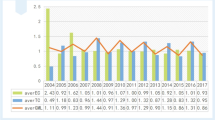
Abstract
Although there are numerous studies on the role of industrial agglomeration on regional innovation, limited research has explored the impact of coagglomeration of manufacturing and producer services on regional innovation with spatial effects. Therefore, based on a unique panel data of 278 cities in China over the period 2003–2017, this paper employs the Spatial Durbin Model (SDM) with space-and-time fixed effect to investigate the direct and spatial effects of coagglomeration of manufacturing and producer services on regional innovation. The results reveal that there is an inverted U-shaped relationship between coagglomeration of manufacturing and producer services and regional innovation in local and neighboring cities, and the negative congestion effect has appeared. Furthermore, the direct and spatial effects of coagglomeration of manufacturing and sub-producer services on regional innovation are heterogeneous. Based on the findings, this paper provides important policy implications for local government in China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Villar, O., & Chamorro-Rivas, J. M. (2001). How do producer services affect the location of manufacturing firms? The role of information accessibility. Environment and Planning a-Economy and Space, 33(9), 1621–1642.
Andersson, M. (2006). Co-location of manufacturing and producer services: A simultaneous equations approach. In Entrepreneurship and dynamics in the knowledge economy, 110–140.Routledge.
Andersson, M., Larsson, J. P., & Wernberg, J. (2019). The economic microgeography of diversity and specialization externalities–firm-level evidence from Swedish cities. Research Policy, 48(6), 1385–1398.
Anselin, L. (2013). Spatial econometrics: methods and models. Springer Science & Business Media.
Arrow, K. J. (1962). The economic implications of learning by doing. The Review of Economic Studies, 29(3), 155–173.
Beaudry, C., & Schiffauerova, A. (2009). Who’s right, Marshall or Jacobs? The localization versus urbanization debate. Research Policy, 38(2), 318–337.
Carlino, G., & Kerr, W. R. (2015). Agglomeration and innovation. In Handbook of regional and urban economics, 5, 349–404. Elsevier.
Castaldi, C., Frenken, K., & Los, B. (2015). Related variety, unrelated variety and technological breakthroughs: An analysis of US state-level patenting. Regional Studies, 49(5), 767–781.
Cheng, Z. H. (2016). The spatial correlation and interaction between manufacturing agglomeration and environmental pollution. Ecological Indicators, 61, 1024–1032.
Chen, X., Liu, Z., & Ma, C. (2017). Chinese innovation-driving factors: Regional structure, innovation effect, and economic development-empirical research based on panel data. Annals of Regional Science, 59(1), 43–68.
Deng, P., Lu, H., Hong, J., Chen, Q., & Yang, Y. (2019). Government R&D subsidies, intellectual property rights protection and innovation. Chinese Management Studies, 13(2), 363–378.
Elhorst, J. P. (2010). Applied spatial econometrics: Raising the bar. Spatial Economic Analysis, 5(1), 9–28.
Elhorst, J. P. (2014). Spatial panel data models. Springer.
Ellison, G., & Glaeser, E. L. (1997). Geographic concentration in US manufacturing industries: A dartboard approach. Journal of Political Economy, 105(5), 889–927.
Ellison, G., Glaeser, E. L., & Kerr, W. R. (2010). What causes industry agglomeration? Evidence from coagglomeration patterns. American Economic Review, 100(3), 1195–1213.
Fang, L. (2019). Manufacturing clusters and firm innovation. Economic Development Quarterly, 33(1), 6–18.
Fang, J. Y., Tang, X., **e, R., & Han, F. (2020). The effect of manufacturing agglomerations on smog pollution. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 54, 92–101.
Feldman, M. P., & Audretsch, D. B. (1999). Innovation in cities: Science-based diversity, specialization and localized competition. European Economic Review, 43(2), 409–429.
Feng, Y. C., Wang, X. H., Du, W. C., Wu, H. Y., & Wang, J. T. (2019). Effects of environmental regulation and FDI on urban innovation in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 235, 210–224.
Frenken, K., van Oort, F., & Verburg, T. (2007). Relate variety, unrelated variety and regional economic growth. Regional Studies, 41(5), 685–697.
Gabe, T. M., & Abel, J. R. (2016). Shared knowledge and the coagglomeration of occupations. Regional Studies, 50(8), 1360–1373.
Gallagher, R. M. (2013). Ship** costs, information costs, and the sources of industrial coagglomeration. Journal of Regional Science, 53(2), 304–331.
Geary, R. C. (1954). The contiguity ratio and statistical map**. The Incorporated Statistician, 5(3), 115–146.
Getis, A., & Ord, J. K. (1992). The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geographical Analysis, 24(3), 189–206.
Ghani, E., Goswami, A. G., & Kerr, W. R. (2016). Spatial development and agglomeration economies in services—Lessons from India. The World Bank.
Greenfield, H. I. (1966). Manpower and the growth of producer services.
Greunz, L. (2004). Industrial structure and innovation - evidence from European regions. Journal of Evolutionary Economics, 14(5), 563–592.
Gujarati, D. N. (2009). Basic econometrics. Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Han, F., **e, R., & Fang, J. Y. (2018a). Urban agglomeration economies and industrial energy efficiency. Energy, 162, 45–59.
Han, F., **e, R., Lu, Y., Fang, J. Y., & Liu, Y. (2018b). The effects of urban agglomeration economies on carbon emissions: Evidence from Chinese cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 172, 1096–1110.
Helsley, R. W., & Strange, W. C. (2014). Coagglomeration, clusters, and the scale and composition of cities. Journal of Political Economy, 122(5), 1064–1093.
Hu, A. G. (2015). Embracing China’s “New Normal” why the economy is still on track. Foreign Affairs, 94(3), 8–12.
Huang, Y., Fang, Y. G., & Gu, G. F. (2022). Innovation effect and regional difference of related variety: An empirical study based on prefecture-level city data of China. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy, 15(2), 441–454.
Innocenti, N., & Lazzeretti, L. (2019). Do the creative industries support growth and innovation in the wider economy? Industry relatedness and employment growth in Italy. Industry and Innovation, 26(10), 1152–1173.
Jacobs, J. (1969). The economy of cities. Random House.
Ke, S. Z., He, M., & Yuan, C. H. (2014). Synergy and co-agglomeration of producer services and manufacturing: A panel data analysis of Chinese cities. Regional Studies, 48(11), 1829–1841.
Kekezi, O., & Klaesson, J. (2019). Agglomeration and innovation of knowledge intensive business services. Industry and Innovation, 27(5), 538–561.
Kolko, J. (2010). Urbanization, agglomeration, and coagglomeration of service industries. In Agglomeration economics, 151–180. University of Chicago Press.
Lanaspa, L., Sanz-Gracia, F., & Vera-Cabello, M. (2016). The (strong) interdependence between intermediate producer services’ attributes and manufacturing location. Economic Modelling, 57, 1–12.
Lesage, J. P., & Pace, R. K. (2009). Introduction to spatial econometrics. CRC Press.
Li, X. B. (2015). Specialization, institutions and innovation within China’s regional innovation systems. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 100, 130–139.
Li, B. Q. (2017). The interaction of clusters between manufacturing and producer services in China. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istrazivanja, 30(1), 1427–1442.
Li, T., & Fu, W. Y. (2015). Spatial processes of regional innovation in Guangdong Province, China: Empirical evidence using a spatial panel data model. Asian Journal of Technology Innovation, 23(3), 304–320.
Li, J., Sutherland, D., Ning, L. T., & Wang, Y. D. (2014). Firm ownership, industrial structure, and regional innovation performance in China’s provinces. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 26(9), 1001–1022.
Li, Z., Li, J., & He, B. (2018). Does foreign direct investment enhance or inhibit regional innovation efficiency? Chinese Management Studies, 12(1), 35–55.
Li, T. C., Han, D. R., Feng, S. S., & Liang, L. (2019). Can industrial co-agglomeration between producer services and manufacturing reduce carbon intensity in China? Sustainability, 11(15), 4024.
Ma, M., Rozema, J., Gianoli, A., & Zhang, W. (2022). The impacts of city size and density on CO2 emissions: Evidence from the Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy, 15(2), 529–555.
Marshall, A. (1890). Principles of economics (Vol. 1). London: Macmillan.
Miguelez, E., & Moreno, R. (2018). Relatedness, external linkages and regional innovation in Europe. Regional Studies, 52(5), 688–701.
Moran, P. A. P. (1950). Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika, 37, 17–23.
Ning, L. T., Wang, F., & Li, J. (2016). Urban innovation, regional externalities of foreign direct investment and industrial agglomeration: Evidence from Chinese cities. Research Policy, 45(4), 830–843.
Peng, C., Song, M., & Han, F. (2017). Urban economic structure, technological externalities, and intensive land use in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 152, 47–62.
Romer, P. M. (1986). Increasing returns and long-run growth. Journal of Political Economy, 94(5), 1002–1037.
Sleuwaegen, L., & Boiardi, P. (2014). Creativity and regional innovation: Evidence from EU regions. Research Policy, 43(9), 1508–1522.
Song, H., & Zhang, M. (2017). Spatial spillovers of regional innovation: Evidence from Chinese provinces. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 53(9), 2104–2122.
Song, H. M., Zhang-Zhang, Y. Y., Tian, M., Rohlfer, S., & Sharkasi, N. (2019). Culture and regional innovation performance: An exploration in China. Chinese Management Studies, 13(2), 397–420.
Tavassoli, S., & Carbonara, N. (2014). The role of knowledge variety and intensity for regional innovation. Small Business Economics, 43(2), 493–509.
Taylor, P. J., Derudder, B., Faulconbridge, J., Hoyler, M., & Ni, P. (2014). Advanced producer service firms as strategic networks, global cities as strategic places. Economic Geography, 90(3), 267–291.
Van der Panne, G. (2004). Agglomeration externalities: Marshall versus Jacobs. Journal of Evolutionary Economics, 14(5), 593–604.
Wang, J. M., & Li, Y. (2020). Does factor endowment allocation improve technological innovation performance? An empirical study on the Yangtze River Delta region. Science of the Total Environment, 716, 137107.
Wang, Y. D., Pan, X., Li, J., & Ning, L. T. (2016). Does technological diversification matter for regional innovation capability? Evidence from China. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 28(3), 323–334.
Wen, Y. Y., Zhao, M., Zheng, L. L., Yang, Y. J., & Yang, X. Y. (2021). Impacts of financial agglomeration on technological innovation: a spatial and nonlinear perspective. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2021.1963702
Yang, N. N., Hong, J., Wang, H. Y., & Liu, Q. M. (2020a). Global value chain, industrial agglomeration and innovation performance in develo** countries: Insights from China’s manufacturing industries. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 32(11), 1307–1321.
Yang, N. N., Liu, Q. M., & Qi, Y. (2020b). Does (un)-related variety promote regional innovation in China? Industry versus services sector. Chinese Management Studies, 14(3), 769–788.
Yang, H. C., Zhang, F. M., & He, Y. X. (2021a). Exploring the effect of producer services and manufacturing industrial co-agglomeration on the ecological environment pollution control in China. Environment Development and Sustainability, 23(11), 16119–16144.
Yang, N. N., Liu, Q. M., & Chen, Y. E. (2021b). Does Industrial Agglomeration Promote Regional Innovation Convergence in China? Evidence From High-Tech Industries. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2021.3084936
Yu, W. T. (2019). Creative industries agglomeration and entrepreneurship in China: Necessity or opportunity? Industry and Innovation, 27(4), 420–443.
Yuan, F., Gao, J., Wang, L., & Cai, Y. (2017). Co-location of manufacturing and producer services in Nan**g, China. Cities, 63, 81–91.
Yuan, H. X., Zhang, T. S., Feng, Y. D., Liu, Y. B., & Ye, X. Y. (2019). Does financial agglomeration promote the green development in China? A spatial spillover perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 237, 117808.
Zhang, M., & Chung, S. H. (2020). Is air pollution detrimental to regional innovation? Evidence from Chinese cities. Growth and Change, 51(4), 1657–1689.
Zhang, R., Sun, B., & Liu, M. (2019). Do external technology sourcing and industrial agglomeration successfully facilitate an increase in the innovation performance of high-tech industries in China? IEEE Access, 7, 15414–15423.
Zhou, C. Y., Hong, J., Wu, Y. R., & Marinova, D. (2019). Outward foreign direct investment and domestic innovation performance: Evidence from China. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 31(1), 81–95.
Zhu, C., Zhao, D., & Qiu, Z. (2019). Internal and external effect of estate investment upon regional innovation in China. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 55(3), 513–530.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Philosophy and Social Science Foundation for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (2021SJA0109), Teachers Research Foundation Project of Nan**g University of Posts and Telecommunications (NYY221008) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (72101108). Thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, N., Yuan, X., Qin, F. et al. Coagglomeration of manufacturing and producer services: How does it affect regional innovation in China?. Appl. Spatial Analysis 15, 1411–1432 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12061-022-09463-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12061-022-09463-1