Abstract
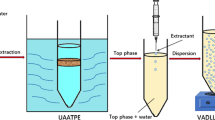
In this research study, a novel deep eutectic solvent was synthetized and used for rapid and simple ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop (USA-DLLME-SFO) method. The proposed method was applied for simultaneous separation and preconcentration of penicillin G, ampicillin, and amoxicillin prior to their analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection (HPLC–PDA). Benzyl triethylammonium chloride (as hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA)) and decanoic acid (as hydrogen bond donor (HBD)) (1:3 mol ratio)) were synthetized and used as hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent (HP-DES) in USA-DLLME-SFO process. Important parameters including pH, DES volume, dispersive solvent type and volume, sonication time, sample volume, and ionic strength were investigated. Under the optimum conditions, the LODs of 0.18–0.35 µg kg−1 for aqueous solutions, 2.8–3.5 µg kg−1 for chicken meat, 1.16–2.35 µg kg−1 for honey, and 2.73–5.08 µg kg−1 for egg were acquired for penicillin G, ampicillin, and amoxicillin. The suitable linearity of 3.0–500 µg kg−1 for penicillin G and amoxicillin and 7.5–750 µg kg−1 for ampicillin was attained for all real samples. The inter-day precision (the relative standard deviations (RSDs %)) below 4.2% was also acquired for three concentrations of 50, 100, and 200 µg kg−1 of analytes within seven replications. In order to consider the reproducibility, the analytical process was carried out at optimum conditions within 4 days and each day for three times. The reproducibility values of 3.1, 2.6, and 3.5% were achieved for penicillin G (Pen. G), ampicillin (Amp.), and amoxicillin (Amox.) (100 µg kg−1), respectively. The proposed method was successfully applied for determination of the target antibiotics in chicken meat, egg, and honey with the relative recoveries over 97.0% which confirms high capability of the method for application in complex matrices.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghaei A, ErfaniJazi M, Mlsna ET, Kamyabi MA (2019) A Novel Method for the Preconcentration and Determination of Ampicillin Using Electromembrane Microextraction Followed by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J Sep Sci 42:3002–3008. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900016
AhmadzadehAnvar S, Torbati M, Farajzadeh MA, AfsharMogaddam MR (2020) Elevated temperature homogeneous liquid phase extraction coupled to ionic liquid–based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography: application of water-miscible ionic liquids as extraction solvent in determination of carbamate pesticides. Food Anal Methods 13:1282–1291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01742-2
Campillo N, Viñas P, Šandrejová J, Andruch V (2017) Ten years of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and derived techniques. ApSRv 52:267–415. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2016.1224240
Caro YS, Cámara MS, De Zan MM (2020) A review of bioanalytical methods for the therapeutic drug monitoring of β-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients: evaluation of the approaches used to develop and validate quality attributes. Talanta 210:120619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120619
El-Deen AK, Shimizu K (2019) Deep eutectic solvent as a novel disperser in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet (DLLME-SFOD) for preconcentration of steroids in water samples: assessment of the method deleterious impact on the environment using Analytical Eco-Scale and Green Analytical Procedure Index. Microchem J 149:103988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.103988
Erarpat S, Bodur S, Öz E, Bakırdere S (2019) Determination of butyltin compounds in fish and mussel samples at trace levels by vortex assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction-gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Food Compos Anal 82:103248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103248
Faraji M (2019) Novel hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for vortex assisted dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction of two auxins in water and fruit juice samples and determination by high performance liquid chromatography. Microchem J 150:104130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104130
Faraji M, Mahmoodi-Maymand M, Dastmalchi F (2020a) Green, fast and simple dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method by using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for analysis of folic acid in fortified flour samples before liquid chromatography determination. Food Chem 320:126486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126486
Faraji M, Noormohammadi F, Adeli M (2020b) Preparation of a ternary deep eutectic solvent as extraction solvent for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of nitrophenols in water samples Journal of Environmental. Chem Eng 8:103948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103948
Golzari Aqda T, Behkami S, Raoofi M, Bagheri H (2019) Graphene oxide-starch-based micro-solid phase extraction of antibiotic residues from milk samples. J Chromatogr A 1591:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.11.069
Li G, Row KH (2019) Utilization of deep eutectic solvents in dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 120:115651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115651
Li G, Row KH (2020) Air assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (AA-DLLME) using hydrophilic–hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the isolation of monosaccharides and amino acids from Kelp. Anal Lett 53:188–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1643358
Li X, Yin Z, Zhai Y, Kang W, Shi H, Li Z (2020) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of four β-lactams using polypyrrole-coated magnetic nanoparticles from water samples by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography analysis. J Chromatogr A 1610:460541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460541
Liu X et al (2019) Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the preconcentration of pyrethroid insecticides prior to determination by high-performance liquid chromatography. Microchem J 146:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.048
Mabrouk MM, Soliman SM, El-Agizy HM, Mansour FR (2020) Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of three gliflozins in human plasma by HPLC/DAD. Journal of Chromatogr B 1136:121932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121932
Macarov CA et al (2012) Multi residue determination of the penicillins regulated by the European Union, in bovine, porcine and chicken muscle, by LC–MS/MS. Food Chem 135:2612–2621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.126
Mammana SB, del C. Abraham E, Camargo AB, Vázquez Á, Altamirano JC (2020) Enzymatic digestion coupled to surfactant-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction: a mild approach for determining polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human hair sample. ChemistrySelect 5:2179–2184. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201904795
Mimini V, Ianni F, Marini F, Hettegger H, Sardella R, Lindner W (2019) Electrostatic attraction-repulsion model with Cinchona alkaloid-based zwitterionic chiral stationary phases exemplified for zwitterionic analytes. Anal Chim Acta 1078:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.006
Mohebi A, Samadi M, Tavakoli HR, Parastouei K (2020) Homogenous liquid–liquid extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the extraction of some antibiotics from milk samples before their determination by HPLC. Microchem J 157:104988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104988
Nemati M, Farajzadeh MA, Mohebbi A, Khodadadeian F, AfsharMogaddam MR (2020) Development of a stir bar sorptive extraction method coupled to solidification of floating droplets dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of acidic pesticides from tomato samples. J Sep Sci 43:1119–1127. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201901000
Pirsaheb M, Hosseini H, MohamadiSorkali H, Fattahi N, Noori N (2019) preconcentration and determination of amoxicillin and ceftriaxone in hospital sewage using vortex-assisted liquid-phase microextraction based on the solidification of the deep eutectic solvent followed by HPLC–UV. Int J Environ Anal Chem 99:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1576866
Rajabi M, Ghassab N, Hemmati M, Asghari A (2018) Emulsification microextraction of amphetamine and methamphetamine in complex matrices using an up-to-date generation of eco-friendly and relatively hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J Chromatogr A 1576:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.040
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Milani Hosseini M-R, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr 1116:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.007
Sajid M (2018) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with derivatization: a review of different modes, applications, and green aspects TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 106:169–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.07.009
Samanidou V, Michaelidou K, Kabir A, Furton KG (2017) Fabric phase sorptive extraction of selected penicillin antibiotic residues from intact milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Food Chem 224:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.12.024
Shahi M, Javadi A, AfsharMogaddam MR, Mirzaei H, Nemati M (2021) Preparation of multiwall carbon nanotube/urea-formaldehyde nanocomposite as a new sorbent in solid-phase extraction and its combination with deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for extraction of antibiotic residues in honey. J Sep Sci 44:576–584. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000679
Shirani M, Habibollahi S, Akbari A (2019) Centrifuge-less deep eutectic solvent based magnetic nanofluid-linked air-agitated liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for simultaneous determination of cadmium, lead, copper, and arsenic in food samples and non-alcoholic beverages. Food Chem 281:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.12.110
Shirazinia SR, Semnani A, Nekoeinia M, Shirani M, Akbari A (2020) Novel sustainable metal complex based deep eutectic solvents for extractive desulphurisation of fuel. J Mol Liq 301:112364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112364
Soledad-Rodríguez B, Fernández-Hernando P, Garcinuño-Martínez RM, Durand-Alegría JS (2017) Effective determination of ampicillin in cow milk using a molecularly imprinted polymer as sorbent for sample preconcentration. Food Chem 224:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.097
Teglia CM, Gonzalo L, Culzoni MJ, Goicoechea HC (2019) Determination of six veterinary pharmaceuticals in egg by liquid chromatography: chemometric optimization of a novel air assisted-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by solid floating organic drop. Food Chem 273:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.034
Torbati M, Farajzadeh MA, Mogaddam MRA, Torbati M (2019) Deep eutectic solvent based homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction coupled with in-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction performed in narrow tube; application in extraction and preconcentration of some herbicides from tea. J Sep Sci 42:1768–1776. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201801016
Yang G, Zhao F (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer grown on multiwalled carbon nanotube surface for the sensitive electrochemical determination of amoxicillin. Electrochim Acta 174:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.05.156
Yao T, Du K (2020) Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides in milk: in-situ magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPLC. Food Chem 331:127342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127342
Zare Khafri B, Akhond M, Absalan G (2019) Carrier-mediated hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction for preconcentration followed by spectrophotometric determination of amoxicillin. J Iran Chem Soc 16:2683–2692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-019-01730-2
Zhang C et al (2019) The application of the QuEChERS methodology in the determination of antibiotics in food: a review TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 118:517–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.012
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully appreciate the Research Council of University of Jiroft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Mahboube Shirani declares that he has no conflict of interest. Behrouz Akbari-adergani declares that he has no conflict of interest. Fatemeh Shahdadi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mohammad Faraji declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ali Akbari declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirani, M., Akbari-adergani, B., Shahdadi, F. et al. A Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Determination of β-Lactam Antibiotics Residues in Food Samples. Food Anal. Methods 15, 391–400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02122-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02122-0