Abstract
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is identified as repetitive and intermittent upper airway collapse or narrowing during sleep. Skeletal advancement through maxillomandibular surgery remains the most effective surgical treatment for OSA but is radical with certain relapse rate. Distraction Osteogenesis of mandible is a single-jaw surgical treatment alternative to bi-jaw surgeries having lesser complications.
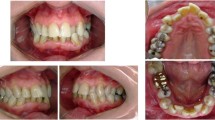
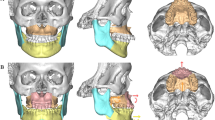
This case report describes successful management of a 46-year-old patient who reported with a chief complain of obstruction in breathing while slee** since one year. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) secondary to a retrognathic mandible was the final diagnosis, which was successfully treated by Distraction Osteogenesis (DO) of the mandible. The case showed enhancement in airway by 13mm and marked forward movement of Point-B (SNB increased by 6 degrees). The Epworth Sleepiness Scale value decreased from 19mm to 8 mm indicating substantial increase in the airway with stable results after 18 months of follow-up (elimination of symptoms and subsequent sound sleep).
Distraction osteogenesis is an effective and reliable method to treat obstructive sleep apnoea secondary to retrognathic mandible.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomonari H, Takada H, Hamada T, Kwon S, Sugiura T, Miyawaki S (2017 Nov) Micrognathia with temporomandibular joint ankylosis and obstructive sleep apnea treated with mandibular distraction osteogenesis using skeletal anchorage: a case report. Head Face Med 10(1):20
Breik O et al (2016) Mandibular distraction osteogenesis for the management of upper airway obstruction in children with micrognathia: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2016.01.009
Prinsell JR (1999) Maxillomandibular advancement surgery in a site-specific treatment approach for obstructive sleep apnoea in 50 consecutive patients. Chest. Dec 1;116(6):1519-29
Li N, Li HP, Wang P, Yan YR, Li SQ, Li QY (2019) Nocturnal Mean Oxygen Saturation is Associated with secondary Polycythemia in Young adults with obstructive sleep apnoea, especially in men. Nat Sci Sleep 11:377
Goyal M, Johnson J. Obstructive sleep apnoea diagnosis and management. Missouri medicine. 2017 Mar;114(2):120.
Brevi B, Di Blasio A, Di Blasio C, Piazza F, D’ASCANIO L, Sesenna E. Which cephalometric analysis for maxillo-mandibular surgery in patients with obstructive sleep apnoeasyndrome?. Acta OtorhinolaryngologicaItalica. 2015 Oct;35(5):332.
Yu X, Wang J, Hou S, Zeng R. Mandibular distraction osteogenesis in the treatment of pediatric temporomandibular joint ankylosis with micrognathia and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A case report with 4-year follow-up. Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4888–4892.
Rejas J, Ballestro S, Angulo JC, Brenes JF, Arumi D, et al. (2017) The Sequential Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis with Secondary Deformities by Distraction Osteogenesis. J Sleep Med Disord 3(7): 1071.
Funding
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandan, S.S., Sane, V.D., Nair, V.S. et al. Distraction Osteogenesis as a reliable method in management of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) secondary to TMJ Ankylosis: A Case Report. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 2470–2476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03770-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03770-w