Abstract
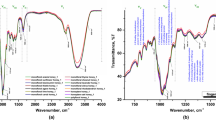
This work proposes a fast and accurate method based on near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy with partial least-squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and aquaphotomics to identify toxic honeys. PLS-DA was used to construct an optimal model for distinguishing toxic honey from a non-toxic honey. The models based on preprocessed NIR spectra have an accuracy of 92.73% and were more accurate than the model based on raw NIR spectra. Based on the aquaphotomics analysis of the first overtone of water (1300–1600 nm), we found that the 1398 nm, 1440 nm, and 1472 nm bands can be used as markers to distinguish toxic honeys. Compared to non-toxic honeys, gelsemium elegans -containing toxic honeys have a significantly smaller number of water molecules with multiple hydrogen bonds, due to the hydrogen bonding of the C–O–C, C = O, and NH2 groups of gelsemine and koumine. These groups replace hydrogen bonds between glucose/polysaccharide molecules and water.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study areavailable from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ (2017) Classification and Regression Trees. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315139470
Beć KB, Grabska J, Huck CW (2020) Near-infrared spectroscopy in bio-applications. Molecules 25(12):2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122948
Bázár G, Romvári R, Szabó A, Somogyi T, Éles V, Tsenkova R (2016) NIR detection of honey adulteration reveals differences in water spectral pattern. Food Chem 194:873–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.092
Barnes RJ, Dhanoa MS, Lister SJ (1989) Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra[J]. Appl Spectrosc 43(5):772–777. https://doi.org/10.1366/00037028942022
Chen LZ, Xue XF, Ye ZH, Zhou JH, Chen F, Zhao J (2011) Determination of Chinese honey adulterated with high fructose corn syrup by near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem 128(4):1110–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.027
Cakmak-Arslan G, Haksoy H, Goc-Rasgele P, Kekecoglu M (2020) Determination of the dose-dependent toxic effects of mad honey on mouse liver using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A: Molec Biomolec Spectrosc 228:117719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117719
Grassi S, Alamprese C (2018) Advances in NIR spectroscopy applied to process analytical technology in food industries. Curr Opin Food Sci 22:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2017.12.008
Geladi P, MacDougall D (1985) Martens H (1985) Linearization and scatter-correction for near-infrared reflectance spectra of meat. Appl Spectrosc 39(3):491–500
Gergely S, Salgó A (2003) Changes in moisture content during wheat maturation—what is measured by near infrared spectroscopy. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 11(1):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.350
Huang FR, Li YP, Guo HX, Xu J, Chen Z, Zhang J, Wang Y (2016) Identification of waste cooking oil and vegetable oil via Raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc 47(7):860–864. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.4895
Han L (2005) Estimating chlorophyll-a concentration using first-derivative spectra in coastal water[J]. Int J Remote Sens 26(23):5235–5244
Islam MK, Sostaric T, Lim LY, Hammer K, Locher C (2020) Sugar profiling of honeys for authentication and detection of adulterants using high-performance thin layer chromatography. Molecules 25(22):5289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225289
Kojić D, Tsenkova R, Tomobe K, Yasuoka K, Yasui M (2014) Water confined in the local field of ions. ChemPhysChem 15(18):4077–4086. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201402381
Kumaravelu C, Gopal A (2015) Detection and quantification of adulteration in honey through near infrared spectroscopy. Int J Food Propert 18(9):1930–1935. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2014.919320
Kraaijeveld K, De Weger LA, Ventayol García M, Buermans H, Frank J, Hiemstra PS, den Dunnen JT (2015) Efficient and sensitive identification and quantification of air borne pollen using next-generation DNA sequencing. Mol Ecol Resour 15(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12288
Kowalczyk E, Kwiatek K (2018) Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in honey: determination with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method. J Vet Res 62(2):173–181. https://doi.org/10.2478/jvetres-2018-0027
Koike H, Kanda M, Hayashi H, Matsushima Y, Yoshikawa S, Ohba Y, Hayashi M, Nagano C, Sekimura M, Otsuka K, Kamiie J, Sasamoto T, Hashimoto T (2020) Development of an alternative approach for detecting botulinum neurotoxin type A in honey: Analysis of non-toxic peptides with a reference labelled protein via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit Contam: A 37(8):1359–1373. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2020.1766121
Li YP, Guo L, Li L, Yang CM, Guang PW, Huang FR, Chen ZQ, Wang LH, Hu JH (2020) Early diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes based on near-infrared spectroscopy combined with machine learning and aquaphotomics. Front Chem 8:580489. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.580489
Liu Y, Li Y, Peng Y, Yang Y, Wang Q (2020) Detection of fraud in high-quality rice by near-infrared spectroscopy. J Food Sci 85(9):2773–2782. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15314
Marcazzan GL, Mucignat-Caretta C, Marina Marchese C, Piana ML (2018) A review of methods for honey sensory analysis. J Journal of Apicultural Research 57(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2017.1357940
Martin K (1998) In vivo measurements of water in skin by near-infrared reflectance. Appl Spectrosc 52(7):1001–1007. https://doi.org/10.1366/0003702981944652
Malegori C, Muncan J, Mustorgi E, Tsenkova R, Oliveri P (2022) Analysing the water spectral pattern by near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics as a dynamic multidimensional biomarker in preservation: Rice germ storage monitoring. Spectrochim Acta A: Molec Biomolec Spectrosc 265:120396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120396
Muncan J, Anantawittayanon S, Furuta T, Kaneko T, Tsenkova R (2022) Aquaphotomics monitoring of strawberry fruit during cold storage-A comparison of two cooling systems. Front Nutr 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.1058173
Muncan J, Tei K, Tsenkova R (2020) Real-time monitoring of yogurt fermentation process by aquaphotomics near-infrared spectroscopy. Sensors. 21(1):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010177
Sun MH, Zhao LG, Wang K, Han LD, Shan JH, Wu LM, Xue XF (2019) Rapid identification of “mad honey” from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. and Macleaya cordata (Willd) R Br Using UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Food Chem 294:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.028
Shen XW, Ma JS, Wang XQ, Wen CC, Zhang ML (2020) Toxicokinetics of 11 Gelsemium Alkaloids in Rats by UPLC-MS/MS. Biomed Res Int 10:8247270. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8247270
Skaff W, El Hajj R, Hanna-Wakim L, Estephan N (2021) Detection of adulteration in honey by infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics: Effect on human health. J Food Process Preserv 46:e15438. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15438
Sakudo A (2016) Near-infrared spectroscopy for medical applications: Current status and future perspectives. Clin Chim Acta 455:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2016.02.009
Tsenkova R (2009) Aquaphotomics: dynamic spectroscopy of aqueous and biological systems describes peculiarities of water. J near Infrared Spectrosc 17(6):303–313
Tsenkova R (2010) Aquaphotomics: Water in the biological and aqueous world scrutinised with invisible light. Spectrosc Eur 22(6):6
Takeuchi M et al (2005) Investigations of the structure of H2O clusters adsorbed on TiO2 surfaces by near-infrared absorption spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 109(15):7387–7391
Tsenkova R, Munćan J, Pollner B, Kovacs Z (2018) Essentials of aquaphotomics and its chemometrics approaches. Front Chem 6:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00363
Tsenkova R (2006) AquaPhotomics: water absorbance pattern as a biological marker. NIR News 17(7):13–23. https://doi.org/10.1255/nirn.926
Xu YK, Yang L, Liao SG, Cao P, Wu B, Hu HB, Guo J, Zhang P (2015) Koumine, humantenine, and yohimbane alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans. J Nat Prod 78(7):1511–1517. https://doi.org/10.1021/np5009619
Yang XH, Guang PW, Xu GZ, Zhu SQ, Chen ZQ, Huang FR (2020) Manuka honey adulteration detection based on near-infrared spectroscopy combined with aquaphotomics. LWT - Food Sci Technol 132:109837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109837
Yakubu HG, Kovacs Z, Toth T, Bazar G (2020) The recent advances of near-infrared spectroscopy in dairy production—A review. Critic Rev Food Sci Nutr 12:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1829540
Yang SP, Liu Y, Sun FF, Zhang JZ, ** Y, Li Y, Zhou JH, Yi L, Zhu K (2020) Gelsedine-type alkaloids: Discovery of natural neurotoxins presented in toxic honey. J Hazard Mater 381:120999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120999
Zhang N, Li WZ, Chen C, Zuo JG (2013) Evaluation of the application of hydrogen bonding criteria to DMSO aqueous solution. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica. 29(9):1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB201307121
Zhang J, Yan YB (2005) Probing conformational changes of proteins by quantitative second-derivative infrared spectroscopy[J]. Anal Biochem 340(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.01.053
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62005056\61975069), Guang** Natural Science Foundation of China (2021JJB110003), Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (202103000095), Guang** Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2018GXNSFBA050028),the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2020B090922006), Science and Technology Commissioner Project of Guangdong Province (GDKTP2020023100), Project of Guangzhou Academician Workstation (h2020-3–01), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2020GXNSFBA159008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuanpeng li, Chuanmei Yang, Yuancui Su and Chengsen Tan designed experiments and wrote the manuscript. Chuanmei Yang collected data on common honey and honey with gelsemium. Yuanpeng li, Hongxia Zhao, and Furong Huang supervised this project. All other authors were involved in the study concept, design, analysis, and interpretation of data, drafting, and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Conflict of interest
Wenchang Huang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lingli Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yuancui Su declares that he has no conflict of interest. Chuanmei Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Chengsen Tan declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yuanpeng Li declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shan Tu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Siqi Zhu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yongmei Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lihu Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Junhui Hu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yuxiang Mo declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hongxia Zhao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Furong Huang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Liu, L., Su, Y. et al. Differentiation of Gelsemium elegans-Containing Toxic Honeys and Non-Toxic Honeys by Near Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Aquaphotomics. Food Anal. Methods 16, 1607–1617 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02525-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02525-1