Abstract
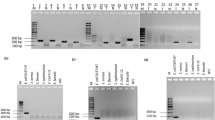
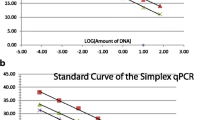
Escherichia coli O157 (E. coli O157) is one of the most dangerous foodborne pathogens worldwide. A convenient, sensitive, and specific method for the E. coli O157 detection is necessary. The present study developed an isothermal real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (real-time RPA) assay and an RPA combined with lateral flow strip (LFS-RPA) to detect E. coli O157 targeting the conserved region of the rfbE gene. Results of this study demonstrated that the real-time RPA was successfully conducted at the constant temperature of 39 °C for 20 min. Furthermore, the LFS-RPA was performed in an incubator block at 39 °C for 15 min, with the products visible with the naked eye within 5 min. It was found that the two RPA assays were highly specific to E. coli O157 and there were no cross-reactions with other microorganisms tested. The detection limit of E. coli O157 DNA or pure culture using LFS-RPA was 3.5 × 102 fg/μL and/or 1.0 × 102 CFU/mL, respectively, which was 10 times higher than that of real-time PCR and real-time RPA. Moreover, the practicality of the way to discover E. coli O157 was validated with artificial contamination assay. Positive results were obtained within 6–15 min in the real-time RPA and within 15 min in the LFS-RPA, while it took approximately between 28 and 45 min in the real-time PCR. Furthermore, these assays require no sophisticated instruments, specialized technicians, and strict laboratory conditions. All of these helps to manifest that the developed RPA assays were simple, highly specific, sensitive, and rapid, and they could be employed in resource-constrained areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ateba CN, Mbewe M (2011) Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 virulence genes in isolates from beef, pork, water, human and animal species in the northwest province, South Africa: public health implications. Res Microbiol 162(3):240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2010.11.008
Bai H, Bu S, Liu W, Wang C, Li Z, Hao Z, Wan J, Han Y (2020) An electrochemical aptasensor based on cocoon-like DNA nanostructure signal amplification for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Analyst 145(22):7340–7348. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an01258k
Boyle DS, Lehman DA, Lillis L, Peterson D, Singhal M, Armes N, Parker M, Piepenburg O, & Overbaugh J (2013) Rapid detection of HIV-1 proviral DNA for early infant diagnosis using recombinase polymerase amplification. mBio, 4(2). https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00135-13
Bruballa AC, Shiromizu CM, Bernal AM, Pineda GE, Sabbione F, Trevani AS, Bentancor LV, Ramos MV, Fernandez-Brando RJ, Munoz MJ, & Palermo MS (2020) Role of Shiga toxins in cytotoxicity and immunomodulatory effects of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during host-bacterial interactions in vitro. Toxins (Basel), 12(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010048
Crannell ZA, Rohrman B, Richards-Kortum R (2014) Equipment-free incubation of recombinase polymerase amplification reactions using body heat. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112146. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112146
Daher RK, Stewart G, Boissinot M, Bergeron MG (2016) Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications. Clin Chem 62(7):947–958. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.245829
Euler M, Wang Y, Otto P, Tomaso H, Escudero R, Anda P, Hufert FT, Weidmann M (2012) Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol 50(7):2234–2238. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.06504-11
Fei Z, Zhou D, Dai W, **ao P (2020) Rapid and highly sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food with loop-mediated isothermal amplification coupled to a new bioluminescent assay. Electrophoresis 41(20):1793–1803. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.202000046
Geng Y, Tan K, Liu L, Sun XX, Zhao B, Wang J (2019) Development and evaluation of a rapid and sensitive RPA assay for specific detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood. BMC Microbiol 19(1):186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1562-z
Gordillo R, Rodriguez A, Werning ML, Bermudez E, & Rodriguez M (2014) Quantification of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 in meat products by duplex real-time PCR assays. Meat Sci, 96(2 Pt A), 964–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.10.018
Han Q, Wang J, Li R, Han Q, Yuan W, Wang J (2020) Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Haemophilus parasuis in tissue samples. Vet Med Sci 6(4):894–900. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3.287
Horr T, Pradhan AK (2020) Evaluation of public health risk for Escherichia coli O157:H7 in cilantro. Food Res Int 136:109545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109545
James A, Macdonald J (2015) Recombinase polymerase amplification: emergence as a critical molecular technology for rapid, low-resource diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 15(11):1475–1489. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.2015.1090877
Kim H, Kane MD, Kim S, Dominguez W, Applegate BM, Savikhin S (2007) A molecular beacon DNA microarray system for rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 that eliminates the risk of a false negative signal. Biosens Bioelectron 22(6):1041–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.04.032
Li J, Macdonald J, von Stetten F (2018) Review: a comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 144(1):31–67. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an01621f
Liu L, Li R, Zhang R, Wang J, An Q, Han Q, Wang J, Yuan W (2019) Rapid and sensitive detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae by recombinase polymerase amplification assay. J Microbiol Methods 159:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2019.02.015
Nitecki SS, Teape N, Carney BF, Slater JW, Bruck WM (2015) A duplex qPCR for the simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes using LNA probes. Lett Appl Microbiol 61(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12427
Piepenburg O, Williams CH, Stemple DL, Armes NA (2006) DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol 4(7):e204. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040204
Ren H, Yang M, Zhang G, Liu S, Wang X, Ke Y, Du X, Wang Z, Huang L, Liu C, Chen Z (2016) Development of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for detection of Brucella in blood samples. Mol Cell Probes 30(2):122–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2016.02.007
Slayton RB, Turabelidze G, Bennett SD, Schwensohn CA, Yaffee AQ, Khan F, Butler C, Trees E, Ayers TL, Davis ML, Laufer AS, Gladbach S, Williams I, Gieraltowski LB (2013) Outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157:H7 associated with romaine lettuce consumption, 2011. PLoS ONE 8(2):e55300. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055300
Slutsker L, Ries AA, Greene KD, Wells JG, Hutwagner L, Griffin PM (1997) Escherichia coli O157:H7 diarrhea in the United States: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med 126(7):505–513. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-126-7-199704010-00002
Wang HM, Zhao GM, Hou PL, Yu L, He CQ, He HB (2018) Rapid detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus using reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick. J Virol Methods 261:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.07.011
Wang R, Zhang F, Wang L, Qian W, Qian C, Wu J, Ying Y (2017) Instant, visual, and instrument-free method for on-site screening of GTS 40–3-2 soybean based on body-heat triggered recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal Chem 89(8):4413–4418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00964
Yang Y, Qin X, Wang G, Zhang Y, Shang Y, Zhang Z (2015) Development of a fluorescent probe-based recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Orf virus. Virol J 12:206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-015-0440-z
Yehia N, Arafa AS, Abd El Wahed A, El-Sanousi AA, Weidmann M, Shalaby MA (2015) Development of reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for avian influenza H5N1 HA gene detection. J Virol Methods 223:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.07.011
Zhao L, Wang J, Sun XX, Wang J, Chen Z, Xu X, Dong M, Guo YN, Wang Y, Chen P, Gao W, Geng Y (2021) Development and evaluation of the rapid and sensitive RPA assays for specific detection of Salmonella spp. in food samples. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:631921. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.631921
Zhao S, Zhou Y, Wang C, Yang Y, Wu X, Wei Y, Zhu L, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Wan C (2013) The N-terminal domain of EspF induces host cell apoptosis after infection with enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. PLoS ONE 8(1):e55164. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055164
Funding
This work was supported by the program of Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research foundation in Hebei Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2020142 and 2019091, Hebei, China), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2020423052), the Project of Excellent Young Teacher Fundamental Research (YQ2019003), and Doctoral Foundation (BSZ2019009) of Hebei University of Chinese Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YYG and JCW designed and conducted the experiment. LWZ, MNC, XXS, and YYW performed the experiments and analyzed the data. YYG drafted the manuscript. All authors read, revised, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Wang, J., Chen, M. et al. Development and Application of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assays for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli O157 in Food. Food Anal. Methods 15, 1843–1850 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02250-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02250-1