Abstract
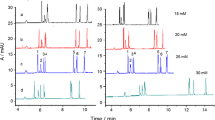
A rapid method for detection of flumequine (FQ) and oxolinic acid (OA) residues from fish tissues was established using pressurized capillary electrochromatography (pCEC). Residual FQ and OA were extracted from fish tissue samples with acidified acetonitrile and purified on an Oasis HLB C18 solid-phase extraction column. The extract was then analyzed by pCEC with the mobile phase (pH = 3) consisting of acetonitrile and 15 mM ammonium acetate (45: 55, v/v, respectively) at the flow rate of 0.07 mL/min, detection wavelength of 324 nm, and applied voltage of −10 kV. Baseline separation of FQ and OA was achieved in 10 min; both drugs showed good linearity in the range of 0.2–5 μg/mL. The recoveries of FQ and OA were between 82 and 92 % (relative standard deviation = 3.63–5.96). The limits of detection for FQ and OA were 0.1 and 0.08 mg/kg, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anadon A, Martinez MA, Martinez M, De La Cruz C, Diaz MJ, Martinez-Larranaga MR (2008) Food Chem Toxicol 46:662
Anonymous (2010) Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Official Journal of the European Communities L15(20 January 2010):1-76
Chen DX, Wang JJ, Jiang YY, Zhou TT, Fan GR, Wu YT (2009) J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:695
Delépée R, Hervé P (2002) J Chromatogr B 775:89
Evaggelopoulou EN, Samanidou VF (2013) Food Chem 136:479
Gajda A, Posyniak A, Zmudzki J, Gbylik M, Bladek T (2012) Food Chem 135:430
Hektoen H, Berge JA, Hormazabal V, Yndestad M (1995) Aquaculture 133:175
Huet AC, Charlier C, Tittlemier SA, Singh G, Benrejeb S, Delahaut P (2006) J Agric Food Chem 54:2822
Jimenez-Diaz I, Hermo MP, Ballesteros O, Zafra-Gomez A, Barron D, Barbosa J, Navalon A (2013) Chromatographia 76:707
Lai HT, Lin JJ (2009) Chemosphere 75:462
Li P, Li SP, Yang FQ, Wang YT (2007) J Sep Sci 30:900
Li M, Lin XC, **e ZH (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:5320
Naviner M, Giraud E, Thorin C, Le Bris H, Pouliquen H, Ganiere J-P (2007) Aquaculture 269:31
Naviner M, Gordon L, Giraud E, Denis M, Mangion C, Le Bris H, Ganiere JP (2011) Aquaculture 315:236
Okerman L, Noppe H, Cornet V, De Zutter L (2007) Food Addit Contam 24:252
Posyniak A (2000) Med Weter 56:296
Roudaut B, Yorke JC (2002) J Chromatogr B 780:481
Samuelsen OB (2006) Aquaculture 255:55
Stoilova N, Surleva A, Stoev G (2013) Food Anal Methods 6:803
Tang HP, Ho C, Lai SS (2006) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:2565
Tao X, Chen M, Jiang H, Shen J, Wang Z, Wang X, Wu X, Wen K (2013) Anal Bioanal Chem 405:7477
Touraki M, Ladoukakis M, Prokopiou C (2001) J Chromatogr B 751:247
Touraki M, Niopas I, Karagiannis V (2012) J Fish Dis 35:513
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21276240) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Z3110487 and Y2111223); Funds of Zhoushan Science and technology bureau (2011C22044, 2013C41006).
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
The authors declare that the design, performance, and reporting of research funded under the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21276240) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Z3110487 and Y2111223); Funds of Zhoushan Science and technology bureau (2011C22044, 2013C41006) are free from bias resulting from investigator financial conflicts of interest. No financial relationship with other institutions or private industry has influenced the results of this study. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Conflict of Interest
**ao-kun OuYang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yu-Yang Luo declares that she has no conflict of interest. Zheng-Shun Wen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Wei-Jian Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Guo-Zhou Cao declares that he has no conflict of interest. **ao-Yan Zhu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Li-ye Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yang-Guang Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jie-Ying Dong declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OuYang, Xk., Luo, YY., Wen, ZS. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Flumequine and Oxolinic Acid Residues in Aquatic Products Using Pressurized Capillary Electrochromatography. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1770–1775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9818-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9818-6