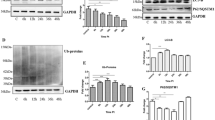
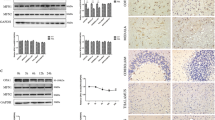
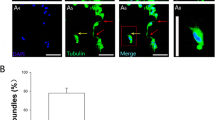
Abstract
Prion diseases are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the accumulation of a disease-associated prion protein and apoptotic neuronal death. Previous studies indicated that the ubiquitous expression of c-Abl tyrosine kinase transduces a variety of extrinsic and intrinsic cellular signals. In this study, we demonstrated that a synthetic neurotoxic prion fragment (PrP106-126) activated c-Abl tyrosine kinase, which in turn triggered the upregulation of MST1 and BIM, suggesting the activation of the c-Abl-BIM signaling pathway. The peptide fragment was found to result in cell death via mitochondrial dysfunction in neuron cultures. Knockdown of c-Abl using small interfering RNA protected neuronal cells from PrP106-126-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, production of reactive oxygen species, and apoptotic events inducing translocation of Bax to the mitochondria, cytochrome c release into the cytosol, and activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3. Blocking the c-Abl tyrosine kinase also prevented neuronal cells from PrP106-126-induced apoptotic morphological changes. This is the first study reporting that c-Abl tyrosine kinase as a novel upstream activator of MST1 and BIM plays an important role in prion-induced neuron apoptosis via mitochondrial dysfunction. Our findings suggest that c-Abl tyrosine kinase is a potential therapeutic target for prion disease.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott JR (1993) Scrapie pathogenesis. Br Med Bull 49(4):778–791
Colby DW, Prusiner SB (2011) Prions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(1):a006833
Kiktev DA, Patterson JC, Muller S, Bariar B, Pan T, Chernoff YO (2012) Regulation of chaperone effects on a yeast prion by cochaperone Sgt2. Mol Cell Biol 32(24):4960–4970
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(23):13363–13383
La Mendola D, Pietropaolo A, Pappalardo G, Zannoni C, Rizzarelli E (2008) Prion proteins leading to neurodegeneration. Curr Alzheimers Res 5(6):579–590
Sakudo A, Ikuta K (2009) Prion protein functions and dysfunction in prion diseases. Curr Med Chem 16(3):380–389
Prusiner SB (1991) Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 252(5012):1515–1522
Della-Bianca V, Rossi F, Armato U, Dal-Pra I, Costantini C, Perini G, Politi V, Della VG (2001) Neurotrophin p75 receptor is involved in neuronal damage by prion peptide-(106-126). J Biol Chem 276(42):38929–38933
Perez M, Rojo AI, Wandosell F, Diaz-Nido J, Avila J (2003) Prion peptide induces neuronal cell death through a pathway involving glycogen synthase kinase 3. Biochem J 372(Pt 1):129–136
Forloni G, Angeretti N, Chiesa R, Monzani E, Salmona M, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F (1993) Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 362(6420):543–546
Henriques ST, Pattenden LK, Aguilar MI, Castanho MA (2008) PrP(106-126) does not interact with membranes under physiological conditions. Biophys J 95(4):1877–1889
Ettaiche M, Pichot R, Vincent JP, Chabry J (2000) In vivo cytotoxicity of the prion protein fragment 106-126. J Biol Chem 275(47):36487–36490
Gu Y, Fujioka H, Mishra RS, Li R, Singh N (2002) Prion peptide 106-126 modulates the aggregation of cellular prion protein and induces the synthesis of potentially neurotoxic transmembrane PrP. J Biol Chem 277(3):2275–2286
Selvaggini C, De Gioia L, Cantu L, Ghibaudi E, Diomede L, Passerini F, Forloni G, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F, Salmona M (1993) Molecular characteristics of a protease-resistant, amyloidogenic and neurotoxic peptide homologous to residues 106-126 of the prion protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 194(3):1380–1386
Milhavet O, Lehmann S (2002) Oxidative stress and the prion protein in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 38(3):328–339
Fairbairn DW, Carnahan KG, Thwaits RN, Grigsby RV, Holyoak GR, O’Neill KL (1994) Detection of apoptosis induced DNA cleavage in scrapie-infected sheep brain. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115(2–3):341–346
Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Buczynski J, Kordek R, Liberski PP (1999) Neuronal loss and apoptosis in experimental Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in mice. Folia Neuropathol 37(4):283–286
Ye X, Scallet AC, Carp RI (1997) The 139H scrapie agent produces hypothalamic neurotoxicity and pancreatic islet histopathology: electron microscopic studies. Neurotoxicology 18(2):533–545
Dorandeu A, Wingertsmann L, Chretien F, Delisle MB, Vital C, Parchi P, Montagna P, Lugaresi E, Ironside JW, Budka H, Gambetti P, Gray F (1998) Neuronal apoptosis in fatal familial insomnia. Brain Pathol 8(3):531–537
Gray F, Chretien F, Adle-Biassette H, Dorandeu A, Ereau T, Delisle MB, Kopp N, Ironside JW, Vital C (1999) Neuronal apoptosis in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58(4):321–328
O’Donovan CN, Tobin D, Cotter TG (2001) Prion protein fragment PrP-(106-126) induces apoptosis via mitochondrial disruption in human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells. J Biol Chem 276(47):43516–43523
Brown DR, Schmidt B, Kretzschmar HA (1996) Role of microglia and host prion protein in neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 380(6572):345–347
Turnbull S, Tabner BJ, Brown DR, Allsop D (2003) Quinacrine acts as an antioxidant and reduces the toxicity of the prion peptide p rP106–126. Neuroreport 14(13):1743–1745
Woodring PJ, Hunter T, Wang JY (2003) Regulation of F-actin-dependent processes by the Abl family of tyrosine kinases. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 13):2613–2626
Zhu J, Wang JY (2004) Death by Abl: a matter of location. Curr Top Dev Biol 59(165–92
Cancino GI, Perez DAK, Castro PU, Toledo EM, von Bernhardi R, Alvarez AR (2011) c-Abl tyrosine kinase modulates tau pathology and Cdk5 phosphorylation in AD transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 32(7):1249–1261
Yang A, Kaghad M, Caput D, McKeon F (2002) On the shoulders of giants: p63, p73 and the rise of p53. Trends Genet 18(2):90–95
Ben-Yehoyada M, Ben-Dor I, Shaul Y (2003) c-Abl tyrosine kinase selectively regulates p73 nuclear matrix association. J Biol Chem 278(36):34475–34482
Brightbill H, Schlissel MS (2009) The effects of c-Abl mutation on develo** B cell differentiation and survival. Int Immunol 21(5):575–585
Yun SW, Ertmer A, Flechsig E, Gilch S, Riederer P, Gerlach M, Schatzl HM, Klein MA (2007) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate delays prion neuroinvasion by inhibiting prion propagation in the periphery. J Neurovirol 13(4):328–337
Ertmer A, Gilch S, Yun SW, Flechsig E, Klebl B, Stein-Gerlach M, Klein MA, Schatzl HM (2004) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 induces cellular clearance of PrPSc in prion-infected cells. J Biol Chem 279(40):41918–41927
Kemmerling U, Munoz P, Muller M, Sanchez G, Aylwin ML, Klann E, Carrasco MA, Hidalgo C (2007) Calcium release by ryanodine receptors mediates hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of ERK and CREB phosphorylation in N2a cells and hippocampal neurons. Cell Calcium 41(5):491–502
Stamer K, Vogel R, Thies E, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM (2002) Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress. J Cell Biol 156(6):1051–1063
Kaech S, Banker G (2006) Culturing hippocampal neurons. Nat Protoc 1(5):2406–2415
Yuan F, Yang L, Zhang Z, Wu W, Zhou X, Yin X, Zhao D (2013) Cellular prion protein (PrPC) of the neuron cell transformed to a PK-resistant protein under oxidative stress, comprising main mitochondrial damage in prion diseases. J Mol Neurosci 51(1):219–224
LeVine HR (1993) Thioflavine T interaction with synthetic Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides: detection of amyloid aggregation in solution. Protein Sci 2(3):404–410
Shi F, Yang L, Wang J, Kouadir M, Yang Y, Fu Y, Zhou X, Yin X, Zhao D (2013) Inhibition of phagocytosis reduced the classical activation of BV2 microglia induced by amyloidogenic fragments of beta-amyloid and prion proteins. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 45(11):973–978
Tian YY, An LJ, Jiang L, Duan YL, Chen J, Jiang B (2006) Catalpol protects dopaminergic neurons from LPS-induced neurotoxicity in mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures. Life Sci 80(3):193–199
Schlatterer SD, Acker CM, Davies P (2011) c-Abl in neurodegenerative disease. J Mol Neurosci 45(3):445–452
Cancino GI, Toledo EM, Leal NR, Hernandez DE, Yevenes LF, Inestrosa NC, Alvarez AR (2008) STI571 prevents apoptosis, tau phosphorylation and behavioural impairments induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid deposits. Brain 131(Pt 9):2425–2442
Schlatterer SD, Tremblay MA, Acker CM, Davies P (2011) Neuronal c-Abl overexpression leads to neuronal loss and neuroinflammation in the mouse forebrain. J Alzheimers Dis 25(1):119–133
Alvarez AR, Sandoval PC, Leal NR, Castro PU, Kosik KS (2004) Activation of the neuronal c-Abl tyrosine kinase by amyloid-beta-peptide and reactive oxygen species. Neurobiol Dis 17(2):326–336
Sato M, Maruoka M, Takeya T (2012) Functional mechanisms and roles of adaptor proteins in abl-regulated cytoskeletal actin dynamics. J, Signal Transduct 2012(414913
Brasher BB, Van Etten RA (2000) c-Abl has high intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that is stimulated by mutation of the Src homology 3 domain and by autophosphorylation at two distinct regulatory tyrosines. J Biol Chem 275(45):35631–35637
Furstoss O, Dorey K, Simon V, Barila D, Superti-Furga G, Roche S (2002) c-Abl is an effector of Src for growth factor-induced c-myc expression and DNA synthesis. EMBO J 21(4):514–524
Tanis KQ, Veach D, Duewel HS, Bornmann WG, Koleske AJ (2003) Two distinct phosphorylation pathways have additive effects on Abl family kinase activation. Mol Cell Biol 23(11):3884–3896
Derkinderen P, Scales TM, Hanger DP, Leung KY, Byers HL, Ward MA, Lenz C, Price C, Bird IN, Perera T, Kellie S, Williamson R, Noble W, Van Etten RA, Leroy K, Brion JP, Reynolds CH, Anderton BH (2005) Tyrosine 394 is phosphorylated in Alzheimer’s paired helical filament tau and in fetal tau with c-Abl as the candidate tyrosine kinase. J Neurosci 25(28):6584–6593
Essafi A, Fernandez DMS, Hassen YA, Soeiro I, Mufti GJ, Thomas NS, Medema RH, Lam EW (2005) Direct transcriptional regulation of Bim by FoxO3a mediates STI571-induced apoptosis in Bcr-Abl-expressing cells. Oncogene 24(14):2317–2329
**ao L, Chen D, Hu P, Wu J, Liu W, Zhao Y, Cao M, Fang Y, Bi W, Zheng Z, Ren J, Ji G, Wang Y, Yuan Z (2011) The c-Abl-MST1 signaling pathway mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 31(26):9611–9619
Harada H, Grant S (2012) Targeting the regulatory machinery of BIM for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 22(2):117–129
Lehtinen MK, Yuan Z, Boag PR, Yang Y, Villen J, Becker EB, DiBacco S, de la Iglesia N, Gygi S, Blackwell TK, Bonni A (2006) A conserved MST-FOXO signaling pathway mediates oxidative-stress responses and extends life span. Cell 125(5):987–1001
Odagiri K, Katoh H, Kawashima H, Tanaka T, Ohtani H, Saotome M, Urushida T, Satoh H, Hayashi H (2009) Local control of mitochondrial membrane potential, permeability transition pore and reactive oxygen species by calcium and calmodulin in rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46(6):989–997
Ramonet D, Perier C, Recasens A, Dehay B, Bove J, Costa V, Scorrano L, Vila M (2013) Optic atrophy 1 mediates mitochondria remodeling and dopaminergic neurodegeneration linked to complex I deficiency. Cell Death Differ 20(1):77–85
Vogler M (2012) BCL2A1: the underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ 19(1):67–74
Boren J, Brindle KM (2012) Apoptosis-induced mitochondrial dysfunction causes cytoplasmic lipid droplet formation. Cell Death Differ 19(9):1561–1570
Gonfloni S, Maiani E, Di Bartolomeo C, Diederich M, Cesareni G (2012) Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and c-Abl signaling: at the crossroad in neurodegenerative diseases? Int, J Cell Biol 2012(683097
Lee JH, Jeong MW, Kim W, Choi YH, Kim KT (2008) Cooperative roles of c-Abl and Cdk5 in regulation of p53 in response to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 283(28):19826–19835
Ciccone S, Maiani E, Bellusci G, Diederich M, Gonfloni S (2013) Parkinson’s disease: a complex interplay of mitochondrial DNA alterations and oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci 14(2):2388–2409
Turnbull S, Tabner BJ, Brown DR, Allsop D (2003) Copper-dependent generation of hydrogen peroxide from the toxic prion protein fragment p rP106–126. Neurosci Lett 336(3):159–162
Carimalo J, Cronier S, Petit G, Peyrin JM, Boukhtouche F, Arbez N, Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Brugg B, Miquel MC (2005) Activation of the JNK-c-Jun pathway during the early phase of neuronal apoptosis induced by PrP106-126 and prion infection. Eur J Neurosci 21(9):2311–2319
Yuan Z, Lehtinen MK, Merlo P, Villen J, Gygi S, Bonni A (2009) Regulation of neuronal cell death by MST1-FOXO1 signaling. J Biol Chem 284(17):11285–11292
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Park SY (2012) Melatonin-induced autophagy protects against human prion protein-mediated neurotoxicity. J Pineal Res 53(2):138–146
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Park SY (2013) Autophagy induced by the class III histone deacetylase Sirt1 prevents prion peptide neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 34(1):146–156
Constance JE, Despres SD, Nishida A, Lim CS (2012) Selective targeting of c-Abl via a cryptic mitochondrial targeting signal activated by cellular redox status in leukemic and breast cancer cells. Pharm Res 29(8):2317–2328
Qi X, Mochly-Rosen D (2008) The PKCdelta-Abl complex communicates ER stress to the mitochondria—an essential step in subsequent apoptosis. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 6):804–813
Brown DR (2001) Microglia and prion disease. Microsc Res Tech 54(2):71–80
Haik S, Peyrin JM, Lins L, Rosseneu MY, Brasseur R, Langeveld JP, Tagliavini F, Deslys JP, Lasmezas C, Dormont D (2000) Neurotoxicity of the putative transmembrane domain of the prion protein. Neurobiol Dis 7(6 Pt B):644–656
Dlaskova A, Hlavata L, Jezek P (2008) Oxidative stress caused by blocking of mitochondrial complex I H(+) pum** as a link in aging/disease vicious cycle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(9):1792–1805
Dan S, Naito M, Seimiya H, Kizaki A, Mashima T, Tsuruo T (1999) Activation of c-Abl tyrosine kinase requires caspase activation and is not involved in JNK/SAPK activation during apoptosis of human monocytic leukemia U937 cells. Oncogene 18(6):1277–1283
Choi CJ, Anantharam V, Saetveit NJ, Houk RS, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2007) Normal cellular prion protein protects against manganese-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Sci 98(2):495–509
Florez-McClure ML, Linseman DA, Chu CT, Barker PA, Bouchard RJ, Le SS, Laessig TA, Heidenreich KA (2004) The p75 neurotrophin receptor can induce autophagy and death of cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci 24(19):4498–4509
Gomez-Santos C, Ferrer I, Santidrian AF, Barrachina M, Gil J, Ambrosio S (2003) Dopamine induces autophagic cell death and alpha-synuclein increase in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurosci Res 73(3):341–350
Rubinsztein DC, DiFiglia M, Heintz N, Nixon RA, Qin ZH, Ravikumar B, Stefanis L, Tolkovsky A (2005) Autophagy and its possible roles in nervous system diseases, damage and repair. Autophagy 1(1):11–22
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Bae BC, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Kang HS, Kim JS, Kang SJ, Park SY (2012) Autophagy induced by resveratrol prevents human prion protein-mediated neurotoxicity. Neurosci Res 73(2):99–105
Ogier-Denis E, Codogno P (2003) Autophagy: a barrier or an adaptive response to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1603(2):113–128
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306(5698):990–995
Marino G, Lopez-Otin C (2004) Autophagy: molecular mechanisms, physiological functions and relevance in human pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(12):1439–1454
Eskelinen EL (2005) Maturation of autophagic vacuoles in mammalian cells. Autophagy 1(1):1–10
Son JH, Shim JH, Kim KH, Ha JY, Han JY (2012) Neuronal autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med 44(2):89–98
Rosello A, Warnes G, Meier UC (2012) Cell death pathways and autophagy in the central nervous system and its involvement in neurodegeneration, immunity and central nervous system infection: to die or not to die—that is the question. Clin Exp Immunol 168(1):52–57
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. ** Zhu, Dr. Sher Hayat Khan, Dr. Yang Yang, Dr. Ting Zhu, and Dr. Fushan Shi for their valuable suggestions and critical reading of this manuscript. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (project nos. 31172293, 31001048, and 31272532), the Ministry of Agriculture Program of China (no. 2013-S11), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (SRFDP, project no. 20100008120002), the Foundation of Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (project no. 2011BAI15B01), and the Program for Cheung Kong Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University of China (no. IRT0866).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bo Pan and Lifeng Yang contributed to this work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, B., Yang, L., Wang, J. et al. c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Mediates Neurotoxic Prion Peptide-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via Regulating Mitochondrial Homeostasis. Mol Neurobiol 49, 1102–1116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8646-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8646-4