Abstract
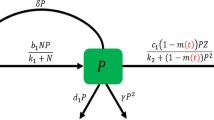
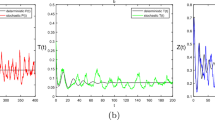
In this paper, we study the stochastic dynamics of a preferred phytoplankton (PP)–nonpreferred phytoplankton (NP)–zooplankton (Z) model with selectivity of zooplankton and nutritional value of phytoplankton. The mathematical theoretical work mainly gives the existence and uniqueness of the positive solution, provides the results related to stochastic ultimate boundedness and stochastic permanence, shows the dynamics of stochastic extinction and persistence in the mean, and proves the existence of a unique ergodic stationary distribution, which in turn provides a theoretical basis for numerical simulations. The numerical simulation work mainly reveals that the selectivity of zooplankton and nutritional of phytoplankton have a significant impact on the PP–NP–Z dynamics under random environmental fluctuation. It is worth emphasizing that the large nutritional value of preferred phytoplankton has the capacity to result in the extinction of nonpreferred phytoplankton, while the large nutritional value of nonpreferred phytoplankton may be able to initiate the occurrence of harmful algal blooms. Furthermore, it should be noted that the increase of zooplankton selectivity or nutritional value of phytoplankton (preferred phytoplankton and nonpreferred phytoplankton) can cause the stationary distribution of preferred phytoplankton to shift to the left, but the stationary distribution of nonpreferred phytoplankton and zooplankton can shift to the right. These results may contribute to further understanding the complex dynamics of plankton models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai, Y.H., Yang, S.B., Zhao, D., Hu, C.M., Xu, W., Anderson, D.M., Li, Y., Song, X.P., Boyce, D.G., Gibson, L., Zheng, C.M., Feng, L.: Coastal phytoplankton blooms expand and intensify in the 21st century. Nature 615, 280–284 (2023)
Valipour, R., Fong, P., McCrimmon, C., Zhao, J., Van Stempvoort, D.R., Rao, Y.R.: Hydrodynamics of a large lake with complex geometry and topography: lake the woods. J. Great Lakes Res. 49, 82–96 (2023)
Hellweger, F.L., Martin, R.M., Eigemann, F., Smith, D.J., Dick, G.J., Wilhelm, S.W.: Models predict planned phosphorus load reduction will make lake Erie more toxic. Science 376, 1001–1005 (2022)
Jiang, J., Shen, A., Wang, H., Yuan, S.L.: Regulation of phosphate uptake kinetics in the bloom-forming dinoflagellates prorocentrum donghaiense with emphasis on two-stage dynamic process. J. Theor. Biol. 463, 12–21 (2019)
Shen, A.L., Gao, S.F., Heggerud, C.M., Wang, H., Ma, Z.L., Yuan, S.L.: Fluctuation of growth and photosynthetic characteristics in Prorocentrum shikokuense under phosphorus limitation: evidence from field and laboratory. Ecol. Model. 479, 110310 (2023)
Deepika, S., Veeresha, P.: Dynamics of chaotic waterwheel model with the asymmetric flow within the frame of Caputo fractional operator. Chaos Solitons Fract. 169, 113298 (2023)
Kavya, K.N., Veeresha, P.K.: Mathematical approach for impact of media awareness on measles disease, Math. Method Appl. Sci., 1–27 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.9645
Naik, M.K., Chandrali Baishya, C., Veeresha, P., Baleanu, D.: Design of a fractional-order atmospheric model via a class of ACT-like chaotic system and its sliding mode chaos control. Chaos 33, 023129 (2023)
Priyadarshini P., Veeresha, P.: Analysis of models describing thermocline depth-ocean temperature and dissolved oxygen concentration in the ocean-plankton community. Waves Random Complex, 1–25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2023.2226762
Veeresha, P., Akinyemi, L.: Fractional approach for mathematical model of phytoplankton-toxic phytoplankton–zooplankton system with Mittag–Leffler kernel. Int. J. Biomath. 16(3), 1–24 (2023)
Veeresha, P.: The efficient fractional order based approach to analyze chemical reaction associated with pattern formation. Chaos Solitons Fract. 165, 112862 (2022)
Veeresha, P.: A numerical approach to the coupled atmospheric ocean model using a fractional operator. Math. Model. Numer. Simulat. Appl. 1(1), 1–10 (2021)
Sailley, S.F., Polimene, L., Mitra, A., Atkinson, A., Allen, J.I.: Impact of zooplankton food selectivity on plankton dynamics and nutrient cycling. J. Plankton Res. 37, 519–529 (2015)
Yang, J.G., Yuan, S.L.: Dynamics of a toxic producing phytoplankton–zooplankton model with three-dimensional patch. Appl. Math. Lett. 118, 107146 (2022)
Huda, M.N., A’yun, Q.Q., Wigantono, S., Sandariria, H., Raming, I., Asmaidi, A.: Effects of harvesting and planktivorous fish on bioeconomic phytoplankton–zooplankton models with ratio-dependent response functions and time delays. Chaos Solitons Fract. 173, 1–22 (2023)
Macdonald, J.C., Gulbudak, H.: Forward hysteresis and hopf bifurcation in an NPZD model with application to harmful algal blooms. J. Math. Biol. 87, 1–35 (2023)
Gao, M.M., Jiang, D.Q., Ding, J.Y.: Dynamical behavior of a nutrient-plankton model with Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process and nutrient recycling. Chaos Solitons Fract. 174, 1–27 (2023)
Mandal, A., Biswas, S., Pal, S.: Toxicity-mediated regime shifts in a contaminated nutrient-plankton system. Chaos 33, 1–19 (2023)
Liao, T.C.: The impact of plankton body size on phytoplankton–zooplankton dynamics in the absence and presence of stochastic environmental fluctuation. Chaos Solitons Fract. 154, 1–16 (2022)
Liao, T.C.: Dynamics of interacting plankton induced by plankton body size in deterministic and stochastic environments. Chinese J. Phys. 77, 2724–2750 (2022)
Harvey, H.W.: Note on selective feeding by Calanus. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 22, 97–100 (1937)
Pal, J., Bhattacharya, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Does predator go for size selection or preferential toxic-nontoxic species under limited resource. OnLine J. Biol. Sci. 10, 11–16 (2010)
Muller-Navarra, D.C., Brett, M.T., Liston, A., Goldman, C.R.: A highly unsaturated fatty acid predicts carbon transfer between primary producers and consumers. Nature 403, 74–77 (2000)
Ravet, J.L., Brett, M.T.: Essential fatty acid and phytoplankton phosphorus content constraints on daphnia somatic growth and reproduction. Limnol. Oceanogr. 51, 2438–2452 (2006)
DeMott, W.R.: Optimal foraging theory as a predictor of chemically mediated food selection by suspension-feeding copepods. Limnol. Oceanography 34, 140–154 (1989)
Bairagi, N., Saha, S., Chaudhuri, S., Dana, S.K.: Zooplankton selectivity and nutritional value of phytoplankton influences a rich variety of dynamics in a plankton population model. Phys. Rev. E 99, 1–12 (2019)
Danielsdottir, M.G., Brett, M.T., Arhonditsis, G.B.: Phytoplankton food quality control of planktonic food web processes. Hydrobiologia 589, 29–41 (2007)
Zheng, Y.L., Gong, X., Gao, H.W.: Selective grazing of zooplankton on phytoplankton defines rapid algal succession and blooms in oceans. Ecol. Model. 468, 1–11 (2022)
Biswas, S., Tiwari, P.K., Kang, Y., Pal, S.: Effects of zooplankton selectivity on phytoplankton in an ecosystem affected by free-viruses and environmental toxins. Math. Bios. Eng. 17, 1272–1317 (2020)
Biswas, S., Tiwari, P.K., Pal, S.: Effects of toxicity and zooplankton selectivity on plankton dynamics under seasonal patterns of viruses with time delay. Math. Method Appl. Sci. 45, 585–617 (2020)
Zhao, S.N., Yuan, S.L., Wang, H.: Threshold behavior in a stochastic algal growth model with stoichiometric constraints and seasonal variation. J. Diff. Equ. 268, 5113–5139 (2020)
Yu, X.W., Yuan, S.L., Zhang, T.H.: The effects of toxin-producing phytoplankton and environmental fluctuations on the planktonic blooms. Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 1653–1668 (2018)
May, R.: Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystem. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2001)
Yu, X.W., Yuan, S.L., Zhang, T.H.: Survival and ergodicity of a stochastic phytoplankton–zooplankton model with toxin-producing phytoplankton in an impulsive polluted environment. Appl. Math. Comput. 347, 249–264 (2019)
Zhao, S.N., Yuan, S.L., Zhang, T.H.: The impact of environmental fluctuations on a plankton model with toxin-producing phytoplankton and patchy agglomeration. Chaos Solitons Fract. 162, 112426 (2022)
Liao, T.C.: Plankton growth dynamic driven by plankton body size in deterministic and stochastic environments. Math. Mathods Appl. Sci. 46, 2569–2601 (2023)
Chen, Z.W., Tian, Z.Y., Zhang, S.W., Wei, C.J.: The stationary distribution and ergodicity of a stochastic phytoplankton–zooplankton model with toxin-producing phytoplankton under regime switching. Physica A 537, 122728 (2020)
Chen, L.F., Yu, X.W., Yuan, S.L.: Effects of random environmental perturbation on the dynamics of a nutrient-phytoplankton–zooplankton model with nutrient recycling. Mathematics 10, 3787 (2022)
Camara, B.I., Yamapi, R., Mokrani, H.: Environmental stochastic effects on phytoplankton–zooplankton dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 2013–2029 (2019)
Zhao, S.N., Yuan, S.L., Zhang, T.H.: Adaptive dynamics of a stoichiometric phosphorus–algae–zooplankton model with environmental fluctuations. J. Nonlinear Sci. 36, 1–61 (2022)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D.Q., Hayat, T., Ahmad, B.: Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic predator–prey model with additional food and nonlinear perturbation. Appl. Math. Comput. 320, 226–239 (2018)
Mao, X.: Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications. Horwood Publishing, Chichester (1997)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Dynamics of a stochastic predator–prey model with stage structure for predator and Holling type II functional response. J. Nonlinear Sci. 28, 1151–1187 (2018)
Cai, Y.L., Kang, Y., Wang, W.M.: A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. Appl. Math. Comput. 305, 221–240 (2017)
Zhang, S.Q., Duan, X.C., Zhang, T.H., Yuan, S.L.: Controlling biological invasions: a stochastic host-generalist parasitoid model. Bull. Math. Biol. 85, 1–31 (2023)
Liu, M., Wang, K., Wu, Q.: Survival analysis of stochastic competitive models in a polluted environment and stochastic competitive exclusion principle. Bull. Math. Biol. 73, 1969–2012 (2011)
Has’minskii, R.Z.: Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations. Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Alphen aan den Rijn (1980)
Murdoch, W.W., Nisbet, R.M., McCauley, E., DeRoos, A.M., Gurney, W.S.C.: Plankton abundance and dynamics across nutrient levels: tests of hypotheses. Ecology 79, 1339–1356 (1998)
Genkai-Kato, M., Yamamura, N.: Unpalatable prey resolves the paradox of enrichment. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 266, 1215–1219 (1999)
Roy, S., Alam, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Competing effects of toxin-producing phytoplankton on overall plankton populations in the bay of Bengal. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 2303–2320 (2006)
Higham, D.J.: An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 43, 525–546 (2001)
Bao, J., Mao, X., Yin, G., Yuan, C.: Competitive Lotka–Volterra population dynamics with jumps. Nonlinear Anal. 74, 6601–6616 (2011)
Tembo, R.: The impact of ocean acidification on aquatic organisms. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 7, 1–5 (2017)
Danane, J.: Stochastic predator–prey levy jump model with Crowley–Martin functional response and stage structure. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 67, 41–67 (2021)
Sajan, K.K., Choudhary, K.K., Dubey, B.: A non-autonomous approach to study the impact of environmental toxins on nutrient-plankton system. Appl. Math. Comput. 458, 128236 (2023)
Chaturvedi, D., Misra, O.P.: Modeling impact of varying ph due to carbondioxide on the dynamics of prey–predator species system. Nonlinear Anal. Real 46, 374–402 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation Project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Education, Jiangsu Province, China(21KJD110005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Interest Statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, T. Stochastic dynamics of a plankton model with zooplankton selectivity and nutritional value of phytoplankton. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 70, 251–283 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-023-01959-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-023-01959-4