Abstract
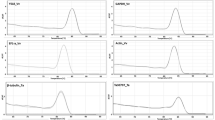
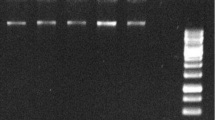
RNA isolation is the first step in the study of gene expression and recombinant protein production. However, the isolation of high quantity and high-quality RNA from tissues containing large amounts of polysaccharides has proven to be a difficult process. Cupressus arizonica pollen, in addition to containing high polysaccharide levels, is a challenging starting material for RNA isolation due to the roughness of the pollen grain’s walls. Here, we describe an improved technique for RNA isolation from C. arizonica pollen grains. The protocol includes a special disruption and homogenization process as well as a two-step modified RNA isolation technique which consists of an acid phenol extraction followed by a final cleanup using a commercial kit. Resulting RNA proved to be free of contaminants as determined by UV spectrophotometry. The quality of the RNA was analyzed on a bioanalyzer and showed visible 25S and 18S bands. This RNA was successfully used in downstream applications such as RT–PCR and phage display library construction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charpin, D., Calleja, M., Lahoz, C., Pichot, C., & Waisel, Y. (2005). Allergy to cypress pollen. Allergy, 60(3), 293–301.
Mistrello, G., Roncarolo, D., Zanoni, D., Zanotta, S., Amato, S., Falagiani, P., et al. (2002). Allergenic relevance of Cupressus arizonica pollen extract and biological characterization of the allergoid. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 129(4), 296–304.
Aceituno, E., Del Pozo, V., Minguez, A., Arrieta, I., Cortegano, I., Cardaba, B., et al. (2000). Molecular cloning of major allergen from Cupressus arizonica pollen: Cup a 1. Clinical and Experimental Allergy, 30(12), 1750–1758.
Cortegano, I., Civantos, E., Aceituno, E., del Moral, A., Lopez, E., Lombardero, M., et al. (2004). Cloning and expression of a major allergen from Cupressus arizonica pollen, Cup a 3, a PR-5 protein expressed under polluted environment. Allergy, 59(5), 485–490.
Rea, G., Iacovacci, P., Ferrante, P., Zelli, M., Brunetto, B., Lamba, D., et al. (2004). Refolding of the Cupressus arizonica major pollen allergen Cup a1.02 overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification, 37(2), 419–425.
Di Felice, G., Barletta, B., Tinghino, R., & Pini, C. (2001). Cupressaceae pollinosis: Identification, purification and cloning of relevant allergens. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 125(4), 280–289.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Combet, C., Blanchet, C., Geourjon, C., & Deleage, G. (2000). NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 25(3), 147–150.
Logemann, J., Schell, J., & Willmitzer, L. (1987). Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Analytical Biochemistry, 163(1), 16–20.
Wilfinger, W. W., Mackey, K., & Chomczynski, P. (1997). Effect of pH and ionic strength on the spectrophotometric assessment of nucleic acid purity. Biotechniques, 22(3), 474–476, 478–481
Di Bernardo, G., Del Gaudio, S., Galderisi, U., Cascino, A., & Cipollaro, M. (2007). Comparative evaluation of different DNA extraction procedures from food samples. Biotechnology Progress, 23(2), 297–301.
Schroeder, A., Mueller, O., Stocker, S., Salowsky, R., Leiber, M., Gassmann, M., et al. (2006). The RIN: An RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Molecular Biology, 7, 3.
Ariano, R., Mistrello, G., Mincigrucci, G., Bricchi, E., Lannotti, O., Frenguelli, G., et al. (2006). In vitro and in vivo biological activities of old and fresh Cupressus arizonica pollen. Journal of Investigation Allergology & Clinical Immunology, 16(3), 177–182.
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by the EU Cooperative Research Action For Technology (CRAFT) Cyprall Project QLK-CT-2002-71661. We would like to thank Fernando Carrasco for several contributions to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pico de Coaña, Y., Parody, N., Fernández-Caldas, E. et al. A Modified Protocol for RNA Isolation from High Polysaccharide Containing Cupressus arizonica Pollen. Applications for RT–PCR and Phage Display Library Construction. Mol Biotechnol 44, 127–132 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9219-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9219-z