Abstract
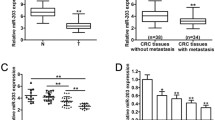
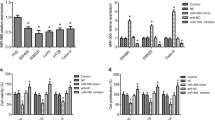
The miR-497-195 cluster facilitates the occurrence and development of cancer. This study aims to investigate whether the miR-195-497 cluster could regulate the progression of colorectal cancer by regulating the common target gene, FOS-related antigen 1 (FRA1). Overexpression of the miR-195/497 vector was used to evaluate the effect of overexpression of miR-195-497 clusters on the biological behavior of colon cancer cells. In animal experiments, tumor growth and metastasis were recorded by constructing a nude mouse model of a subcutaneously implanted tumor. miR-195 and miR-497 were expressed to varying degrees in Caco-2, LoVo, and HT-29 cells. Overexpression of miR-195/497 and inhibition of FRA1 decreased HT-29 cell proliferation, inhibited cell invasion and migration, and promoted Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In vivo experiments showed that the overexpression of miR-195/497 or inhibition of FRA1 inhibited tumor growth, affected EMT in tumor cells, and inhibited the expression of FRA1. Additionally, the aforementioned conditions had the best effect when used together. The miR-195-497 cluster can regulate the proliferation, EMT, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the common target gene FRA1, thereby affecting the development of colorectal cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Dekker, E., Tanis, P. J., Vleugels, J. L. A., Kasi, P. M., & Wallace, M. B. (2019). Colorectal cancer. Lancet, 394(10207), 1467–1480.
Carter, J. V., Galbraith, N. J., Yang, D., Burton, J. F., Walker, S. P., & Galandiuk, S. (2017). Blood-based microRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Cancer, 116(6), 762–774.
Hao, S., Huo, S., Du, Z., Yang, Q., Ren, M., Liu, S., et al. (2019). MicroRNA-related transcription factor regulatory networks in human colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore), 98(15), e15158.
Cojocneanu, R., Braicu, C., Raduly, L., Jurj, A., Zanoaga, O., Magdo, L., et al. (2020). Plasma and tissue specific miRNA expression pattern and functional analysis associated to colorectal cancer patients. Cancers (Basel)., 12(4), 843.
Falzone, L., Scola, L., Zanghì, A., Biondi, A., Di Cataldo, A., Libra, M., et al. (2018). Integrated analysis of colorectal cancer microRNA datasets: Identification of microRNAs associated with tumor development. Aging (Albany NY), 10(5), 1000–1014.
Lin, X., Wang, S., Sun, M., Zhang, C., Wei, C., Yang, C., et al. (2019). miR-195-5p/NOTCH2-mediated EMT modulates IL-4 secretion in colorectal cancer to affect M2-like TAM polarization. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 12(1), 20.
Gharib, E., Nasri Nasrabadi, P., & Reza, Z. M. (2020). miR-497-5p mediates starvation-induced death in colon cancer cells by targeting acyl-CoA synthetase-5 and modulation of lipid metabolism. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 235(7–8), 5570–5589.
Jiang, X., **e, H., Dou, Y., Yuan, J., Zeng, D., & **ao, S. (2020). Expression and function of FRA1 protein in tumors. Molecular Biology Reports, 47(1), 737–752.
Zhang, N., Shen, Q., & Zhang, P. (2016). miR-497 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting fos-related antigen-1. OncoTargets and Therapy, 9, 6597–6604.
Wu, J., Ji, A., Wang, X., Zhu, Y., Yu, Y., Lin, Y., et al. (2015). MicroRNA-195-5p, a new regulator of Fra-1, suppresses the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Journal of Translational Medicine, 13, 289.
Pidíkova, P., Reis, R., & Herichova, I. (2020). miRNA clusters with down-regulated expression in human colorectal cancer and their regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(13), 4633.
Bai, J., Xu, J., Zhao, J., & Zhang, R. (2020). lncRNA SNHG1 cooperated with miR-497/miR-195-5p to modify epithelial-mesenchymal transition underlying colorectal cancer exacerbation. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 235(2), 1453–1468.
Rao, X., Huang, X., Zhou, Z., & Lin, X. (2013). An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. The Biostatistics, Bioinformatics and Biomathematics, 3(3), 71–85.
Ladner, C. L., Yang, J., Turner, R. J., & Edwards, R. A. (2004). Visible fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels without staining. Analytical Biochemistry, 326(1), 13–20.
Wang, H. (2020). MicroRNAs and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5353.
Graham, J. S., & Cassidy, J. (2012). Adjuvant therapy in colon cancer. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy, 12(1), 99–109.
Michael, M. Z., O’Connor, S. M., van Holst Pellekaan, N. G., Young, G. P., & James, R. J. (2003). Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Molecular Cancer Research, 1(12), 882–891.
To, K. K., Tong, C. W., Wu, M., & Cho, W. C. (2018). MicroRNAs in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to bedside. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 24(27), 2949–2973.
Zhang, N., Hu, X., Du, Y., & Du, J. (2021). The role of miRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and chemoradiotherapy. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 134, 111099.
Lataniotis, L., Albrecht, A., Kok, F. O., Monfries, C. A. L., Benedetti, L., Lawson, N. D., et al. (2017). CRISPR/Cas9 editing reveals novel mechanisms of clustered microRNA regulation and function. Science and Reports, 7(1), 8585.
Itesako, T., Seki, N., Yoshino, H., Chiyomaru, T., Yamasaki, T., Hidaka, H., et al. (2014). The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: The functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster. PLoS ONE, 9(2), e84311.
Flavin, R. J., Smyth, P. C., Laios, A., O’Toole, S. A., Barrett, C., Finn, S. P., et al. (2009). Potentially important microRNA cluster on chromosome 17p13.1 in primary peritoneal carcinoma. Modern Pathology, 22(2), 197–205.
Hong, S., Yan, Z., Wang, H., Ding, L., & Bi, M. (2019). Up-regulation of microRNA-497-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion via targeting PTPN3. Bioscience Reports. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20191123
Bayat, A., Raad, M., Sharafshah, A., Ahmadvand, M., & Aminian, H. (2022). Identification of miR-195-5p as a novel prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Molecular Biology Reports, 49(7), 6453–6457.
Singh, A., & Settleman, J. (2010). EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene, 29(34), 4741–4751.
Carstens, J. L., Lovisa, S., & Kalluri, R. (2014). Microenvironment-dependent cues trigger miRNA-regulated feedback loop to facilitate the EMT/MET switch. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 124(4), 1458–1460.
Ning, X., Wang, C., Zhang, M., & Wang, K. (2019). Ectopic expression of miR-147 Inhibits stem cell marker and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related protein expression in colon cancer cells. Oncology Research, 27(4), 399–406.
Vu, T., & Datta, P. K. (2017). Regulation of EMT in colorectal cancer: A culprit in metastasis. Cancers (Basel), 9(12), 171.
**ng, Y., **g, H., Zhang, Y., Suo, J., & Qian, M. (2020). MicroRNA-141-3p affected proliferation, chemosensitivity, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by targeting EGFR. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 118, 105643.
Liu, Z., Liu, X., Li, Y., Ren, P., Zhang, C., Wang, L., et al. (2019). miR-6716-5p promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer through downregulating NAT10 expression. Cancer Management Research, 11, 5317–5332.
Shuai, F., Wang, B., & Dong, S. (2018). MicroRNA-204 inhibits the growth and motility of colorectal cancer cells by downregulation of CXCL8. Oncology Research, 26(8), 1295–1305.
Wang, L., Guo, J., Zhou, J., Wang, D., Kang, X., & Zhou, L. (2020). NF-κB maintains the stemness of colon cancer cells by downregulating miR-195-5p/497–5p and upregulating MCM2. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 225.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH and WD conceptualized, designed the study and write manuscript. HW responsible for data collection and analysis. JZ responsible for article checking literature search.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Wuhan Myhalic Biotechnology Co., Ltd (HLK-20220520-005). All animal experiments are in compliance with the relevant regulations of the Hubei Provincial Animal Management Committee “Experimental Animal Ethics Certificate”. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Ding, W., Wu, H. et al. miR-497/195 Cluster Affects the Development of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting FRA1. Mol Biotechnol 66, 1019–1030 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01000-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01000-w