Abstract
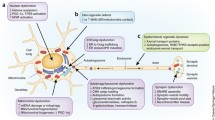
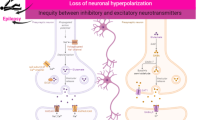
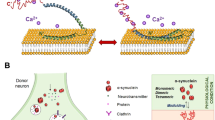
Alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) is a specific neuronal protein that regulates neurotransmitter release and trafficking of synaptic vesicles. Exosome-associated α-Syn which is specific to the central nervous system (CNS) is involved in the pathogenesis of epilepsy. Therefore, this review aimed to elucidate the possible link between α-Syn and epilepsy, and how it affects the pathophysiology of epilepsy. A neurodegenerative protein such as α-Syn is implicated in the pathogenesis of epilepsy. Evidence from preclinical and clinical studies revealed that upregulation of α-Syn induces progressive neuronal dysfunctions through induction of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and inhibition of autophagy in a vicious cycle with subsequent development of severe epilepsy. In addition, accumulation of α-Syn in epilepsy could be secondary to the different cellular alterations including oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, reduction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and progranulin (PGN), and failure of the autophagy pathway. However, the mechanism of α-Syn-induced-epileptogenesis is not well elucidated. Therefore, α-Syn could be a secondary consequence of epilepsy. Preclinical and clinical studies are warranted to confirm this causal relationship.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Abbreviations
- α-Syn:
-
Alpha-synuclein
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- SNARE:
-
N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- AEDs:
-
Anti-epileptic drugs
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors
- NFTs:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-β
- GSK3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- MAPs:
-
Microtubule-associated proteins
- PTZ:
-
Pentylenetetrazole
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- TLE:
-
Temporal lobe epilepsy
- ApoE4:
-
Apolipoprotein E4
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MTLE:
-
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
- SE:
-
Status epileptics
- KA:
-
Kainic acid
- SOD2:
-
Superoxide dismutase 2
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- TrkB:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptor B
- NPY:
-
Neuroprotective neuropeptide Y
- PGN:
-
Progranulin
- SNARE:
-
N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment protein receptors
References
Cheng F, Vivacqua G, Yu S (2011) The role of alpha-synuclein in neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. J Chem Neuroanat 42(4):242–248
Atsmon-Raz Y, Miller Y (2015) A proposed atomic structure of the self-assembly of the non-amyloid-β component of human α-synuclein as derived by computational tools. J Phys Chem B 119(31):10005–10015
Lau A, So RW, Lau HH, Sang JC, Ruiz-Riquelme A, Fleck SC et al (2020) α-Synuclein strains target distinct brain regions and cell types. Nat Neurosci 23(1):21–31
Schaser AJ, Osterberg VR, Dent SE, Stackhouse TL, Wakeham CM, Boutros SW et al (2019) Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders. Sci Rep 9(1):10919
Korff A, Liu C, Ginghina C, Shi M, Zhang J, AsDN I (2013) α-Synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 36(4):679–688
Singh B, Covelo A, Martell-Martínez H, Nanclares C, Sherman MA, Okematti E et al (2019) Tau is required for progressive synaptic and memory deficits in a transgenic mouse model of α-synucleinopathy. Acta Neuropathol 138:551–574
Zhu M, Qin Z-J, Hu D, Munishkina LA, Fink AL (2006) α-synuclein can function as an antioxidant preventing oxidation of unsaturated lipid in vesicles. Biochemistry 45(26):8135–8142
Shin JY, Kim D-Y, Lee J, Shin YJ, Kim YS, Lee PH (2022) Priming mesenchymal stem cells with α-synuclein enhances neuroprotective properties through induction of autophagy in Parkinsonian models. Stem Cell Res Ther 13(1):1–15
Serratos IN, Hernández-Pérez E, Campos C, Aschner M, Santamaría A (2022) An update on the critical role of α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies: from tissue to cellular and molecular levels. Mol Neurobiol 59(1):620–642
Vaikath NN, Erskine D, Morris CM, Majbour NK, Vekrellis K, Li JY et al (2019) Heterogeneity in α-synuclein subtypes and their expression in cortical brain tissue lysates from Lewy body diseases and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 45(6):597–608
Minakaki G, Krainc D, Burbulla LF (2020) The convergence of alpha-synuclein, mitochondrial, and lysosomal pathways in vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:580634
Li W, Fu Y, Halliday GM, Sue CM (2021) PARK genes link mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-synuclein pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:612476
Ganjam GK, Bolte K, Matschke LA, Neitemeier S, Dolga AM, Höllerhage M et al (2019) Mitochondrial damage by α-synuclein causes cell death in human dopaminergic neurons. Cell Death Dis 10(11):865
Das T, Eliezer D (1867) Membrane interactions of intrinsically disordered proteins: the example of alpha-synuclein. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteomics 1867(10):879–89
Brzozowski CF, Hijaz BA, Singh V, Gcwensa NZ, Kelly K, Boyden ES et al (2021) Inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity promotes anterograde axonal transport and presynaptic targeting of α-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9(1):1–18
Seebauer L, Schneider Y, Drobny A, Plötz S, Koudelka T, Tholey A et al (2022) Interaction of alpha synuclein and microtubule organization is linked to impaired neuritic integrity in Parkinson’s patient-derived neuronal cells. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1812
Gao V, Briano JA, Komer LE, Burré J (2023) Functional and pathological effects of α-synuclein on synaptic SNARE complexes. J Mol Biol 435(1):167714
Mahoney-Sanchez L, Bouchaoui H, Boussaad I, Jonneaux A, Timmerman K, Berdeaux O et al (2022) Alpha synuclein determines ferroptosis sensitivity in dopaminergic neurons via modulation of ether-phospholipid membrane composition. Cell Rep 40(8):111231
Tanaka Y, Engelender S, Igarashi S, Rao RK, Wanner T, Tanzi RE et al (2001) Inducible expression of mutant α-synuclein decreases proteasome activity and increases sensitivity to mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet 10(9):919–926
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) A story of the potential effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in Parkinson’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 31(2):673–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01192-2
Paudel YN, Angelopoulou E, Piperi C, Othman I, Shaikh MF (2020) Revisiting the impact of neurodegenerative proteins in epilepsy: focus on alpha-synuclein, beta-amyloid, and tau. Biology 9(6):122
Galanopoulou AS, Buckmaster PS, Staley KJ, Moshé SL, Perucca E, Engel J Jr et al (2012) Identification of new epilepsy treatments: issues in preclinical methodology. Epilepsia 53(3):571–582
Lazarini-Lopes W, Do Val-da Silva RA, da Silva-Júnior RM, Leite JP, Garcia-Cairasco N (2020) The anticonvulsant effects of cannabidiol in experimental models of epileptic seizures: From behavior and mechanisms to clinical insights. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 111:166–182
Anderson WW (2020) Epileptogenesis. Garland Sci, Cortical Plast, pp 149–89
Sedwick C (2019) Investigating an epileptogenic mutation. J Gen Physiol 151(2):96
Liu Y, Schubert J, Sonnenberg L, Helbig KL, Hoei-Hansen CE, Koko M et al (2019) Neuronal mechanisms of mutations in SCN8A causing epilepsy or intellectual disability. Brain 142(2):376–390
Nazarov A (2022) Consequences of seizures and epilepsy in children. Web Sci: Int Sci Res J 3(02):483–489
Perrig S, Jallon P (2008) Is the first seizure truly epileptic? Epilepsia 49:2–7
Magiorkinis E, Sidiropoulou K, Diamantis A (2010) Hallmarks in the history of epilepsy: epilepsy in antiquity. Epilepsy Behav 17(1):103–108
Ghosh S, Sinha JK, Khan T, Devaraju KS, Singh P, Vaibhav K et al (2021) Pharmacological and therapeutic approaches in the treatment of epilepsy. Biomedicines 9(5):470
Nandini H, Paudel YN, Krishna K (2019) Envisioning the neuroprotective effect of Metformin in experimental epilepsy: a portrait of molecular crosstalk. Life Sci 233:116686
Alva-Díaz C, Navarro-Flores A, Rivera-Torrejon O, Huerta-Rosario A, Molina RA, Velásquez-Rimachi V et al (2021) Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy in Latin America and the Caribbean: a systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based studies. Epilepsia 62(4):984–996
Jiménez-Villegas MJ, Lozano-García L, Carrizosa-Moog J (2021) Update on first unprovoked seizure in children and adults: a narrative review. Seizure 90:28–33
Newton CR, Garcia HH (2012) Epilepsy in poor regions of the world. The Lancet 380(9848):1193–1201
Mbizvo GK, Bennett K, Simpson CR, Duncan SE, Chin RF (2019) Epilepsy-related and other causes of mortality in people with epilepsy: a systematic review of systematic reviews. Epilepsy Res 157:106192
DeGiorgio CM, Curtis A, Hertling D, Moseley BD (2019) Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: risk factors, biomarkers, and prevention. Acta Neurol Scand 139(3):220–230
Eadie MJ (2012) Shortcomings in the current treatment of epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 12(12):1419–1427
Laxer KD, Trinka E, Hirsch LJ, Cendes F, Langfitt J, Delanty N et al (2014) The consequences of refractory epilepsy and its treatment. Epilepsy Behav 37:59–70
Santulli L, Coppola A, Balestrini S, Striano S (2016) The challenges of treating epilepsy with 25 antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacol Res 107:211–219
Alsubaie N, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alharbi B, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M et al (2022) Statins use in Alzheimer disease: bane or boon from frantic search and narrative review. Brain Sci 12(10):1290
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alsayegh AA, Hakami ZH, Khamjan NA, Saad HM et al (2022) A potential link between visceral obesity and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 48(3):745–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03817-4
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Benzodiazepines in alzheimer’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 31(1):221–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01099-4
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) Long-term use of metformin and Alzheimer’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology 31(3):1107–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01163-7
Upaganlawar AB, Wankhede NL, Kale MB, Umare MD, Sehgal A, Singh S et al (2021) Interweaving epilepsy and neurodegeneration: vitamin E as a treatment approach. Biomed Pharmacother 143:112146
Wong M (2013) Cleaning up epilepsy and neurodegeneration: the role of autophagy in epileptogenesis: autophagy and epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Curr 13(4):177–178
Nicastro N, Assal F, Seeck M (2016) From here to epilepsy: the risk of seizure in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Epileptic Disord 18(1):1–12
Paudel YN, Angelopoulou E, Jones NC, O’Brien TJ, Kwan P, Piperi C et al (2019) Tau related pathways as a connecting link between epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(10):4199–4212
Toral-Rios D, Pichardo-Rojas PS, Alonso-Vanegas M, Campos-Peña V (2020) GSK3β and tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy. Front Cell Neurosci 14:19
Hall AM, Throesch BT, Buckingham SC, Markwardt SJ, Peng Y, Wang Q et al (2015) Tau-dependent Kv4. 2 depletion and dendritic hyperexcitability in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 35(15):6221–30
Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T et al (2007) Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid ß-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science 316(5825):750–754
Holth JK, Bomben VC, Reed JG, Inoue T, Younkin L, Younkin SG et al (2013) Tau loss attenuates neuronal network hyperexcitability in mouse and Drosophila genetic models of epilepsy. J Neurosci 33(4):1651–1659
DeVos SL, Goncharoff DK, Chen G, Kebodeaux CS, Yamada K, Stewart FR et al (2013) Antisense reduction of tau in adult mice protects against seizures. J Neurosci 33(31):12887–12897
Kwan J (2010) Predicting the risk of poststroke epilepsy—why and how? Nat Rev Neurol 6(10):532–533
Casillas-Espinosa PM, Ali I, O’Brien TJ (2020) Neurodegenerative pathways as targets for acquired epilepsy therapy development. Epilepsia Open 5(2):138–154
Vossel KA, Tartaglia MC, Nygaard HB, Zeman AZ, Miller BL (2017) Epileptic activity in Alzheimer’s disease: causes and clinical relevance. Lancet Neurol 16(4):311–322
Twohig D, Nielsen HM (2019) α-Synuclein in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):1–19
Baldacci F, Daniele S, Piccarducci R, Giampietri L, Pietrobono D, Giorgi FS et al (2019) Potential diagnostic value of red blood cells α-synuclein heteroaggregates in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 56:6451–6459
Fang Y, Si X, Wang J, Wang Z, Chen Y, Liu Y et al (2023) Alzheimer disease and epilepsy: a mendelian randomization study. Neurology 101(4):e399–e409. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000207423
Lam AD (2023) Linking late-onset epilepsy with alzheimer disease: insights from plasma amyloid measurements. AAN Enterprises 101(13):551–552. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000207683
Batiha GE-S, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Elekhnawy E (2022) SIRT1 pathway in parkinson’s disease: a faraway snapshot but so close. Inflammopharmacology 31(1):37–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01125-5
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Alsayegh AA, Almohmadi NH et al (2023) Pros and cons for statins use and risk of Parkinson’s disease: an updated perspective. Pharmacol Res Perspect 11(2):e01063
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Elewa YHA, Zahran MH, Alexiou A, Papadakis M et al (2023) Parkinson’s disease risk and hyperhomocysteinemia: the possible link. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43(6):2743–2759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01350-8
Alnaaim SA, Al-Kuraishy HM, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) Role of brain liver x receptor in Parkinson’s disease: hidden treasure and emerging opportunities. Mol Neurobiol 61(1):341–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03561-y
Alrouji M, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Ashour NA, Jabir MS, Negm WA et al (2023) Metformin role in Parkinson’s disease: a double-sword effect. Mol Cell Biochem 479(4):975–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04771-7
Al-kuraishy HM, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Elhussieny O, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) New insights on the potential effect of vinpocetine in Parkinson’s disease: one of the neglected warden and baffling topics. Metab Brain Dis 38(6):1831–1840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01254-y
Consortium B, Anttila V, Bulik-Sullivan B, Finucane HK, Walters RK, Bras J et al (2018) Analysis of shared heritability in common disorders of the brain. Science 360(6395):eaap8757
Szot P (2012) Common factors among Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy: possible role of the noradrenergic nervous system. Epilepsia 53:61–66
Gourie-Devi M (2014) Epidemiology of neurological disorders in India: review of background, prevalence and incidence of epilepsy, stroke, Parkinson’s disease and tremors. Neurol India 62(6):588
Kleppner SR, Tobin AJ (2001) GABA signalling: therapeutic targets for epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease. Emerging Therapeutic Targets 5(2):219–239
Son AY, Biagioni MC, Kaminski D, Gurevich A, Stone B, Di Rocco A (2016) Parkinson’s disease and cryptogenic epilepsy. Case Rep Neurol Med 2016:3745631. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3745631
Son AY, Cucca A, Agarwal S, Liu A, Di Rocco A, Biagioni MC (2017) Are we missing non-motor seizures in Parkinson’s disease? Two case reports. J Clin Mov Disord 4:1–4
Spagnoli C, Fusco C, Pisani F (2023) Pediatric-onset epilepsy and developmental epileptic encephalopathies followed by early-onset Parkinsonism. Int J Mol Sci 24(4):3796
Feddersen B, Rémi J, Einhellig M, Stoyke C, Krauss P, Noachtar S (2014) Parkinson’s disease: less epileptic seizures more status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 108(2):349–354
Gruntz K, Bloechliger M, Becker C, Jick SS, Fuhr P, Meier CR et al (2018) Parkinson disease and the risk of epileptic seizures. Ann Neurol 83(2):363–374
Clinckers R, Smolders I, Meurs A, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2004) Anticonvulsant action of hippocampal dopamine and serotonin is independently mediated by D2 and 5-HT1A receptors. J Neurochem 89(4):834–843
Estrada-Sánchez AM, Levine MS, Cepeda C (2017) Epilepsy in other neurodegenerative disorders: Huntington’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Elsevier, Models of seizures and epilepsy, pp 1043–1058
Buddhala C, Loftin SK, Kuley BM, Cairns NJ, Campbell MC, Perlmutter JS et al (2015) Dopaminergic, serotonergic, and noradrenergic deficits in Parkinson disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2(10):949–959
Dolgacheva L, Fedotova E, Abramov AY, Berezhnov A (2018) Alpha-synuclein and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem (Moscow) Suppl Ser A: Membr Cell Biol 12:10–19
Rong H, ** L, Wei W, Wang X, ** Z (2015) Alpha-synuclein is a potential biomarker in the serum and CSF of patients with intractable epilepsy. Seizure 27:6–9
Murphy DD, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2000) Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and α-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 20(9):3214–3220
Hussein AM, Eldosoky M, El-Shafey M, El-Mesery M, Ali AN, Abbas KM et al (2019) Effects of metformin on apoptosis and α-synuclein in a rat model of pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 97(1):37–46
Li A, Choi YS, Dziema H, Cao R, Cho HY, Jung YJ et al (2010) Proteomic profiling of the epileptic dentate gyrus. Brain Pathol 20(6):1077–1089
Eller M, Williams DR (2011) α-Synuclein in Parkinson disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(3):403–408
Yang J, Czech T, Felizardo M, Baumgartner C, Lubec G (2006) Aberrant expression of cytoskeleton proteins in hippocampus from patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Amino Acids 30:477–493
Kohlhase K, Zöllner JP, Tandon N, Strzelczyk A, Rosenow F (2021) Comparison of minimally invasive and traditional surgical approaches for refractory mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes. Epilepsia 62(4):831–845
Choi J, Kim SY, Kim H, Lim BC, Hwang H, Chae JH et al (2020) Serum α-synuclein and IL-1β are increased and correlated with measures of disease severity in children with epilepsy: potential prognostic biomarkers? BMC Neurol 20:1–11
Choi J, Kim SY, Kim H, Lim BC, Hwang H, Chae JH et al (2020) Serum α-synuclein and IL-1β are increased and correlated with measures of disease severity in children with epilepsy: potential prognostic biomarkers? BMC Neurol 20(1):1–11
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Niemi MS, Aljowaie RM, Almutairi SM, Alexiou A et al (2022) The prospective effect of allopurinol on the oxidative stress index and endothelial dysfunction in Covid-19. Inflammation 45(4):1651–1667
Alorabi M, Cavalu S, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Negm WA et al (2022) Pentoxifylline and berberine mitigate diclofenac-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male rats via modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 152:113225
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Nami MS (2019) Vinpocetine improves oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mediators in acute kidney injury. Int J Prev Med 10:142. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_5_19
Geronzi U, Lotti F, Grosso S (2018) Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 18(5):427–434
Shin E-J, Jeong JH, Chung YH, Kim W-K, Ko K-H, Bach J-H et al (2011) Role of oxidative stress in epileptic seizures. Neurochem Int 59(2):122–137
Aguiar CCT, Almeida AB, Araújo PVP, Abreu RNDCd, Chaves EMC, Vale OCd et al (2012) Oxidative stress and epilepsy: literature review. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012:795259. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/795259
Liang L-P, Patel M (2006) Seizure-induced changes in mitochondrial redox status. Free Radic Biol Med 40(2):316–322
Liang L, Ho Y, Patel M (2000) Mitochondrial superoxide production in kainate-induced hippocampal damage. Neuroscience 101(3):563–570
Goodwin J, Nath S, Engelborghs Y, Pountney D (2013) Raised calcium and oxidative stress cooperatively promote alpha-synuclein aggregate formation. Neurochem Int 62(5):703–711
Levin J, Högen T, Hillmer AS, Bader B, Schmidt F, Kamp F et al (2011) Generation of ferric iron links oxidative stress to α-synuclein oligomer formation. J Parkinsons Dis 1(2):205–216
Quilty MC, King AE, Gai WP, Pountney DL, West AK, Vickers JC et al (2006) Alpha-synuclein is upregulated in neurones in response to chronic oxidative stress and is associated with neuroprotection. Exp Neurol 199(2):249–256
Scudamore O, Ciossek T (2018) Increased oxidative stress exacerbates α-synuclein aggregation in vivo. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 77(6):443–453
Kanda S, Bishop J, Eglitis M, Yang Y, Mouradian M (2000) Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by α-synuclein mutations and C-terminal truncation. Neuroscience 97(2):279–284
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A, Rockenstein E, Sisk A, Mallory M et al (2000) α-Synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157(2):401–410
Parihar M, Parihar A, Fujita M, Hashimoto M, Ghafourifar P (2008) Mitochondrial association of alpha-synuclein causes oxidative stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1272–1284
Musgrove RE, Helwig M, Bae E-J, Aboutalebi H, Lee S-J, Ulusoy A et al (2019) Oxidative stress in vagal neurons promotes parkinsonian pathology and intercellular α-synuclein transfer. J Clin Investig 129(9):3738–3753
Cheng A, Wang Y-f, Shinoda Y, Kawahata I, Yamamoto T, Jia W-b et al (2022) Fatty acid-binding protein 7 triggers α-synuclein oligomerization in glial cells and oligodendrocytes associated with oxidative stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(3):552–562
Zhao N, Yang X, Calvelli HR, Cao Y, Francis NL, Chmielowski RA et al (2020) Antioxidant nanoparticles for concerted inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillization, and attenuation of microglial intracellular aggregation and activation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:112
Li S, Raja A, Noroozifar M, Kerman K (2022) Understanding the inhibitory and antioxidant effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) on copper (II)-induced α-synuclein-119 aggregation. ACS Chem Neurosci 13(8):1178–1186
Martinc B, Grabnar I, Vovk T (2014) Antioxidants as a preventive treatment for epileptic process: a review of the current status. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(6):527–550
Yang N, Guan Q-W, Chen F-H, **a Q-X, Yin X-X, Zhou H-H et al (2020) Antioxidants targeting mitochondrial oxidative stress: promising neuroprotectants for epilepsy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:6687185. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6687185
Alkuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Waheed HJ (2018) Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 is linked with poor cardio-metabolic profile in patients with ischemic stroke: a study of effects of statins. J Neurosci Rural Pract 9(04):496–503
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2019) Effects of rosuvastatin on metabolic profile: versatility of dose-dependent effect. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 10(1):33
Shabab T, Khanabdali R, Moghadamtousi SZ, Kadir HA, Mohan G (2017) Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci 127(7):624–633
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL et al (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14(4):388–405
Hodges SL, Lugo JN (2020) Therapeutic role of targeting mTOR signaling and neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 161:106282
Parsons AL, Bucknor E, Castroflorio E, Soares TR, Oliver PL, Rial D (2022) The interconnected mechanisms of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Antioxidants 11(1):157
Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J (2006) NF-κB activation by reactive oxygen species: fifteen years later. Biochem Pharmacol 72(11):1493–1505
Vezzani A, Balosso S, Ravizza T (2019) Neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarkers in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 15(8):459–472
Choi JH, Kwon TW, Jo HS, Ha Y, Cho I-H (2023) Gintonin, a Panax ginseng-derived LPA receptor ligand, attenuates kainic acid-induced seizures and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activities. J Ginseng Res 47(3):390–399
Sabzali M, Eidi A, Khaksari M, Khastar H (2022) Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic action of metformin attenuates ethanol neurotoxicity in the animal model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Neurotox Res 40(2):605–613
Pracucci E, Pillai V, Lamers D, Parra R, Landi S (2021) Neuroinflammation: a signature or a cause of epilepsy? Int J Mol Sci 22(13):6981
Meng F, Yao L (2020) The role of inflammation in epileptogenesis. Acta Epileptologica 2(1):1–19
Kim I, Mlsna LM, Yoon S, Le B, Yu S, Xu D et al (2015) A postnatal peak in microglial development in the mouse hippocampus is correlated with heightened sensitivity to seizure triggers. Brain and behavior 5(12):e00403
Rocha EM, De Miranda B, Sanders LH (2018) Alpha-synuclein: pathology, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 109:249–257
Surguchov A, Surgucheva I, Sharma M, Sharma R, Singh V (2017) Pore-forming proteins as mediators of novel epigenetic mechanism of epilepsy. Front Neurol 8:3
Marques O, Outeiro TF (2012) Alpha-synuclein: from secretion to dysfunction and death. Cell Death Dis 3(7):e350-e
Lim S, Chun Y, Lee JS, Lee SJ (2016) Neuroinflammation in synucleinopathies. Brain Pathol 26(3):404–409
Choi D-Y, Liu M, Hunter RL, Cass WA, Pandya JD, Sullivan PG et al (2009) Striatal neuroinflammation promotes Parkinsonism in rats. PLoS One 4(5):e5482
Gao H-M, Zhang F, Zhou H, Kam W, Wilson B, Hong J-S (2011) Neuroinflammation and α-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Environ Health Perspect 119(6):807–814
Eyileten C, Kaplon-Cieslicka A, Mirowska-Guzel D, Malek L, Postula M (2017) Antidiabetic effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its association with inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res 2017:2823671. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2823671
Wang C, Bomberg E, Billington C, Levine A, Kotz CM (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus increases energy expenditure by elevating metabolic rate. Am J Physiol-Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293(3):R992–R1002
Rozanska O, Uruska A, Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz D (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):841
Binder DK, Croll SD, Gall CM, Scharfman HE (2001) BDNF and epilepsy: too much of a good thing? Trends Neurosci 24(1):47–53
Iughetti L, Lucaccioni L, Fugetto F, Predieri B, Berardi A, Ferrari F (2018) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and epilepsy: a systematic review. Neuropeptides 72:23–29
Koyama R, Ikegaya Y (2005) To BDNF or not to BDNF: that is the epileptic hippocampus. Neuroscientist 11(4):282–287
Binder DK (2004) The role of BDNF in epilepsy and other diseases of the mature nervous system. Recent Adv Epilepsy Res 548:34–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-6376-8_3
LaFrance W, Leaver K, Stopa E, Papandonatos G, Blum A (2010) Decreased serum BDNF levels in patients with epileptic and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Neurology 75(14):1285–1291
McNamara JO, Scharfman HE (2012) Temporal lobe epilepsy and the BDNF receptor, TrkB
Lin TW, Harward SC, Huang YZ, McNamara JO (2020) Targeting BDNF/TrkB pathways for preventing or suppressing epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 167:107734
Porcher C, Medina I, Gaiarsa J-L (2018) Mechanism of BDNF modulation in GABAergic synaptic transmission in healthy and disease brains. Front Cell Neurosci 12:273
Cattaneo S, Verlengia G, Marino P, Simonato M, Bettegazzi B (2021) NPY and gene therapy for epilepsy: how, when,... and Y. Front Mol Neurosci 13:608001
Gu F, Parada I, Yang T, Longo FM, Prince DA (2018) Partial TrkB receptor activation suppresses cortical epileptogenesis through actions on parvalbumin interneurons. Neurobiol Dis 113:45–58
Falcicchia C, Paolone G, Emerich DF, Lovisari F, Bell WJ, Fradet T et al (2018) Seizure-suppressant and neuroprotective effects of encapsulated BDNF-producing cells in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Mol Ther-Methods Clin Dev 9:211–224
Shetty AK (2014) Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection? Epilepsy Behav 38:117–124
Li B, Jiang Y, Xu Y, Li Y, Li B (2019) Identification of miRNA-7 as a regulator of brain-derived neurotrophic factor/α-synuclein axis in atrazine-induced Parkinson’s disease by peripheral blood and brain microRNA profiling. Chemosphere 233:542–548
Segura-Ulate I, Yang B, Vargas-Medrano J, Perez RG (2017) FTY720 (Fingolimod) reverses α-synuclein-induced downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in OLN-93 oligodendroglial cells. Neuropharmacology 117:149–157
Kohno R, Sawada H, Kawamoto Y, Uemura K, Shibasaki H, Shimohama S (2004) BDNF is induced by wild-type α-synuclein but not by the two mutants, A30P or A53T, in glioma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318(1):113–118
Bateman A, Cheung ST, Bennett HP (2018) A brief overview of progranulin in health and disease. Progranulin: Methods Protocols 1806:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8559-3_1
Kao AW, McKay A, Singh PP, Brunet A, Huang EJ (2017) Progranulin, lysosomal regulation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(6):325–333
Simon MJ, Logan T, DeVos SL, Di Paolo G (2022) Lysosomal functions of progranulin and implications for treatment of frontotemporal dementia. Trends Cell Biol 33(4):324–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2022.09.006
Huchtemann T, Körtvélyessy P, Feistner H, Heinze H, Bittner D (2015) Progranulin levels in status epilepticus as a marker of neuronal recovery and neuroprotection. Epilepsy Behav 49:170–172
Zhu S, Tai C, Petkau TL, Zhang S, Liao C, Dong Z et al (2013) Progranulin promotes activation of microglia/macrophage after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res 1530:54–65
Hanin A, Denis JA, Frazzini V, Cousyn L, Imbert-Bismut F, Rucheton B et al (2022) Neuron specific enolase, S100-beta protein and progranulin as diagnostic biomarkers of status epilepticus. J Neurol 269(7):3752–3760
Lui H, Zhang J, Makinson SR, Cahill MK, Kelley KW, Huang H-Y et al (2016) Progranulin deficiency promotes circuit-specific synaptic pruning by microglia via complement activation. Cell 165(4):921–935
Leverenz J, Yu C, Montine T, Steinbart E, Bekris L, Zabetian C et al (2007) A novel progranulin mutation associated with variable clinical presentation and tau, TDP43 and alpha-synuclein pathology. Brain 130(5):1360–1374
Takahashi H, Bhagwagar S, Nies SH, Chiasseu MT, Wang G, Mackenzie IR et al (2022) Reduced progranulin increases tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions and alters phenotypes of tauopathy mice via glucocerebrosidase. bioRxiv:2022.12. 25.521308
Valdez C, Ysselstein D, Young TJ, Zheng J, Krainc D (2020) Progranulin mutations result in impaired processing of prosaposin and reduced glucocerebrosidase activity. Hum Mol Genet 29(5):716–726
Zhu H, Wang W, Li Y (2022) Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy and its potential role in epilepsy. Cells 11(17):2621
Lv M, Ma Q (2020) Autophagy and epilepsy. Autophagy: Biol Dis Clin Sci 163–9
Gan J, Qu Y, Li J, Zhao F, Mu D (2015) An evaluation of the links between microRNA, autophagy, and epilepsy. Rev Neurosci 26(2):225–237
Giorgi FS, Biagioni F, Lenzi P, Frati A, Fornai F (2015) The role of autophagy in epileptogenesis and in epilepsy-induced neuronal alterations. J Neural Transm 122:849–862
Zeng LH, Xu L, Gutmann DH, Wong M (2008) Rapamycin prevents epilepsy in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Ann Neurol: Off J Am Neurol Assoc Child NeurolSoc 63(4):444–453
Zeng L-H, Rensing NR, Wong M (2009) The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway mediates epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 29(21):6964–6972
Guo D, Zeng L, Brody DL, Wong M (2013) Rapamycin attenuates the development of posttraumatic epilepsy in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 8(5):e64078
Buckmaster PS, Lew FH (2011) Rapamycin suppresses mossy fiber sprouting but not seizure frequency in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 31(6):2337–2347
Chen W, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Li W, Sha L et al (2023) Pharmacological modulation of autophagy for epilepsy therapy: opportunities and obstacles. Drug Discov Today 28(6):103600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103600
**louri M, Brekk OR, Stefanis L (2016) Autophagy and alpha-synuclein: relevance to Parkinson’s disease and related synucleopathies. Mov Disord 31(2):178–192
Limanaqi F, Biagioni F, Busceti CL, Ryskalin L, Polzella M, Frati A et al (2019) Phytochemicals bridging autophagy induction and alpha-synuclein degradation in parkinsonism. Int J Mol Sci 20(13):3274
Klucken J, Poehler A-M, Ebrahimi-Fakhari D, Schneider J, Nuber S, Rockenstein E et al (2012) Alpha-synuclein aggregation involves a bafilomycin A1-sensitive autophagy pathway. Autophagy 8(5):754–766
Tang BL (2021) SNAREs and developmental disorders. J Cell Physiol 236(4):2482–2504
Zhang Y, Hughson FM (2021) Chaperoning SNARE folding and assembly. Annu Rev Biochem 90:581–603
Clasadonte J, Dong J, Hines DJ, Haydon PG (2013) Astrocyte control of synaptic NMDA receptors contributes to the progressive development of temporal lobe epilepsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(43):17540–17545
Cali E, Rocca C, Salpietro V, Houlden H (2022) Epileptic phenotypes associated with SNAREs and related synaptic vesicle exocytosis machinery. Front Neurol 12:806506
Yu H, Yang X, Tang X, Tang R (2018) Effects of spontaneous recurrent seizures on cognitive function via modulation of SNAREs expression. Int J Neurosci 128(4):376–383
Matveeva EA, Price DA, Whiteheart SW, Vanaman TC, Gerhardt GA, Slevin JT (2012) Reduction of vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 expression leads to a kindling-resistant phenotype in a murine model of epilepsy. Neuroscience 202:77–86
Noor A, Zahid S (2017) A review of the role of synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP-25) in neurological disorders. Int J Neurosci 127(9):805–811
Burré J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Südhof TC (2010) α-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329(5999):1663–1667
Choi B-K, Choi M-G, Kim J-Y, Yang Y, Lai Y, Kweon D-H et al (2013) Large α-synuclein oligomers inhibit neuronal SNARE-mediated vesicle docking. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(10):4087–4092
Scott DA, Tabarean I, Tang Y, Cartier A, Masliah E, Roy S (2010) A pathologic cascade leading to synaptic dysfunction in α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 30(24):8083–8095
Toh WS, Zhang B, Lai RC, Lim SK (2018) Immune regulatory targets of mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes/small extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration. Cytotherapy 20(12):1419–1426
Grey M, Dunning CJ, Gaspar R, Grey C, Brundin P, Sparr E et al (2015) Acceleration of α-synuclein aggregation by exosomes. J Biol Chem 290(5):2969–2982
Emmanouilidou E, Melachroinou K, Roumeliotis T, Garbis SD, Ntzouni M, Margaritis LH et al (2010) Cell-produced α-synuclein is secreted in a calcium-dependent manner by exosomes and impacts neuronal survival. J Neurosci 30(20):6838–6851
**a Y, Zhang G, Han C, Ma K, Guo X, Wan F et al (2019) Microglia as modulators of exosomal alpha-synuclein transmission. Cell Death Dis 10(3):174
**a Y, Zhang G, Kou L, Yin S, Han C, Hu J et al (2021) Reactive microglia enhance the transmission of exosomal α-synuclein via toll-like receptor 2. Brain 144(7):2024–2037
Dai M, Yan L, Yu H, Chen C, **e Y (2023) TNFRSF10B is involved in motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease by regulating exosomal α-synuclein secretion from microglia. J Chem Neuroanat 129:102249
Lin Z, Gu Y, Zhou R, Wang M, Guo Y, Chen Y et al (2020) Serum exosomal proteins F9 and TSP-1 as potential diagnostic biomarkers for newly diagnosed epilepsy. Front Neurosci 14:737
Chen Y, Chen J, Chen Y, Li Y (2022) miR-146a/KLF4 axis in epileptic mice: a novel regulator of synaptic plasticity involving STAT3 signaling. Brain Res 1790:147988
Yan S, Zhang H, **e W, Meng F, Zhang K, Jiang Y et al (2017) Altered microRNA profiles in plasma exosomes from mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Oncotarget 8(3):4136
**aoying G, Guo M, Jie L, Yanmei Z, Ying C, Shengjie S et al (2020) CircHivep2 contributes to microglia activation and inflammation via miR-181a-5p/SOCS2 signalling in mice with kainic acid-induced epileptic seizures. J Cell Mol Med 24(22):12980–12993
Melachroinou K, **louri M, Emmanouilidou E, Masgrau R, Papazafiri P, Stefanis L et al (2013) Deregulation of calcium homeostasis mediates secreted α–synuclein-induced neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 34(12):2853–2865
Laryushkin DP, Maiorov SA, Zinchenko VP, Gaidin SG, Kosenkov AM (2021) Role of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels in epileptiform activity of neurons. Int J Mol Sci 22(19):10342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NHA, HMA-K, and AIA conceptualized the manuscript; wrote, edited, and reviewed the main text; and approved the final edition of the manuscript. SAA, HFH, HMS, and GE-SB prepared the figures and wrote, corrected, amended, and approved the final edition of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N.H., Al-kuraishy, H.M., Al-Gareeb, A.I. et al. A Mutual Nexus Between Epilepsy and α-Synuclein: A Puzzle Pathway. Mol Neurobiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04204-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-024-04204-6