Abstract
Objective
To assess whether the combined evaluation of vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) expression and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake correlates with lymph node metastasis and post-operative recurrence in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods
Forty-six patients with lung adenocarcinomas, who had undergone both preoperative FDG PET imaging and thoracotomy, were enrolled in this study. The surgically resected tumor specimens were used to assess the protein levels of VEGF-D as measured by immunohistochemical assay.
Results
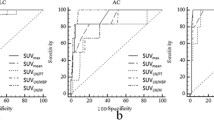
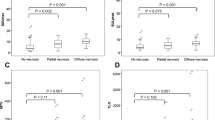
The patients were divided into the following four groups: those who were VEGF-D negative and had low FDG uptake (group I, 3 patients), VEGF-D positive and had low FDG uptake (group II, 20 patients), VEGF-D negative and had high FDG uptake (group III, 13 patients), and VEGF-D positive and had high FDG uptake (group IV, 10 patients). Lymph node metastases were seen only in group III. The 5-year disease-free survival rates were 66.7% in group I, 83.9% in group II, 8.3% in group III, and 64.0% in group IV (p < 0.0001). Thus, patients in group III exhibited the most unfavorable prognoses for recurrence. In multivariate analysis, the combined evaluation of VEGF-D expression and FDG uptake was an independent parameter for post-operative recurrence (p = 0.018).
Conclusion
A combination of low VEGF-D expression and high FDG uptake may be a biological indicator of lymph node metastasis and post-operative recurrence in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller DL, Rowland CM, Deschamps C, Allen MS, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC. Surgical treatment of non-small cell lung cancer 1 cm or less in diameter. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73:1545–51.
Naruke T, Goya T, Tsuchiya R, Suemasu K. The importance of surgery to non-small cell carcinoma of lung with mediastinal lymph node metastasis. Ann Thorac Surg. 1988;46:603–10.
Higashi K, Ito K, Hiramatsu Y, Ishikawa T, Sakuma T, Matsunari I, et al. 18F-FDG uptake by primary tumor as a predictor of intratumoral lymphatic vessel invasion and lymph node involvement in non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of a multicenter study. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:267–73.
Okada M, Tauchi S, Iwanaga K, Mimura T, Kitamura Y, Watanabe H, et al. Associations among bronchioloalveolar carcinoma components, positron emission tomographic and computed tomographic findings, and malignant behavior in small lung adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:1448–54.
Nomori H, Watanabe K, Ohtsuka T, Naruke T, Suemasu K, Kobayashi T, et al. Fluorine 18-tagged fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomographic scanning to predict lymph node metastasis, invasiveness, or both, in clinical T1 N0 M0 lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;128:396–401.
Vansteenkiste J, Fischer BM, Dooms C, Mortensen J. Positron-emission tomography in prognostic and therapeutic assessment of lung cancer: systemic review. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:531–40.
Hanin FX, Lonneux M, Cornet J, Noirhomme P, Coulon C, Distexhe J, et al. Prognostic value of FDG uptake in early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33:819–23.
Sasaki R, Komaki R, Macapinlac H, Erasmus J, Allen P, Forster K, et al. [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by positron emission tomography predicts outcome of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1136–43.
Cheran SK, Nielsen ND, Patz EF. False-negative findings for primary lung tumors on FDG positron emission tomography: staging and prognostic implications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:1129–32.
Achen MG, Jeltsch M, Kukk E, Mäkinen T, Vitali A, Wilks AF, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:548–53.
Niki T, Iba S, Tokunou M, Yamada T, Matsuno Y, Hirohashi S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, B, C, and D and their relationships to lymph node status in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2431–9.
Maekawa S, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Enatsu S, Kawakami T, Kuroki M, et al. Correlation between lymph node metastasis and the expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in T1 lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:3735–42.
Carrillo de Santa Pau E, Arias FC, Caso Peláez E, Muñoz Molina GM, Sánchez Hernández I, Muguruza Trueba I, et al. Prognostic significance of the expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, B, C, and D and their receptors R1, R2, and R3 in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:1701–12.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Shimizu K, Ishikita T, Higuchi T, Imai H, et al. Correlation of angiogenesis with 18F-FMT and 18F-FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:753–8.
Guo J, Higashi K, Ueda Y, Oguchi M, Takegami T, Toga H, et al. Microvessel density: correlation with 18F-FDG uptake and prognostic impact in lung adenocarcinomas. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:419–25.
Yokoyama Y, Charnock-Jones DS, Licence D, Yanaihara A, Hastings JM, Holland CM, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D and its receptor, VEGF receptor 3, as a prognostic factor in endometrial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1361–9.
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989;246:1306–9.
Zhang F, Tang Z, Hou X, Lennartsson J, Li Y, Koch AW, et al. VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:6152–7.
Plate KH. From angiogenesis to lymphangiogenesis. Nat Med. 2001;7:151–2.
Jüttner S, Wissmann C, Jöns T, Vieth M, Hertel J, Gretschel S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D and its receptor VEGFR-3: two novel independent prognostic markers in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:228–40.
White JD, Hewett PW, Kosuge D, McCulloch T, Enholm BC, Carmichael J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D expression is an independent prognostic marker for survival in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1669–75.
Onogawa S, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Kuwai T, Kimura S, Chayama K. Expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D at the invasive edge correlates with lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2004;95:32–9.
Yokoyama Y, Charnock-Jones DS, Licence D, Yanaihara A, Hastings JM, Holland CM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D is an independent prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:237–44.
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Yang Q, Imabun S, Nakahara M, et al. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor D in breast carcinoma with long-term follow-up. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:716–21.
O-charoenrat P, Rhys-Evans P, Eccles SA. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor family members in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph node metastasis. Cancer. 2001;92:556–68.
George ML, Tutton MG, Janssen F, Arnaout A, Abulafi AM, Eccles SA, et al. VEGF-A, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D in colorectal cancer progression. Neoplasia. 2001;3:420–7.
Al-Rawi MA, Watkins G, Mansel RE, Jiang WG. Interleukin 7 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor D in breast cancer cells and induces lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Br J Surg. 2005;92:305–10.
Hu DE, Hori Y, Fan TP. Interleukin-8 stimulates angiogenesis in rats. Inflammation. 1993;17:135–43.
Akagi Y, Liu W, **e K, Zebrowski B, Shaheen RM, Ellis LM. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human colon cancer by interleukin-1beta. Br J Cancer. 1999;80:1506–11.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant for Project Research from High-Tech Research Center of Kanazawa Medical University (H2010-12, H2009-12, H2008-12, H2007-12, H2008-11, H2008-10, H2007-10, S2005-6, S2006-2), by a Grant-in Aid (19590370) for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Japan, and by the policy based medical services network from the National Hospital Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Higashi, K., Ishigaki, Y. et al. Assessment of VEGF-D expression measured by immunohistochemical staining and F-18 FDG uptake on PET as biological prognostic factors for recurrence in patients with surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Nucl Med 24, 533–540 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0392-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0392-8