Abstract
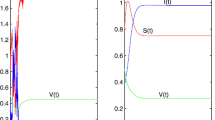
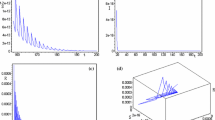
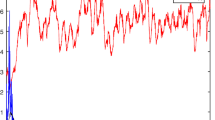
In this paper, a SIS epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and ratio dependent pulse control is proposed and analyzed. Firstly, for the system that ignores the effect of pulses, the basic reproductive number \(R_0\) is derived using the next-generation matrix method, and the stability of the equilibria of the system is analyzed. And then the dynamics of the system containing pulse effects was investigated. The existence of periodic solutions has been proven by constructing appropriate Poincaré map**s and using the fixed point theorem. We found that pulses have a significant impact on system dynamics. Under the influence of pulses, the system trajectory undergoes periodic oscillations, which are verified by numerical simulations.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
World Health Organization. COVID-19 situation [EB/OL]. https://covid19.who.int/
World Health Organization. Monkeypox situation [EB/OL]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON381
General Administration of Customs People’s Republic of China. The situation of Monkeypox infection [EB/OL]. http://wss.customs.gov.cn/wss/zcfg32/flfg70/5292628/index.html
Sherman, M.: Nuevas estrategias de tratamiento en la hepatitis B crónica. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 4(2), 3–6 (2007)
Larsen, S.L., Shin, I., Joseph, J., West, H., Anorga, R., Mena, G.E., Mahmud, A.S., Martinez, P.P.: Quantifying the impact of SARS-CoV-2 temporal vaccination trends and disparities on disease control. Sci. Adv. 9(31), 9920 (2023)
Gibas, K.M., Kelly, S.G., Arribas, J.R., Cahn, P., Orkin, C., Daar, E.S., Sax, P.E., Taiwo, B.O.: Two-drug regimens for HIV treatment. Lancet HIV 9(12), 868–883 (2022)
Peng, Q., **e, Y., Kuai, L., Wang, H., Qi, J., Gao, G.F., Shi, Y.: Structure of monkeypox virus DNA polymerase holoenzyme. Science 379(6627), 100–105 (2023)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 115(772), 700–721 (1927)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics. II—The problem of endemicity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 138(834), 55–83 (1932)
Yang, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, S., Zhang, T.: Dynamical analysis of a fractional order HCV infection model with acute and chronic and general incidence rate. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 12(6), 2283–2298 (2022)
Wang, W., Wang, X., Fan, X.: Threshold dynamics of a reaction–advection–diffusion waterborne disease model with seasonality and human behavior change. Int. J. Biomath. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793524523501061
Xu, R., Ma, Z.: Global stability of a SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and time delay. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10(5), 3175–3189 (2009)
Wang, W.: Global behavior of an SEIRS epidemic model with time delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 15(4), 423–428 (2002)
Guo, K., Ma, W.: Permanence and extinction for a nonautonomous Kawasaki disease model with time delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 122, 107511 (2021)
Lv, J., Ma, W.: Global asymptotic stability of a delay differential equation model for SARS-CoV-2 virus infection mediated by ACE2 receptor protein. Appl. Math. Lett. 142, 108631 (2023)
Sun, G., **, Z., Mai, A.: Dynamics of a two-patch SIR model with disease surveillance mediated infection force. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 132, 107872 (2024)
Pei, Y., Shen, N., Zhao, J., Yu, Y., Chen, Y.: Analysis and simulation of a delayed HIV model with reaction-diffusion and sliding control. Math. Comput. Simul. 212, 382–405 (2023)
Ren, X., Wang, K., Liu, X.: Dynamics on a degenerated reaction-diffusion Zika transmission model. Appl. Math. Lett. 150, 108935 (2024)
Chen, Y., Song, H., Liu, S.: Evaluations of COVID-19 epidemic models with multiple susceptible compartments using exponential and non-exponential distribution for disease stages. Infect. Dis. Model. 7(4), 795–810 (2022)
Chen, X., Cui, R.: Analysis on a spatial SIS epidemic model with saturated incidence function in advective environments: I. Conserved Total Population. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 83(6), 2522–2544 (2023)
Cui, W., Zhao, Y.: Saddle-node bifurcation and Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation of a SIRS epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. J. Differ. Equ. 384, 252–278 (2024)
Whittaker, D.G., Herrera-Reyes, A.D., Hendrix, M., Owen, M.R., Band, L.R., Mirams, G.R., Bolton, K.J., Preston, S.P.: Uncertainty and error in SARS-CoV-2 epidemiological parameters inferred from population-level epidemic models. J. Theor. Biol. 558, 111337 (2023)
**e, Y., Wang, Z.: A ratio-dependent impulsive control of an SIQS epidemic model with non-linear incidence. Appl. Math. Comput. 423, 127018 (2022)
**ao, D., Ruan, S.: Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 208(2), 419–429 (2007)
**ao, Y., Tang, S.: Dynamics of infection with nonlinear incidence in a simple vaccination model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(5), 4154–4163 (2010)
Fan, G., Song, H., Yip, S., Zhang, T., He, D.: Impact of low vaccine coverage on the resurgence of COVID-19 in Central and Eastern Europe. One Health 14, 100402 (2022)
Xu, R.: Global stability of a delayed epidemic model with latent period and vaccination strategy. Appl. Math. Model. 36(11), 5293–5300 (2012)
Tian, X., Xu, R., Lin, J.: Mathematical analysis of a cholera infection model with vaccination strategy. Appl. Math. Comput. 361, 517–535 (2019)
Makinde, O.D.: Adomian decomposition approach to a SIR epidemic model with constant vaccination strategy. Appl. Math. Comput. 184(2), 842–848 (2007)
Li, J., Ma, Z., Zhou, Y.: Global analysis of SIS epidemic model with a simple vaccination and multiple endemic equilibria. Acta Math. Sci. 26(1), 83–93 (2006)
Tang, B., **ao, Y., Tang, S., Cheke, R.A.: A feedback control model of comprehensive therapy for treating immunogenic tumours. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 26(03), 1650039 (2016)
Deng, J., Tang, S., Shu, H.: Joint impacts of media, vaccination and treatment on an epidemic Filippov model with application to COVID-19. J. Theor. Biol. 523, 110698 (2021)
De la Sen, M., Alonso-Quesada, S., Ibeas, A., Nistal, R.: On an SEIADR epidemic model with vaccination, treatment and dead-infectious corpses removal controls. Math. Comput. Simul. 163, 47–79 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Suo, Y.: Qualitative analysis of a SIR epidemic model with saturated treatment rate. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 34(1), 177–194 (2010)
Li, L., Bai, Y., **, Z.: Periodic solutions of an epidemic model with saturated treatment. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(2), 1099–1108 (2014)
Eckalbar, J.C., Eckalbar, W.L.: Dynamics of an epidemic model with quadratic treatment. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12(1), 320–332 (2011)
Agur, Z., Cojocaru, L., Mazor, G., Anderson, R.M., Danon, Y.L.: Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(24), 11698–11702 (1993)
d’Onofrio, A.: Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model: global asymptotic stable eradication in presence of vaccine failures. Math. Comput. Model. 36(4), 473–489 (2002)
Zhou, Y., Liu, H.: Stability of periodic solutions for an SIS model with pulse vaccination. Math. Comput. Model. 38(3), 299–308 (2003)
Pang, G., Chen, L.: A delayed SIRS epidemic model with pulse vaccination. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34(5), 1629–1635 (2007)
Wei, H., Jiang, Y., Song, X., Su, G.H., Qiu, S.Z.: Global attractivity and permanence of a SVEIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and time delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 229(1), 302–312 (2009)
Alonso-Quesada, S., De la Sen, M., Ibeas, A.: On the discretization and control of an SEIR epidemic model with a periodic impulsive vaccination. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 42, 247–274 (2017)
Yang, Y., **ao, Y.: The effects of population dispersal and pulse vaccination on disease control. Math. Comput. Model. 52(9), 1591–1604 (2010)
Liu, H., Yu, J., Zhu, G.: Global behaviour of an age-infection-structured HIV model with impulsive drug-treatment strategy. J. Theor. Biol. 253(4), 749–754 (2008)
Zhao, Z., Pang, L., Li, Q.: Analysis of a hybrid impulsive tumor-immune model with immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Chaos Solitons Fractals 144, 110617 (2021)
Tang, B., Li, Q., **ao, Y., Sivaloganathan, S.: A novel hybrid model of tumor control, combining pulse surveillance with tumor size-guided therapies. Appl. Math. Model. 104, 259–278 (2022)
Li, J., Yang, Y.: SIR-SVS epidemic models with continuous and impulsive vaccination strategies. J. Theor. Biol. 280(1), 108–116 (2011)
Guo, H., Chen, L.: Periodic solution of a chemostat model with Monod growth rate and impulsive state feedback control. J. Theor. Biol. 260(4), 502–509 (2009)
Sun, K., Tian, Y., Chen, L., Kasperski, A.: Nonlinear modelling of a synchronized chemostat with impulsive state feedback control. Math. Comput. Model. 52(1), 227–240 (2010)
Li, Z., Chen, L., Liu, Z.: Periodic solution of a chemostat model with variable yield and impulsive state feedback control. Appl. Math. Model. 36(3), 1255–1266 (2012)
Yang, J., Tan, Y., Cheke, R.A.: Complex dynamics of an impulsive chemostat model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(08), 1950101 (2019)
Zhao, Z., Zhang, J., Pang, L., Chen, Y.: Nonlinear modelling of ethanol inhibition with the state feedback control. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 48(1), 205–219 (2015)
Zhang, Q., Tang, S.: Bifurcation analysis of an ecological model with nonlinear state-dependent feedback control by poincaré map defined in phase set. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 108, 106212 (2022)
Tang, S., Li, C., Tang, B., Wang, X.: Global dynamics of a nonlinear state-dependent feedback control ecological model with a multiple-ump discrete map. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 79, 104900 (2019)
Tang, S., Cheke, R.A.: Models for integrated pest control and their biological implications. Math. Biosci. 215(1), 115–125 (2008)
Tian, Y., Li, C., Liu, J.: Non-smooth competitive systems and complex dynamics induced by linearly dependent feedback control. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 51, 101442 (2024)
Tian, Y., Li, H., Sun, K.: Complex dynamics of a fishery model: Impact of the triple effects of fear, cooperative hunting and intermittent harvesting. Math. Comput. Simul. 218, 31–48 (2024)
Zhang, Q., Tang, B., Cheng, T., Tang, S.: Bifurcation analysis of a generalized impulsive Kolmogorov model with applications to pest and disease control. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 80(4), 1796–1819 (2020)
Guo, H., Tian, Y., Sun, K., Song, X.: Study on dynamic behavior of two fishery harvesting models: effects of variable prey refuge and imprecise biological parameters. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 69(6), 4243–4268 (2023)
Zhang, Q., Tang, S., Zou, X.: Rich dynamics of a predator-prey system with state-dependent impulsive controls switching between two means. J. Differ. Equ. 364, 336–377 (2023)
Zhang, M., **ao, X., Feng, X.: Numerical simulations for the predator-prey model on surfaces with lumped mass method. Eng. Comput. 37(3), 2047–2058 (2021)
Tang, S., Tang, B., Wang, A., **ao, Y.: Holling II predator-prey impulsive semi-dynamic model with complex poincaré map. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(3), 1575–1596 (2015)
Tang, G., Tang, S., Cheke, R.A.: Global analysis of a Holling type II predator-prey model with a constant prey refuge. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(1), 635–647 (2014)
Cheng, T., Tang, S., Cheke, R.A.: Threshold dynamics and bifurcation of a state-dependent feedback nonlinear control susceptible-infected-recovered model. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 14(7), 071001 (2019)
Zhang, Q., Tang, B., Tang, S.: Vaccination threshold size and backward bifurcation of SIR model with state-dependent pulse control. J. Theor. Biol. 455, 75–85 (2018)
Nie, L., Teng, Z., Torres, A.: Dynamic analysis of an SIR epidemic model with state dependent pulse vaccination. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 13(4), 1621–1629 (2012)
Nie, L., Teng, Z., Guo, B.: A state dependent pulse control strategy for a SIRS epidemic system. Bull. Math. Biol. 75(10), 1697–1715 (2013)
Nie, L., Shen, J., Yang, C.: Dynamic behavior analysis of SIVS epidemic models with state-dependent pulse vaccination. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 27, 258–270 (2018)
Huang, M., Li, J., Song, X., Guo, H.: Modeling impulsive injections of insulin: towards artificial pancreas. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 72(5), 1524–1548 (2012)
Liu, Q., Zhang, M., Chen, L.: State feedback impulsive therapy to SIS model of animal infectious diseases. Physica A 516, 222–232 (2019)
Kim, K.S., Cho, G., Nie, L.-F., Jung, I.H., Kon, R.: State-dependent impulsive control strategies for a tumor-immune model. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2016, 2979414 (2016)
Li, W., Ji, J., Huang, L.: Global dynamic behavior of a predator-prey model under ratio-dependent state impulsive control. Appl. Math. Model. 77, 1842–1859 (2020)
Li, W., Ji, J., Huang, L., Zhang, Y.: Complex dynamics and impulsive control of a chemostat model under the ratio threshold policy. Chaos Solitons Fractals 167, 113077 (2023)
Simeonov, P.S., Bainov, D.D.: Orbital stability of the periodic solutions of autonomous systems with impulse effect. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 19(12), 2561–2585 (1988)
LaSalle, J.P.: An Invariance Principle in the Theory of Stability. Technical report. Academic Press, New York (1966)
Fečkan, M.: A generalization of Bendixson’s criterion. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 129(11), 3395–3399 (2001)
Agarwal, R.P., Meehan, M., O’regan, D.: Fixed Point Theory and Applications. Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12271308).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Zhang, T. Dynamic analysis of a SIS epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and ratio dependent pulse control. J. Appl. Math. Comput. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02109-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-024-02109-0