) Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Science of the Total Environment 607–608: 586–599
Maidment DR (1992) Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, USA, 18.53–18.54
Mellor GL, Yamada T (1982) Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Reviews of Geophysics 20(4): 851–875, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/RG020i004p00851
MOLIT (2009) The basic plan of stream-improvement for Seom** River. CM00054310, Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Gunpo, Korea
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidlines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers 50(3):885–900, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Nguyen MT, Renaud FG, Sebesvari Z (2019) Drivers of change and adaptation pathways of agricultural systems facing increased salinity intrusion in coastal areas of the Mekong and Red River deltas in Vietnam. Environmental Science and Policy 92:331–348
Noh J, Lee J, Shin J (2011) Analysis of saltwater intrusion by flushing discharge in the Seom** River estuary. Environmental Impact Assessment 20(3):325–335, DOI: https://doi.org/10.14249/eia.2011.20.3.325
Park SD (2003) Dimensionless flow duration curve in natural river. Journal of Korea Water Resources Association 36(1):33–44, DOI:https://doi.org/10.3741/JKWRA.2003.36.1.033
Uncles RJ, Stephens JA (2011) The effects of wind, runoff and tides on salinity in a strongly tidal sub-estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 34(4): 758–774, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-010-9365-3
Zhou J, Falconer RA, Lin B (2014) Refinements to the EFDC model for predicting the hydro-environmental impacts of a barrage across the Severn Estuary. Renewable Energy 62:490–505, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.08.012
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER) funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea, and the Changwon National University Research Fund in 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, J.M., Lee, K. & Lyu, S. Effect of Changes in Watershed Runoff Characteristics on Salinity Intrusion in Estuary Using EFDC. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 87–98 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1306-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1306-5