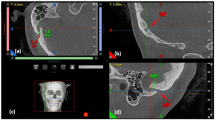
Abstract
To compare the depth of mastoid antrum on High Resolution Computed Tomography and per operatively in cases undergoing mastoidectomy. This prospective observational study was done in a tertiary care Army Hospital with 35 patients meriting cortical mastoidectomy surgery. The patients underwent HRCT of temporal bone as a routine pre-operative work up, where depth of mastoid antrum was measured from dome of lateral semicircular canal to outer cortex of temporal bone. Depth was also recorded per-operatively with the help of measuring scale. Measurements were correlated and data was analysed statistically. There were 12 male patients and 23 females. 6 patients were < 3 years of age and 29 above. Study included 29 cases of Chronic Otitis Media and 6 of Bilateral Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Mean depth of mastoid antrum was 1.625 cm ± 0.228 on HRCT, and 1.651 cm ± 0.245 per-operatively. Depths of mastoid antrum on HRCT and per operatively amongst paediatrics as well as adult cases were comparable, but were more than the standard depth of 1 cm in 5 (82.3%) paediatrics cases and ˃1.5 cm in 24 (82.9%) adult patients. In absence of Koerner’s Septum, mean HRCT depth was 1.60 cm ± SD 0.23 and per operatively was 1.63 cm ± SD 0.21; whereas in its presence mean HRCT depth was 1.84 cm ± SD 0.069 and per-operatively was 1.85 cm ± SD 0.42. Significant difference in depth was noted between adults and children, and between the cases with or without Koerner’s Septum. However, difference in depth was not significant when compared between different genders, laterality of disease or disease pathology.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Available data has not been not acquired via a biobank/biorepository.
Code Availability
Available.
References
Senthil KB (2021) Morphometric study of MacEwan’s triangle in relation to depth of the sigmoid sinus plate. Indian J Forensic Med Toxicol 15(1):641–645. https://doi.org/10.3750/ijfmt.v15i1.13486
Valentine P, Wright T (2010) Anatomy and embryology of external and middle ear. In: Watkinson JC, Clarke RW (eds) Scott-Brown’s Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery, 8th edn. CRC Press Taylor & Francis group, Boca Raton, pp 525–543
Aslan A, Multu C, Celik O, Govsa F, Ozgur T (2004) Surgical implication of anatomical landmarks on the lateral surface of mastoid bone. Surg Radiolog Anatomy 26:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-004-0235-1
Tos M (1982) Mastoid pneumatization: a critical analysis of the hereditary theory. Acta Otolaryngol 94(1–2):73–80
Ueda T, Eguchi S (1962) Distribution of pneumatization of the temporal bone in chronic otitis media seen during the age of antibiotic therapy. J Otol Rhinol Laryngol 64:1539–1542. https://doi.org/10.3950/jibiinkoka.64.1539
Allam AF (1969) Pneumatization of the temporal bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 78(1):49–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348946907800105
Goycoolea MV, Paparella MM, Nissen RL (1989) Atlas of otologic surgery. WB Saunders company, Philadelphia
Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH (1993) Gray’s anatomy, 37th edn. ELBS Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 145–154
Sellars SL (1974) The origins of mastoid surgery. S Afr Med J 48(6):234–242
Bento RF, Fonseca AC (2013) A brief history of mastoidectomy. Int arch Otorhinolaryngol 17(2):168–178. https://doi.org/10.7162/s1809-97772013000200009
Hashemi J, Rajati M, Rezayani L, Bahadori A (2014) Temporal bone measurements; a comparison between rendered spiral CT and surgery. Iran J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.5812/iranjradiol.9400
Yılmazer R, Erdur Ö, Başkadem Yılmazer A (2019) A new landmark for superior semicircular canal: spine of Henle. Tr ENT 29(2):67–71. https://doi.org/10.5606/Tr-ENT.2019.24855
Funding
This research was not supported by any funding from any agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Divya Sethi: Work up of patients, per-operative measurement of depth of mastoid. antrum, data acquisition, statistical analysis and drafting the manuscript. B.K. Prasad: Concept, study design, performing mastoid surgeries and critically reviewing the draft and its finalization for publication. Manoj Gopinath: Radio-imaging and measurement of depth of mastoid antrum on HRCT.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, D., Prasad, B.K. & Gopinath, M. Comparison of Depth of Mastoid Antrum on High Resolution Computed Tomography and Per Operatively in Cases Undergoing Mastoidectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04760-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04760-2