Abstract
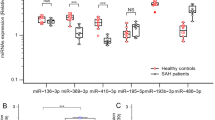
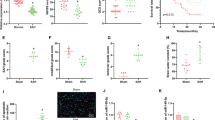
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a devastating disease associated with a high mortality and morbidity. Exosomes have been considered as a potential therapeutic target for SAH. However, the effect of exosomes in SAH remains to be elucidated. In this study, we focused on investigating the effect of plasma exosomal lncRNA TM7SF3-AU1 in white matter injury after SAH. The SAH model was established by means of endovascular perforation. Exosomes were extracted from rat plasma samples. The expression of RNAs in the exosomes was detected by the transcriptomic microarray. Differentially expressed circRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA were obtained. The ceRNA network showed that the lncRNA TM7SF3-AU1 and miR-702-3p were closely associated with SARM1. Knocking down TM7SF3-AU1 promoted the expression of miR-702-3p and suppressed the expression of SARM1, and knocking down TM7SF3-AU1 also attenuated white matter injury after SAH. In addition, knocking down TM7SF3-AU1 improved the neurological deficits in locomotion, anxiety, learning, memory, and electrophysiological activity after SAH. Mechanistically, TM7SF3-AU1 was able to absorb miR-702-3p, which directly bind the SARM1 mRNA. Furthermore, the white matter injury attenuated by knockdown of TM7SF3-AU1 was partially reversed by the miR-702-3p antagomir in SAH rats. Taken together, this study showed that TM7SF3-AU1 acts as a sponge for miR-702-3p, reducing the inhibitory effect of miR-702-3p on SARM1, resulting in increased SARM1 expression and thus leading to white matter injury after SAH. Our study provides new insights into exosome-associated white matter injury. It also highlights TM7SF3-AU1 as a potential therapeutic target for white matter injury after SAH.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Zhang Z, Zhang A, Liu Y, Hu X, Fang Y, Wang X et al (2022) New mechanisms and targets of subarachnoid hemorrhage: a focus on mitochondria. Curr Neuropharmacol 20:1278–1296. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X19666211101103646
Claassen J, Park S (2022) Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. The Lancet 400:846–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(22)00938-2
Daou BJ, Koduri S, Thompson BG, Chaudhary N, Pandey AS (2019) Clinical and experimental aspects of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. CNS Neurosci Ther 25:1096–1112. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13222
Eagles ME, Tso MK, Macdonald RL (2019) Cognitive impairment, functional outcome, and delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.152
Neifert SN, Chapman EK, Martini ML, Shuman WH, Schupper AJ, Oermann EK et al (2021) Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the last decade. Transl Stroke Res 12:428–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-020-00867-0
Coulibaly AP, Provencio JJ (2020) Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: an overview of inflammation-induced cellular changes. Neurotherapeutics 17:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00829-x
Noonin C, Thongboonkerd V (2021) Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics 11:4436–4451. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.54004
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ (2019) Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 88:487–514. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Pinnell JR, Cui M, Tieu K (2021) Exosomes in Parkinson disease. J Neurochem 157:413–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15288
Zhang T, Ma S, Lv J, Wang X, Afewerky HK, Li H et al (2021) The emerging role of exosomes in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 68:101321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101321
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M et al (2021) Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol 32:466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074
Zhou B, Xu K, Zheng X, Chen T, Wang J, Song Y et al (2020) Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00258-9
Xu M, Feng T, Liu B, Qiu F, Xu Y, Zhao Y et al (2021) Engineered exosomes: desirable target-tracking characteristics for cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disease therapies. Theranostics 11:8926–8944. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.62330
Liang Y, Duan L, Lu J, **a J (2021) Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics 11:3183–3195. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.52570
Chen X, Jiang M, Li H, Wang Y, Shen H, Li X et al (2020) CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis attenuates early brain injury via promoting the delivery of exosomal microRNA-124 from neuron to microglia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 17:209. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01882-6
Gao X, **ong Y, Li Q, Han M, Shan D, Yang G et al (2020) Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of miR-21-5p from mesenchymal stromal cells to neurons alleviates early brain injury to improve cognitive function via the PTEN/Akt pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Death Dis 11:363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2530-0
Lai N, Wu D, Liang T, Pan P, Yuan G, Li X et al (2020) Systemic exosomal miR-193b-3p delivery attenuates neuroinflammation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. J Neuroinflammation 17:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01745-0
Wu P, Cai J, Chen Q, Han B, Meng X, Li Y et al (2019) Lnc-TALC promotes O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression via regulating the c-Met pathway by competitively binding with miR-20b-3p. Nat Commun 10:2045. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10025-2
Wang J, Tang W, Yang M, Yin Y, Li H, Hu F et al (2021) Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy. Biomaterials 273:120784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120784
Ru X, Qu J, Li Q, Zhou J, Huang S, Li W et al (2021) MiR-706 alleviates white matter injury via downregulating PKCalpha/MST1/NF-kappaB pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Exp Neurol 341:113688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113688
Ru X, Gao L, Zhou J, Li Q, Zuo S, Chen Y et al (2021) Secondary white matter injury and therapeutic targets after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Neurol 12:659740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.659740
Figley MD, Gu W, Nanson JD, Shi Y, Sasaki Y, Cunnea K et al (2021) SARM1 is a metabolic sensor activated by an increased NMN/NAD(+) ratio to trigger axon degeneration. Neuron 109:1118–36 e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.02.009
Ko KW, Milbrandt J, DiAntonio A (2020) SARM1 acts downstream of neuroinflammatory and necroptotic signaling to induce axon degeneration. J Cell Biol 219. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201912047
Summers DW, Frey E, Walker LJ, Milbrandt J, DiAntonio A (2020) DLK activation synergizes with mitochondrial dysfunction to downregulate axon survival factors and promote SARM1-dependent axon degeneration. Mol Neurobiol 57:1146–1158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01796-2
Zhang Z, Zhao G, Liu L, He J, Darwazeh R, Liu H et al (2019) Bexarotene exerts protective effects through modulation of the cerebral vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic transformation by regulating PPARgamma/FLAP/LTB4 after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Cell Transplant 963689719842161. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719842161
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V, Zhang JH (2008) A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods 167:327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.08.004
Liu L, Zhang P, Zhang Z, Hu Q, He J, Liu H et al (2019) LXA4 ameliorates cerebrovascular endothelial dysfunction by reducing acute inflammation after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neuroscience 408:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.03.038
Niatsetskaya Z, Sosunov S, Stepanova A, Goldman J, Galkin A, Neginskaya M et al (2020) Cyclophilin D-dependent oligodendrocyte mitochondrial ion leak contributes to neonatal white matter injury. J Clin Invest 130:5536–5550. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI133082
Chen H, Zhou C, Zheng J, Zhang Z, Deng Y, Cheng C et al (2022) PTEN and AKT/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 signaling pathway are involved in neuronal apoptosis and axonal injury in early brain injury after SAH in rats. Genes Dis 9:252–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.05.002
Xu W, Yan J, Ocak U, Lenahan C, Shao A, Tang J et al (2021) Melanocortin 1 receptor attenuates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage by controlling mitochondrial metabolism via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1alpha pathway in rats. Theranostics 11:522–539. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.49426
Xu P, Tao C, Zhu Y, Wang G, Kong L, Li W et al (2021) TAK1 mediates neuronal pyroptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 18:188. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02226-8
Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W, Olefsky JM (2021) Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab 33:1744–1762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.08.006
Jeppesen DK, Fenix AM, Franklin JL, Higginbotham JN, Zhang Q, Zimmerman LJ et al (2019) Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell 177:428–45 e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.029
Liu H, Zhang J, Xu X, Lu S, Yang D, **e C et al (2021) SARM1 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neural regeneration after spinal cord injury through NF-kappaB signaling. Theranostics 11:4187–4206. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.49054
Bradshaw DV Jr, Knutsen AK, Korotcov A, Sullivan GM, Radomski KL, Dardzinski BJ et al (2021) Genetic inactivation of SARM1 axon degeneration pathway improves outcome trajectory after experimental traumatic brain injury based on pathological, radiological, and functional measures. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-021-01193-8
Zhang LY, Pan J, Mamtilahun M, Zhu Y, Wang L, Venkatesh A et al (2020) Microglia exacerbate white matter injury via complement C3/C3aR pathway after hypoperfusion. Theranostics 10:74–90. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.35841
Chamberlain KA, Huang N, **e Y, LiCausi F, Li S, Li Y et al (2021) Oligodendrocytes enhance axonal energy metabolism by deacetylation of mitochondrial proteins through transcellular delivery of SIRT2. Neuron 109:3456–72 e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.08.011
Michaels NJ, Lemmon K, Plemel JR, Jensen SK, Mishra MK, Brown D et al (2020) Aging-exacerbated acute axon and myelin injury is associated with microglia-derived reactive oxygen species and is alleviated by the generic medication indapamide. J Neurosci 40:8587–8600. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1098-20.2020
Peng J, Pang J, Huang L, Enkhjargal B, Zhang T, Mo J et al (2019) LRP1 activation attenuates white matter injury by modulating microglial polarization through Shc1/PI3K/Akt pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Redox Biol 21:101121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101121
Pang J, Peng J, Yang P, Kuai L, Chen L, Zhang JH et al (2019) White matter injury in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Transplant 28:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718812054
Reijmer YD, van den Heerik MS, Heinen R, Leemans A, Hendrikse J, de Vis JB et al (2018) Microstructural white matter abnormalities and cognitive impairment after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 49:2040–2045. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021622
Du M, Wu C, Yu R, Cheng Y, Tang Z, Wu B et al (2022) A novel circular RNA, circIgfbp2, links neural plasticity and anxiety through targeting mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress-induced synapse dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01711-7
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank ** **a
Contributions
ZZ and XS conceived and designed the study. ZZ, JY, and HC performed all the experiments. GZ, LL, and XX analyzed the data. ZZ and XS wrote the manuscript. CZ and JY supervised the project. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.