Abstract
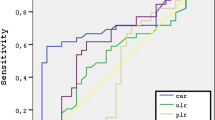
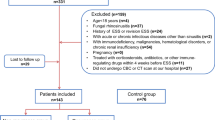
The study was carried out to correlate the inflammatory markers (NLR, ELR, PLR) before and after endoscopic sinus surgery and their role in the prediction of recurrent nasal polyps. This was a hospital-based observational study carried out the 43 patients, aged between 18-45 years, admitted to the department of ENT with CRSwNP and underwent endoscopic sinus surgery. NLR, ELR & PLR values were compared for each patient and calculated from complete blood counts taken before and after surgery follow-up period at post-op 1st week, 3rd week, 3rd month, and 6th month. In our study, 12 out of 43 patients who underwent ESS showed recurrence. The mean value of ELR was higher in the pre-operative and post-operative 1st week in recurrent nasal polyp patients than in non-recurrent nasal polyps. (p-value < 0.05) but there were no significant changes in ELR values in subsequent follow-ups. There were no significant changes in NLR & PLR in the pre-operative and post-operative periods. Although recurrence was common in CRSwNP after endoscopic sinus surgery. Inflammatory markers could be used to predict the chances of recurrence. In our study, ELR is a better parameter than NLR and PLR in the assessment of the chance of recurrence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badia L, Lund V (2001) Topical corticosteroids in nasal polyposis. Drugs 61:573–578
Tosun F, Arslan HH, Karslioglu Y, Deveci MS, Durmaz A (2010) Relationship between postoperative recurrence rate and eosinophil density of nasal polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(7):455–459
Chaaban MR, Walsh Em, Woodworth BA (2013) Epidemiology and differential diagnosis of nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27(6):473–478
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J et al (2012) EPOS 2012: european position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 50(1):1–12
Baumgarten C, Kunkel G, Rudolph R, Staud RD, Sperner I, Gelderblom H (1980) Histopathological examinations of nasal polyps of different etiology. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 226(3):187–197
Cengiz AB, Gumuslu BC, Tansuker HD et al (2020) The comparison of inflammatory markers for the prediction of recurrence of the nasal polyp after endoscopic sinus surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C et al (2011) Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe–an underestimated disease. A GA²LEN study. Allergy 66(9):1216–1223
Alanin MC, Hopkins C (2020) Effect of functional endoscopic sinus surgery on Outcomes in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 20(7):27
Kara A, Guven M, Yilmaz MS, Demir D, Elden H (2018) Are neutrophil, platelet, and eosinophil- to lymphocyte ratio and red blood cell distribution width can be used for nasal polyposis? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(2):409–414
Yilmaz B, Özgür A, Şereflican M, Uysal İÖ, Şengül E, Özbay M, Yıldırım H, Dursun E, Topçu İ (2016) New Predictive Hematologic Parameters in Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Multicenter Study. Acta Med Anatol. Dec 1;4(4):137 – 40
Bayer K, Hamidovic S, Brkic FF, Besser G, Mueller CA, Liu DT (2022) Peripheral eosinophil count and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with revision sinus surgery Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. ;10.1007/s00405-022-07497-2
Yenigun A (2015) Assessment of patients with nasal polyposis by the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 25(4):193–199
Boztepe OF, Gun T, Demir M, Gur OE, Ozel D, Dogru H (2016) A novel predictive marker for the recurrence of nasal polyposis following endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(6):1439–1444
Brescia G, Pedruzzi B, Barion U et al (2016) Are neutrophil-, eosinophil-, and basophil-to-lymphocyte ratios useful markers for pinpointing patients at higher risk of recurrent sinonasal polyps? Am J Otolaryngol 37(4):339–345
Brescia G, Barion U, Zanotti C, Parrino D, Marioni G (2017) Pre- and postoperative blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratios in patients with sinonasal polyps: A preliminary investigation. Allergy Asthma Proc. ;38(5):64–69
Acknowledgements
I express my sincere and deepest gratitude to my esteemed teacher, mentor, and Chief Supervisor Prof. (Dr.) Sachin Jain sir, Dr. Shivendra Pratap Singh sir, and Dr. Sankalp Keshari sir have been a constant source of encouragement and enthusiasm, not only during this thesis project but also during my master’s program. His expertise, valuable suggestions, constant encouragement, affectionate gratitude, understanding, patience, and healthy criticism added considerably to my experience. Without his continual inspiration, it would have not been possible to complete my thesis as well as my master’s program. I sincerely express my gratitude from the core of my heart to my patients for their cooperation and trust, without whose cooperation the work would not have materialized.
Funding
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Consent
Written and informed consent were taken while doing the study. No animal or person were harmed during the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.P., Jain, S., Keshari, S. et al. Comparison of Inflammatory Markers for Prediction of Recurrence of Nasal Polyp after Functional Endoscopy Sinus Surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 3596–3601 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04062-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04062-z