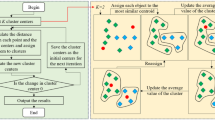
Abstract
Disaggregating rainfall data is a crucial step in producing accurate hydrological and meteorological assessments because it refines coarse-resolution rainfall data into finer temporal or spatial scales. To generate high-resolution rainfall data, the Microcanonical Multiplicative Random Cascade (MMRC) model is a stochastic method used in rainfall disaggregation. The MMRC model is a reliable process for producing high-resolution rainfall data. However, it tends to overstate extreme precipitation events. This is because MMRC assumes a predefined method of classification which does not always represent the behaviour of extreme events. To address overestimation in the basic MMRC model, it was modified into MMRC with K-means clustering (MMRC-K), resulting in improved outcomes. Seeking additional enhancements, DBSCAN was integrated into the MMRC model to refine classification and further improve accuracy, especially in preserving extreme precipitation characteristics. An unsupervised machine learning approach called DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) is used to categorize data points based on their density and spatial proximity. By automatically calculating the number of clusters based on the data and successfully recognizing and controlling outliers, DBSCAN can improve outcomes. In this study, we used DBSCAN for data categorization and combined it with the MMRC model for rainfall disaggregation to successfully preserve the characteristics of extreme events. The results showed a considerable improvement in the intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curve, effectively protecting the representation of extreme rainfall. This approach can be an efficient approach for disaggregating daily rainfall into an hourly scale when high-resolution data is unavailable. MMRC-DBSCAN can be used in a variety of hydrological and meteorological applications, such as flood forecasting, water resource management, and climate change studies.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Bhattacharyya D, Saha U (2023) Deep learning application for disaggregation of rainfall with emphasis on preservation of extreme rainfall characteristics for Indian monsoon conditions. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37:1021–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02331-x
Cowpertwait PSP, O’Connell PE, Metcalfe AV, Mawdsley JA (1996) Stochastic point process modelling of rainfall. II. Regionalisation and disaggregation. J Hydrol 175:47–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(96)80005-9
Deka P, Saha U (2023) Introduction of k-means clustering into random cascade model for disaggregation of rainfall from daily to 1-hour resolution with improved preservation of extreme rainfall. J Hydrol 620:129478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129478
Dlamini NS, Rowshon MK, Sahab U et al (2015) Develo** and calibrating a stochastic rainfall generator model for simulating daily rainfall by Markov chain approach. Jurnal Teknologi 76. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v76.5946
Ester M, Kriegel H-P, Sander J, Xu X (1996) A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. Inkdd 96:226–231
Güntner A, Olsson J, Calver A, Gannon B (2001) Cascade-based disaggregation of continuous rainfall time series: the influence of climate. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 5:145–164. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-5-145-2001
Halder S, Saha U (2021) Future Projection of Extreme Rainfall for Flood Management due to Climate Change in an Urban Area. J Sustain Water Built Environ 7:04021012. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSWBAY.0000954
Hubert P, Tessier Y, Lovejoy S et al (1993) Multifractals and extreme rainfall events. Geophys Res Lett 20:931–934. https://doi.org/10.1029/93GL01245
Jeganathan A, Andimuthu R, Kandasamy P (2021) Challenges in Chennai City to Cope with Changing Climate. Eur J Clim Ch 3:33–43. https://doi.org/10.34154/2021-EJCC-0017/euraass
Koutsoyiannis D, Onof C, Wheater HS (2003) Multivariate rainfall disaggregation at a fine timescale. Water Resour Res 39:2002WR001600. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002WR001600
Lall AB, Pandit M, Kulshreshta N, Appasamy P (1991) Climate and housing form — a case study of New Delhi. Energy Build 16:837–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7788(91)90079-I
Licznar P, Łomotowski J, Rupp DE (2011) Random cascade driven rainfall disaggregation for urban hydrology: An evaluation of six models and a new generator. Atmos Res 99:563–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.12.014
Licznar P, De Michele C, Adamowski W (2015) Precipitation variability within an urban monitoring network via microcanonical cascade generators. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:485–506. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-485-2015
Lisniak D, Franke J, Bernhofer C (2013) Circulation pattern based parameterization of a multiplicative random cascade for disaggregation of observed and projected daily rainfall time series. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:2487–2500. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-2487-2013
Müller H, Haberlandt U (2018) Temporal rainfall disaggregation using a multiplicative cascade model for spatial application in urban hydrology. J Hydrol 556:847–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.01.031
Müller-Thomy H (2020) Temporal rainfall disaggregation using a micro-canonical cascade model: possibilities to improve the autocorrelation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 24:169–188. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-169-2020
Olsson J (1998) Evaluation of a scaling cascade model for temporal rain- fall disaggregation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 2:19–30. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-2-19-1998
Olsson J, Niemczynowicz J, Berndtsson R, Larson M (1992) An analysis of the rainfall time structure by box counting—some practical implications. J Hydrol 137:261–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(92)90060-9
Olsson J, Berndtsson R (1998) Temporal rainfall disaggregration based on scaling properties. Water Sci Technol 37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00318-7
Onof C, Wang L-P (2020) Modelling rainfall with a Bartlett-Lewis process: new developments. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 24:2791–2815. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-2791-2020
Onof C, Northrop P, Wheater HS, Isham V (1996) Spatiotemporal storm structure and scaling property analysis for modeling. J Geophys Res 101:26415–26425. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JD01378
Pui A, Sharma A, Mehrotra R et al (2012) A comparison of alternatives for daily to sub-daily rainfall disaggregation. J Hydrol 470–471:138–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.08.041
Rana A, Foster K, Bosshard T et al (2014) Impact of climate change on rainfall over Mumbai using Distribution-based Scaling of Global Climate Model projections. J Hydrol: Reg Stud 1:107–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2014.06.005
Rodriguez-Iturbe I, Cox D (1987) Some models for rainfall based on stochastic point processes. Proc R Soc Lond A 410:269–288. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1987.0039
Rodriguez-Iturbe I, Roxbee C, Valerie I (1988) A point process model for rainfall: further developments. Proc R Soc Lond A 417:283–298. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1988.0061
Waymire E, Gupta VK (1981) The mathematical structure of rainfall representations: 1. A review of the stochastic rainfall models. Water Resour Res 17:1261–1272. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR017i005p01261
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank IIEST Shibpur for providing the facilities and infrastructure to complete this study. We would also like to thank India Meteorological Department for providing the required data to carry out the project.
Funding
The authors declare that no funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.P.C.: Methodology, Software, Conceptualization, Writing—original draft.
U.S.: Supervision, Writing—review &; editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable to the current study.
Consent to participate
The authors express their consent to participate in the research and review.
Consent for publication
The authors express their consent for the publication of research work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, D.P., Saha, U. Improvement of extreme rainfall characteristics for disaggregation of rainfall using MMRC with machine learning based DBSCAN clustering algorithm. Earth Sci Inform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01309-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01309-3