Abstract
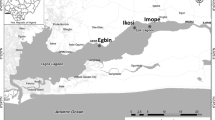
Ecosystem level changes in water quality and biotic communities in coastal lagoons have been associated with intensification of anthropogenic pressures. In light of incipient changes in Asia’s largest brackish water lagoon (Chilika, India), an examination of different dissolved nutrients distribution and phytoplankton biomass, was conducted through seasonal water quality monitoring in the year 2011. The lagoon showed both spatial and temporal variation in nutrient concentration, mostly altered by freshwater input, regulated the chlorophyll distribution as well. Dissolved inorganic N:P ratio in the lagoon showed nitrogen limitation in May and December, 2011. Chlorophyll in the lagoon varied between 3.38 and 17.66 mg m −3. Spatially, northern part of the lagoon showed higher values of DIN and chlorophyll during most part of the year, except in May, when highest DIN was recorded in the southern part. Statistical analysis revealed that dissolved NH\(_{4}^{\mathrm {+}}\)–N and urea could combinedly explain 43% of Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) variability which was relatively higher than that explained by NO\(_{3}^{\mathrm {-}}\)–N and NO\(_{2}^{\mathrm {-}}\)–N (12.4%) in lagoon water. Trophic state index calculated for different sectors of the lagoon confirmed the inter-sectoral and inter-seasonal shift from mesotrophic to eutrophic conditions largely depending on nutrient rich freshwater input.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen A E, Howard-Jones M H, Booth M G, Frischer M E, Verity P G, Bronk D A and Sanderson M P 2002 Importance of heterotrophic bacterial assimilation of ammonium and nitrate in the Barents Sea during summer; J. Mar. Syst. 38 93–108.
An K G and Park S S 2003 Influence of seasonal monsoon on the trophic state deviation in an Asian reservoir; Water Air Soil Pollut. 145 267–287.
Annual report on natural calamities 2011–2012 Revenue & Disaster Management Department, Special Relief Commissioner, Government of Odisha, pp. 7–8.
Berman T and Bronk D A 2003 Dissolved organic nitrogen: A dynamic participant in aquatic ecosystems; Aq. Microb. Ecol. 31 279–305.
Bronk D and Glibert P 1993 Application of a 15N tracer method to the study of dissolved organic nitrogen uptake during spring and summer in Chesapeake Bay; Mar. Biol. 115 501–508.
Carlson R E 1977 A trophic state index for lakes; Limnol. Oceanogr. 22 361–369.
Carlson R E 1991 Expanding the trophic state concept to identify non-nutrient limited lakes and reservoirs; In: Enhancing the states’s lake management programs, pp. 59–71.
Cho B C, Park M G, Shim J H and Azam F 1996 Significance of bacteria in urea dynamics in coastal surface waters; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 142 19–26.
Cochlan W P and Wikner J 1993 Nitrogen uptake by size-fractionated micro-organisms in the Gulf of Bothnia, Sweden; The Oceanography Society Meeting, Seattle, WA (abstract only).
Collier C J, Villacorta-Rath C, van Dijk K -J, Takahashi M and Waycott M 2014 Seagrass proliferation precedes mortality during hypo-salinity events: A stress-induced morphometric response; PLoS One 9 (4) e94014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094014.
Cozzi S, Mistaro A, Sparnocchia S, Colugnati L, Bajt O and Toniatti L 2014 Anthropogenic loads and biogeochemical role of urea in the Gulf of Trieste; Sci. Total Environ. 493 271–281.
Di H J and Cameron K C 2008 Sources of nitrous oxide from N-15-labelled animal urine and urea fertilizer with and without a nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide (DCD); Aust. J. Soil Res. 46 76–82. doi: 10.1071/SR07093.
Duarte C M 1995 Submerged aquatic vegetation in relation to different nutrient regimes; Ophelia 41 (1) 87–112.
Dunn Ryan J K, Welsh David T B, Jordan Mark A, Waltham N. J, Lemckert Charles J and Teasdale Peter R 2012 Benthic metabolism and nitrogen dynamics in a sub-tropical coastal lagoon: Microphytobenthos stimulate nitrification and nitrate reduction through photosynthetic oxygen evolution; Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 113 272–282.
Fertig B, O’Neil J M, Beckert K A, Cain C J, Needham D M, Carruthers T J B and Dennison W C 2013 Elucidating terrestrial nutrient sources to a coastal lagoon, Chincoteague Bay, Maryland, USA; Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 116 1–10.
Ganguly D, Robin R S, Vishnu V K, Muduli P R, Abhilash K R, Patra S and Subhramanian B R 2013 Variable response of two tropical phytoplankton species at different salinity and nutrient condition; J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 440 244–249.
Glibert P M, Garside C, Fuhrman J and Roman M R 1991 Time- and size-dependent coupling of organic and inorganic nitrogen uptake and NH\(_{4}^{\mathrm {+}}\) regeneration in the plume of the Chesapeake Bay, and its regulation by large heterotrophs; Limnol. Oceanogr. 36 895–909.
Glibert P M, Magnien R, Lomas M W et al. 2001 Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, USA: Comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events; Estuaries 24 875–883.
Glibert P M, Heil C A, Hollander D, Revilla M, Hoare A, Alexander J and Murasko S 2004 Evidence for dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake during a cyanobacterial bloom in Florida Bay; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 280 73–83.
Glibert P M, Trice T M, Michael B and Lane L 2005 Urea in the tributaries of the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland; Water Air Soil Pollut. 160 229–43.
Glibert P M, Harrison J, Heil C and Seitzinger S 2006 Escalating worldwide use of urea – a global change contributing to coastal eutrophication; Biogeochemistry 77 441–463.
Grasshoff K, Kremlimg K and Ehrhardt M 1999 Analysis by electrochemical methods; In: Methods of sea water analysis, Wiley VCH, pp. 159–226.
Gopinath A, Joseph N, Sujatha C H and Nair S M 2002 Forms of nitrogen (NO\(_{3}^{-}\) −N; NO\(_{2}^{-}\) −N and NH 2CONH 2 −N) and their relations to A.O.U. in the Indian coastal waters of Arabian sea; Chemistry and Ecology 18 233–244.
Gupta G V M, Sarma V V S S, Robin R S, Raman A V, Jai Kumar M, Rakesh M and Subramanian B R 2008 Influence of net ecosystem metabolism in transferring riverine organic carbon to atmospheric CO 2 in a tropical coastal lagoon (Chilika lagoon, India); Biogeochem. 87 265– 285.
Huot Y M, Babin F, Bruyant C, Grob M S and Twardowski H C 2007 Does chlorophyll-a provide the best index of phytoplankton biomass for primary productivity studies? Biogeosci. Discuss. 4 707–745.
Kaufman Z G, Lively J S and Carpenter E J 1983 Uptake of nitrogenous nutrients by phytoplankton in a barrier island estuary: Great South Bay, New York; Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 17 483–493.
Kanuri Vishnu Vardhan, Muduli Pradipta R, Robin R S, Charan Kumar B, Lovaraju A, Ganguly D, Sivaji P., Nageswara Rao G, Raman A V and Subramanian B R 2013 Plankton metabolic processes and its significance on dissolved organic carbon pool in a tropical brackish water lagoon; Cont. Shelf Res. 61–62 52–61.
Kratzer C R and Brezonik P L 1981 A carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in florida lakes; Water Resour. Bull. 17 713–715.
Kudela R M and Cochlan W P 2000 Nitrogen and carbon uptake kinetics and the influence of irradiance for a red tide bloom off southern California; Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 21 31–47.
Labry C, Herbland A and Delmas D 2002 The role of phosphorous on planktonic production of the Gironde Plume waters in the Bay of Biscay; J. Plankton Res. 24 (2) 97–117.
Lee J, Kim J M, Kim D S, Hwang S J and An K G 2010 Nutrients and chlorophyll-a dynamics in a temperate reservoir influenced by Asian monsoon along with in situ nutrient enrichment bioassays; Limnology 11 49–62.
Lomas M W, Trice T M, Glibert P M, Bronk D A and McCarthy J J 2002 Temporal and spatial dynamics of urea uptake and regeneration rates, and concentrations in Chesapeake Bay; Estuaries 25 469–482.
Mace K A, Artaxo P and Duce R A 2003 Water-soluble organic nitrogen in Amazon Basin aerosols during the dry (biomass burning) and wet seasons; J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 108 4512, doi: 10.1029/2003JD003557.
Mahapatro D, Panigrahy R C and Panda B 2013 Coastal Lagoon: Present status and future challenges; Int. J. Mar. Sci. 3 (23) 178–186.
Matthews R, Hilles M and Pelletier G 2002 Determining trophic state in Lake Whatcom, Washington (USA), a soft water lake exhibiting seasonal nitrogen limitation; Hydrobiologia 468 107–121.
Middelburg J J and Nieuwenhuize J 2000 Nitrogen uptake by heterotrophic bacteria and phytoplankton in the nitrate-rich Thames estuary; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 203 13–21.
Mishra P K and Shaw B P 2003 Spatiotemporal variation of optically active substances; In: The coastal water off Orissa from Rishikulla to Dharma; Indian J. Mar. Sci. 32 133–140.
Miyazaki Y, Kawamura K and Sawano M 2010 Size distributions of organic nitrogen and carbon in remote marine aerosols: Evidence of marine biological origin based on their isotopic ratios; Geophys. Res. Lett. 37 L06803, doi: 10.1029/2010GL042483.
Muduli P R, Kanuri V. V., Robin R S, Charan Kumar B, Sivaji P., Raman A V, Nageswarara Rao G and Subramanian B R 2012 Spatio-temporal variation of CO 2 emission from Chilika Lake, a tropical coastal lagoon, on the east coast of India; Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 113 305–313.
Muduli P R, Kanuri V V, Robin R S, Charan Kumar B, Patra S, Raman A V, Nageswara Rao G and Subramanian B R 2013 Distribution of dissolved inorganic carbon and net ecosystem production in a tropical brackish water lagoon, India; Cont. Shelf Res. 64 75–87.
Nayak B K, Acharya B C, Panda U C, Nayak B B and Acharya S K 2004 Variation in the water quality in the Chilika lake; Indian J. Mar. Sci. 33 164–169.
Panigrahi S, Acharya B C, Panigrahy R C, Nayak B K, Banarjee K and Sarkar S K 2007 Anthropogenic impact on water quality of Chilika lagoon RAMSAR site: A statistical approach; Wetlands Ecol. Manag. 15 113–126.
Panigrahi S, Wikner J, Panigrahy R C, Satapathy K K and Acharya B C 2009 Variability of nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in a shallow brackish water ecosystem (Chilika lagoon, India); Limnology 10 73–85.
Pujo-Pay M and Raimbault P 1994 Improvement of the wet-oxidation procedure for simultaneous determination of particulate organic nitrogen and phosphorous collected on filters; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 105 203–207.
Revilla M., Jeffrey A. and Glibert Patricia M 2005 Urea analysis in coastal waters: Comparison of enzymatic and direct methods; Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 3 290–299.
Rysgaard S, Thamdrup B a., Risgaard-Petersen N et al. 1998 Seasonal carbon and nutrient mineralization in a high-Arctic coastal marine sediment, Young Sound, Northeast Greenland; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 175 261–276.
Seitzinger S P, Kroeze C, Bouwman A F, Caraco N, Dentener F and Styles R V 2002 Global patterns of dissolved inorganic and particulate nitrogen inputs to coastal systems: Recent conditions and future projections; Estuaries 25 640–655.
Siddiqui S Z and Rao K V 1995 Limnology of Chilika lake; In: Fauna of Chilika Lake (Wetland Ecosystem Series I), by Director of Zoological Survey of India Calcutta: Zoological Survey of India.
Silva R G, Cameron K C, Di H J and Jorgensen E E 2005 A lysimeter study to investigate the effect of dairy effluent and urea on cattle urine N losses, plant uptake and soil retention; Water Air Soil Pollut. 164 57–78.
UNESCO 1994 Protocols for the Joint Global Ocean Flux Study; Manuals and Guides 29, 190p.
Valderrama J C 1981 The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphrous in natural waters; Mar. Chem. 10 109–122.
Violaki K, Zarbas P and Mihalopoulos N 2010 Long-term measurements of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in atmospheric deposition in the Eastern Mediterranean: Fluxes, origin and biogeochemical implications; Mar. Chem. 120 179–186.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Secretary, MoES, Government of India, and Project-Director, ICMAM for the encouragement and support. Authors are also grateful to the Indian Navy (INS Chilika) for logistic support rendered during the course of this investigation. They are also thankful to the research staff of Andhra University for their support in executing the fieldwork. This study is a part of MoES-ICMAM’s comprehensive project “Ecosystem Modelling for Chilika Lagoon”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganguly, D., Patra, S., Muduli, P.R. et al. Influence of nutrient input on the trophic state of a tropical brackish water lagoon. J Earth Syst Sci 124, 1005–1017 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0582-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0582-9