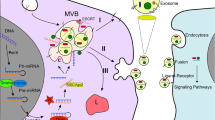
Abstract
Introduction
S100A4 promotes the establishment of tumor microenvironment for malignant cancer cells, and knockdown of S100A4 can inhibit tumorigenesis. However, there is no efficient way to target S100A4 in metastatic tumor tissues. Here, we investigated the role of siS100A4-loaded iRGD-modified extracellular vesicles (siS100A4-iRGD-EVs) in postoperative breast cancer metastasis.
Methods
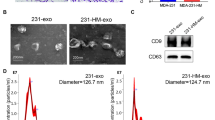
siS100A4-iRGD-EVs nanoparticles were engineered and analyzed using TEM and DLS. siRNA protection, cellular uptake, and cytotoxicity of EV nanoparticles were examined in vitro. Postoperative lung metastasis mouse model was created to investigate the tissue distribution and anti-metastasis roles of nanoparticles in vivo.
Results
siS100A4-iRGD-EVs protected siRNA from RNase degradation, enhanced the cellular uptake and compatibility in vitro. Strikingly, iRGD-modified EVs significantly increased tumor organotropism and siRNA accumulation in lung PMNs compared to siS100A4-EVs in vivo. Moreover, siS100A4-iRGD-EVs treatment remarkedly attenuated lung metastases from breast cancer and increased survival rate of mice through suppressing S100A4 expression in lung.
Conclusions
siS100A4-iRGD-EVs nanoparticles show more potent anti-metastasis effect in postoperative breast cancer metastasis mouse model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfattah, N., P. Kumar, C. Wang, J. S. Leu, W. F. Flynn, R. Gao, D. S. Baskin, K. Pichumani, O. B. Ijare, S. L. Wood, S. Z. Powell, D. L. Haviland, B. C. Parker Kerrigan, F. F. Lang, S. S. Prabhu, K. M. Huntoon, W. Jiang, B. Y. S. Kim, J. George, and K. Yun. Single-cell analysis of human glioma and immune cells identifies S100A4 as an immunotherapy target. Nat. Commun. 13(1):767, 2022.
Ambartsumian, N., J. Klingelhofer, and M. Grigorian. The multifaceted S100A4 protein in cancer and inflammation. Methods Mol. Biol. 339–365:2019, 1929.
Bergin, A. R. T., and S. Loi. Triple-negative breast cancer: recent treatment advances. F1000Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.18888.1.
Bian, Y., J. Guo, L. Qiao, and X. Sun. miR-3189-3p mimics enhance the effects of S100A4 siRNA on the inhibition of proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting CFL2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(1):236, 2018.
Bianchini, G., J. M. Balko, I. A. Mayer, M. E. Sanders, and L. Gianni. Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 13(11):674–690, 2016.
Chen, B. Y., C. W. Sung, C. Chen, C. M. Cheng, D. P. Lin, C. T. Huang, and M. Y. Hsu. Advances in exosomes technology. Clin. Chim. Acta. 493:14–19, 2019.
Chulpanova, D. S., K. V. Kitaeva, V. James, A. A. Rizvanov, and V. V. Solovyeva. Therapeutic prospects of extracellular vesicles in cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 9:1534, 2018.
D’Abreo, N., and S. Adams. Immune-checkpoint inhibition for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: safety first? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16(7):399–400, 2019.
Dahlmann, M., A. Monks, E. D. Harris, D. Kobelt, M. Osterland, F. Khaireddine, P. Herrmann, W. Kemmner, S. Burock, W. Walther, R. H. Shoemaker, and U. Stein. Combination of Wnt/beta-catenin targets S100A4 and DKK1 improves prognosis of human colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14(1):37, 2021.
Fei, F., K. Liu, C. Li, J. Du, Z. Wei, B. Li, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, and S. Zhang. Molecular mechanisms by which S100A4 regulates the migration and invasion of PGCCs with their daughter cells in human colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 10:182, 2020.
Harbeck, N., F. Penault-Llorca, J. Cortes, M. Gnant, N. Houssami, P. Poortmans, K. Ruddy, J. Tsang, and F. Cardoso. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 5(1):66, 2019.
Ishikawa, M., M. Osaki, M. Yamagishi, K. Onuma, H. Ito, F. Okada, and H. Endo. Correlation of two distinct metastasis-associated proteins, MTA1 and S100A4, in angiogenesis for promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 38(24):4715–4728, 2019.
Kalluri, R., and V. S. LeBleu. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977.
Kargaard, A., J. P. G. Sluijter, and B. Klumperman. Polymeric siRNA gene delivery—transfection efficiency versus cytotoxicity. J. Control. Release. 316:263–291, 2019.
Kim, M. S., M. J. Haney, Y. Zhao, V. Mahajan, I. Deygen, N. L. Klyachko, E. Inskoe, A. Piroyan, M. Sokolsky, O. Okolie, S. D. Hingtgen, A. V. Kabanov, and E. V. Batrakova. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 12(3):655–664, 2016.
Kim, B., S. Jung, H. Kim, J. O. Kwon, M. K. Song, M. K. Kim, H. J. Kim, and H. H. Kim. The role of S100A4 for bone metastasis in prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 21(1):137, 2021.
Li, J., Y. Tian, D. Shan, A. Gong, L. Zeng, W. Ren, L. **ang, E. Gerhard, J. Zhao, J. Yang, and A. Wu. Neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor-mediated biodegradable photoluminescent nanobubbles as ultrasound contrast agents for targeted breast cancer imaging. Biomaterials. 116:106–117, 2017.
Limbach, L. K., Y. Li, R. N. Grass, T. J. Brunner, M. A. Hintermann, M. Muller, D. Gunther, and W. J. Stark. Oxide nanoparticle uptake in human lung fibroblasts: effects of particle size, agglomeration, and diffusion at low concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(23):9370–9376, 2005.
Mishra, S. K., H. R. Siddique, and M. Saleem. S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31(1–2):163–172, 2012.
Nader, J. S., J. Guillon, C. Petit, A. Boissard, F. Franconi, S. Blandin, S. Lambot, M. Gregoire, V. Verriele, B. Nawrocki-Raby, P. Birembaut, O. Coqueret, C. Guette, and D. L. Pouliquen. S100A4 is a biomarker of tumorigenesis, EMT, invasion, and colonization of host organs in experimental malignant mesothelioma. Cancers (Basel). 12(4):939, 2020.
Ochiya, T., K. Takenaga, and H. Endo. Silencing of S100A4, a metastasis-associated protein, in endothelial cells inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. Angiogenesis. 17(1):17–26, 2014.
Pecot, C. V., G. A. Calin, R. L. Coleman, G. Lopez-Berestein, and A. K. Sood. RNA interference in the clinic: challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 11(1):59–67, 2011.
Pofali, P., A. Mondal, and V. Londhe. Exosome as a natural gene delivery vector for cancer treatment. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 20(11):821–830, 2020.
Rakha, E. A., and S. Chan. Metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.). 23(9):587–600, 2011.
Rezaie, J., S. Ajezi, C. B. Avci, M. Karimipour, M. H. Geranmayeh, A. Nourazarian, E. Sokullu, A. Rezabakhsh, and R. Rahbarghazi. Exosomes and their application in biomedical field: difficulties and advantages. Mol. Neurobiol. 55(4):3372–3393, 2018.
Sugahara, K. N., G. B. Braun, T. H. de Mendoza, V. R. Kotamraju, R. P. French, A. M. Lowy, T. Teesalu, and E. Ruoslahti. Tumor-penetrating iRGD peptide inhibits metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 14(1):120–128, 2015.
Tannock, I. F., and J. A. Hickman. Limits to personalized cancer medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 375(13):1289–1294, 2016.
Thery, C., L. Zitvogel, and S. Amigorena. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2(8):569–579, 2002.
Van den Boorn, J. G., M. Schlee, C. Coch, and G. Hartmann. SiRNA delivery with exosome nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 29(4):325–326, 2011.
Van der Pol, E., F. A. Coumans, A. E. Grootemaat, C. Gardiner, I. L. Sargent, P. Harrison, A. Sturk, T. G. van Leeuwen, and R. Nieuwland. Particle size distribution of exosomes and microvesicles determined by transmission electron microscopy, flow cytometry, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and resistive pulse sensing. J. Thromb. Haemost. 12(7):1182–1192, 2014.
Yin, H., J. Yang, Q. Zhang, J. Yang, H. Wang, J. Xu, and J. Zheng. iRGD as a tumor penetrating peptide for cancer therapy (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 15(5):2925–2930, 2017.
Zhang, X., H. Zhang, J. Gu, J. Zhang, H. Shi, H. Qian, D. Wang, W. Xu, J. Pan, and H. A. Santos. Engineered extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy. Adv. Mater.33(14):e2005709, 2021.
Zhao, L., C. Gu, Y. Gan, L. Shao, H. Chen, and H. Zhu. Exosome-mediated siRNA delivery to suppress postoperative breast cancer metastasis. J. Control. Release. 318:1–15, 2020.
Zhao, Z., A. Ukidve, J. Kim, and S. Mitragotri. Targeting strategies for tissue-specific drug delivery. Cell. 181(1):151–167, 2020.
Zhou, Y., M. Han, and J. Gao. Prognosis and targeting of pre-metastatic niche. J. Control. Release. 325:223–234, 2020.
Funding
This study was supported by Science and technology innovation project of Foshan (2220001003854, 2220001004847), Medical research project of Foshan Health Bureau (20220479), GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515111087), Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (A2022509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
All animal studies were carried out following the protocols established by the Ethics Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Foshan.
Additional information
Associate Editor Alyssa Panitch oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, R., He, T., Zhang, K. et al. Tumor-Targeting Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with siS100A4 for Suppressing Postoperative Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 16, 117–125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00757-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00757-5