Abstract
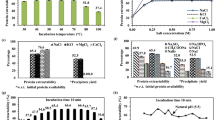
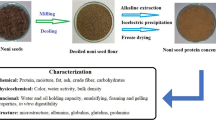
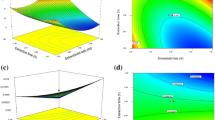
Vicia villosa )V. villosa ( seed is considered a good source of protein, fiber, and minerals (iron, magnesium, potassium, etc.) and is helpful for human health. This study focused on optimizing the extraction of V. villosa seed protein and investigating the physicochemical and functional properties of V. villosa protein isolate (VVPI) as a food additive. The response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to optimize the extraction process of protein isolate using the face central composite design (FCCD). The optimal conditions for maximum protein yield (12.47%), protein content (87.90 %), and protein solubility (8.17 mg/mL( were obtained under conditions of pH 11 and extraction time of 26 min. The primary VVPI amino acids glutamine (Glu) and asparagine (Asp) were 16.4% and 10.16%, respectively. The results indicated that VVPI had significant solubility, foaming, and emulsifying properties, which the lowest of these properties were observed at the isoelectric point (pI). Also, VVPI showed that it has water holding capacity (WHC) and oil absorption capacity adequate. The denaturation temperature (76.17 °C) of VVPI was determined by using a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that VVPI has a rough surface. Regarding the good nutritional and functional properties of VVPI, it can be recommended to be used in various food formulations as an additive.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Abbou A et al (2019) Effect of precipitation solvent on some biological activities of polysaccharides from Pinus halepensis Mill seeds. Int J Biol Macromol 141:663–670
Abd El Moneim AM, Ryan J (2004) Forage legumes for dryland agriculture in Central and West Asia and North Africa. Challenges and Strategies of Dryland Agriculture 32:243–256
Aletor O, Oshodi A, Ipinmoroti K (2002) Chemical composition of common leafy vegetables and functional properties of their leaf protein concentrates. Food Chem 78:63–68
Alpizar-Reyes E, Castaño J, Carrillo-Navas H, Alvarez-Ramírez J, Gallardo-Rivera R, Pérez-Alonso C, Guadarrama-Lezama A (2018) Thermodynamic sorption analysis and glass transition temperature of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) protein. J Food Sci Technol 55:935–943
Attar FR, Rezagholi F, Hesarinejad MA (2018) Vicia villosa protein isolate: a new source of protein to make a biodegradable film. Potravinarstvo 12(1)
Aydemir LY, Yemenicioğlu A (2013) Potential of Turkish Kabuli type chickpea and green and red lentil cultivars as source of soy and animal origin functional protein alternatives. LWT Food Sci Technol 50:686–694
Baloch M, Zubair M (2010) Effect of nip** on growth and yield of chickpea. J Anim Plant Sci 20:208–210
Benelhadj S, Gharsallaoui A, Degraeve P, Attia H, Ghorbel D (2016) Effect of pH on the functional properties of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis protein isolate. Food Chem 194:1056–1063
Berber İ, Yaşar F (2011) Characterization of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars grown in turkey by SDS-page of seed proteins
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977
Bressani R, Elías LG (1979) Nutritional role of polyphenols in beans. In: Polyphenols in cereals and legumes: proceedings of a symposium. IDRC, Ottawa
Burlingame-Frey JP, Marth EH (1984) Method to determine foaming property of reconstituted nonfat dry milk. J Food Prot 47:140–141
Chandi GK, Sogi D (2007) Functional properties of rice bran protein concentrates. J Food Eng 79:592–597
Chouaibi M, Boussaid A, Donsì F, Ferrari G, Hamdi S (2019) Optimization of the extraction process by response surface methodology of protein isolate from defatted jujube (Zizyphus lotus L) seeds. Int J Peptide Res Ther 25:1509–1521
Coffmann C, Garciaj V (1977) Functional properties and amino acid content of a protein isolate from mung bean flour. Int J Food Sci Technol 12:473–484
Damodaran S (2005) Protein stabilization of emulsions and foams. J Food Sci 70:R54–R66
Deng Y, Huang L, Zhang C, **e P, Cheng J, Wang X, Li S (2019) Physicochemical and functional properties of Chinese quince seed protein isolate. Food Chem 283:539–548
Dickinson E (2010) Flocculation of protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 81:130–140
Du M et al (2018) Extraction, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of mung bean protein. Food Hydrocoll 76:131–140
Fasolin LH, Pereira RN, Pinheiro AC, Martins JT, Andrade C, Ramos O, Vicente A (2019) Emergent food proteins–towards sustainability, health and innovation. Food Res Int 125:108586
Ferreira S, Duarte AP, Ribeiro MH, Queiroz JA, Domingues FC (2009) Response surface optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of Cistus ladanifer and Cytisus striatus for bioethanol production. Biochem Eng J 45:192–200
Feyzi S, Varidi M, Zare F, Varidi M (2013) Study of chemical compositions, color carameters, and functional properties of fenugreek flour and their comparison with those of soy flour. J Res Innov Food Sci Technol 2:121–138
Feyzi S, Varidi M, Zare F, Varidi MJ (2015) Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed protein isolate: extraction optimization, amino acid composition, thermo and functional properties. J Sci Food Agric 95:3165–3176
Feyzi S, Milani E, Golimovahhed QA (2018) Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) protein isolate: the effect of extraction optimization and drying methods on the structure and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll 74:187–196
Firatligil-Durmus E, Evranuz O (2010) Response surface methodology for protein extraction optimization of red pepper seed (Capsicum frutescens). LWT Food Sci Technol 43:226–231
Henchion M, Hayes M, Mullen AM, Fenelon M, Tiwari B (2017) Future protein supply and demand: strategies and factors influencing a sustainable equilibrium. Foods 6:53
Hojilla-Evangelista MP, Evangelista RL, Wu YV (2009) Characterization of milkweed (Asclepias spp.) seed proteins. Ind Crop Prod 29:275–280
Homayounpour P, Shariatifar N, Alizadeh-Sani M (2021) Development of nanochitosan-based active packaging films containing free and nanoliposome caraway (Carum carvi L.) seed extract. Food Sci Nutr 9:553–563
Horax R, Hettiarachchy N, Kannan A, Chen P (2011) Protein extraction optimisation, characterisation, and functionalities of protein isolate from bitter melon (Momordica charantia) seed. Food Chem 124:545–550
Karaca AC, Low N, Nickerson M (2011) Emulsifying properties of chickpea, faba bean, lentil and pea proteins produced by isoelectric precipitation and salt extraction. Food Res Int 44:2742–2750
Kinsella JE (1979) Functional properties of soy proteins. J Am Oil Chem Soc 56:242–258
Kole C, Hall TC (2008) Compendium of transgenic crop plants. Wiley, Chichester
Lahuta LB, Ciak M, Rybiński W, Bocianowski J, Börner A (2018) Diversity of the composition and content of soluble carbohydrates in seeds of the genus Vicia (Leguminosae). Genet Resour Crop Evol 65:541–554
Lawal OS (2004) Functionality of African locust bean (Parkia biglobosa) protein isolate: effects of pH, ionic strength and various protein concentrations. Food Chem 86:345–355
León-Espinosa EB et al (2016) Hypocholesterolemic and anticarcinogenic effect of Vicia faba protein hydrolyzates. Nutr Cancer 68:856–864
López DdJP, Huerta AG, Mora OF, Arriaga MR, Dávila JFR, Vildózola ÁC, Martínez JGA (2014) Aplicación de métodos multivariados para identificar cultivares sobresalientes de haba para el Estado de México, Mexico. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Agrícolas 5:265–278
Majeed T, Wani IA, Hamdani AM, Bhat NA (2018) Effect of sonication and γ-irradiation on the properties of pea (Pisum sativum) and vetch (Vicia villosa) starches: a comparative study. Int J Biol Macromol 114:1144–1150
Malomo SA, Aluko RE (2015) Conversion of a low protein hemp seed meal into a functional protein concentrate through enzymatic digestion of fibre coupled with membrane ultrafiltration. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 31:151–159
Mandal DK, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK, Kushwaha JP, Chaudhari CV, Dubey KA, Varshney L (2017) Optimization of acrylic acid grafting onto polypropylene using response surface methodology and its biodegradability. Radiat Phys Chem 132:71–81
Martínez-Velasco A, Lobato-Calleros C, Hernández-Rodríguez BE, Román-Guerrero A, Alvarez-Ramirez J, Vernon-Carter EJ (2018) High intensity ultrasound treatment of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) protein: effect on surface properties, foaming ability and structural changes. Ultrason Sonochem 44:97–105
Megías C, Cortés-Giraldo I, Giron-Calle J, Alaiz M, Vioque J (2016) Free amino acids, including canavanine, in the seeds from 32 Vicia species belonging to subgenus Vicilla. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:126–129
Mohamed A, Hussain S, Alamri M, Qasem AAA, Ibraheem M, Alhazmi M (2019) Dynamic rheological properties of corn starch-date syrup gels. J Food Sci Technol 56:927–936
Mohd Sharif NSA, Thor ES, Zainol N, Jamaluddin MF (2017) Optimization of ferulic acid production from banana stem waste using central composite design. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36:1217–1223
Mundi S, Aluko R (2012) Physicochemical and functional properties of kidney bean albumin and globulin protein fractions. Food Res Int 48:299–306
Mune MAM, Minka SR, Mbome IL (2014) Optimising functional properties during preparation of cowpea protein concentrate. Food Chem 154:32–37
Navrátilová A, Neumann P, Macas J (2003) Karyotype analysis of four Vicia species using in situ hybridization with repetitive sequences. Ann Bot 91:921–926
Neto VQ, Narain N, Silva J, Bora P (2001) Functional properties of raw and heat processed cashew nut (Anacardium occidentale L.) kernel protein isolates. Nahrung 45:258–262
Ovando-Martínez M, Bello-Pérez LA, Whitney K, Osorio-Díaz P, Simsek S (2011) Starch characteristics of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) grown in different localities. Carbohydr Polym 85:54–64
Paredes-López O, Ordorica-Falomir C, Olivares-Vazquez M (1991) Chickpea protein isolates: physicochemical, functional and nutritional characterization. J Food Sci 56:726–729
Pastor-Cavada E, Juan R, Pastor JE, Alaiz M, Giron-Calle J, Vioque J (2011) Antioxidative activity in the seeds of 28 Vicia species from Southern Spain. J Food Biochem 35:1373–1380
Rabey J, Vered Y, Shabtai H, Graff E, Korczyn A (1992) Improvement of parkinsonian features correlate with high plasma levodopa values after broad bean (Vicia faba) consumption. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:725–727
Ragab DM, Babiker EE, Eltinay AH (2004) Fractionation, solubility and functional properties of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) proteins as affected by pH and/or salt concentration. Food Chem 84:207–212
Rodrigo R, Toro CA, Cuellar J (2012) Influence of the geometric factors of the experimental device used in suspension polymerization on the properties of poly (styrene-co-divinylbenzene) microparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 124:1431–1446
Sai-Ut S, Ketnawa S, Chaiwut P, Rawdkuen S (2009) Biochemical and functional properties of proteins from red kidney, navy and adzuki beans. Asian J Food Agro-Industry 2:493–504
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2015) Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll 43:679–689
Silva MLS, Rangel MG (2017) A Vicia villosa agglutinin biosensor for cancer-associated Tn antigen. Sensors Actuators B Chem 252:777–784
Tang C-H, Ten Z, Wang X-S, Yang X-Q (2006) Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 54:8945–8950
Thaiphanit S, Anprung P (2016) Physicochemical and emulsion properties of edible protein concentrate from coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) processing by-products and the influence of heat treatment. Food Hydrocoll 52:756–765
Vered Y, Grosskopf I, Palevitch D, Harsat A, Charach G, Weintraub MS, Graff E (1997) The influence of Vicia faba (broad bean) seedlings on urinary sodium excretion. Planta Med 63:237–240
Vioque J, Alaiz M, Girón-Calle J (2012) Nutritional and functional properties of Vicia faba protein isolates and related fractions. Food Chem 132:67–72
Wang J-S et al (2019) Physicochemical, functional and emulsion properties of edible protein from avocado (Persea americana Mill.) oil processing by-products. Food Chem 288:146–153
Westhoek H, Rood G, van den Berg M, Janse J, Nijdam D, Reudink M, Stehfest E (2011) The protein puzzle: the consumption and production of meat, dairy and fish in the European Union. Eur J Nutr Food Saf:123-144
Zayas JF (2012) Functionality of proteins in food. Springer science & business media
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Zhong J, Tan L, Liu C (2019) Effect of pH on emulsification performance of a new functional protein from jackfruit seeds. Food Hydrocoll 93:325–334
Funding
The study project was supported by Semnan University of Medical Sciences and approved by Ethics committe (Approval ID: IR.SEMUMS.REC.1398.200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Behdad Shokrolahi Yancheshmeh : Conceptualization, methodology, software. Arezoo Ebrahimi: Rewiting—original draft preparation and data curation. Leila Monjazeb Marvdashti: Investigation and visualization. Nabi Shariatifar: Design of study, supervision, rewriting—original draft preparation. Alireza Emadi1: Software, validation. Anna Abdolshahi1: Rewriting—original draft preparation, conceptualization, methodology.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Ethics endorsement: This article does not include any studies with human or animal participants conducted by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Behdad Shokrollahi Yancheshmeh declares that he has no conflict of interest. Leila Monjazeb Marvdashti declares that she has no conflict of interest. Alireza Emadi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Anna Abdolshahi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Arezoo Ebrahimi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Nabi Shariatifar declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yancheshmeh, B.S., Marvdashti, L.M., Emadi, A. et al. Evaluation of Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Vicia villosa Seed Protein. Food Anal. Methods 15, 1187–1202 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02185-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02185-z